What are the Functional competencies of accounting?
Accounting professionals require a range of functional competencies to perform their roles effectively. These competencies encompass various skills and knowledge areas necessary for financial reporting, analysis, and decision-making. Here are some key functional competencies of accounting professionals:
Financial Reporting:
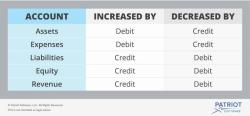
- GAAP Knowledge: A strong understanding of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is essential for preparing accurate financial statements that adhere to regulatory standards.
- Financial Statement Preparation: Competence in creating balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements to accurately represent a company's financial position and performance.
- Audit Preparation: Knowledge of audit processes and the ability to prepare financial records for external audits.
Accounting Software Proficiency:
- Proficiency in Accounting Software: Familiarity with accounting software packages such as QuickBooks, Xero, or enterprise-level systems like SAP or Oracle.
Bookkeeping and Record-Keeping:
- Accurate Data Entry: The ability to maintain precise records of financial transactions and journal entries.
- Reconciliation: Skills in reconciling bank statements, accounts payable, and accounts receivable to ensure data accuracy.
Financial Analysis:
- Financial Ratios and Analysis: Competence in calculating and interpreting financial ratios to assess a company's performance and financial health.
- Trend Analysis: The ability to identify and analyze financial trends and patterns over time.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Skills in creating budgets and financial forecasts based on historical data and current business trends.
Taxation Knowledge:
- Tax Compliance: Proficiency in tax laws and regulations to ensure accurate tax compliance, including income tax, sales tax, and payroll tax.
- Tax Planning: Ability to identify tax-saving opportunities and optimize a company's tax position.
Internal Controls:
- Internal Control Assessment: Competence in assessing and implementing internal controls to safeguard company assets and ensure financial integrity.
Financial Management:
- Cash Flow Management: Skills in managing and optimizing a company's cash flow to meet financial obligations and investment needs.
- Working Capital Management: The ability to effectively manage a company's working capital to ensure smooth operations.
Cost Accounting:
- Cost Allocation: Competence in allocating and assigning costs to products or services, as well as analyzing cost structures to improve cost-efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Knowledge of Regulations: Understanding of industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements, especially in sectors like healthcare or financial services.
Ethical Conduct:
- Ethical Standards: Adherence to ethical and professional standards, including confidentiality, integrity, and objectivity in financial reporting and decision-making.
Communication Skills:
- Oral and Written Communication: Effective communication skills to convey financial information and analysis to colleagues, management, and stakeholders.
Problem-Solving:
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze complex financial data, identify issues, and develop solutions to financial challenges.
Management and Leadership:
- Supervision: Skills in supervising and managing accounting teams, if in a leadership role.
- Project Management: Managing financial projects, such as system implementations or process improvements.
Continuous Learning:
- Professional Development: A commitment to ongoing learning, keeping up with changes in accounting standards, regulations, and technology.
Data Analysis and Technology:
- Data Analytics: Proficiency in using data analysis tools and techniques to extract insights from financial data.
- Technology Integration: Ability to integrate financial data with technology systems, including enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
These functional competencies are essential for accounting professionals to perform their roles effectively and contribute to the financial well-being and success of their organizations. Depending on the specific job role and industry, the level of expertise required in each competency area may vary. Continuing education and professional certifications, such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Certified Management Accountant (CMA), can further enhance an accountant's functional competencies.
Functional Competencies in Accounting: Essential Skills
Functional competencies in accounting are the skills and knowledge that are essential for success in accounting roles. These competencies can be divided into two broad categories: technical and professional.
Technical competencies include the ability to:
- Prepare and analyze financial statements
- Record and track financial transactions
- Identify and apply relevant accounting principles and standards
- Use accounting software and technology
Professional competencies include the ability to:
- Communicate effectively with both internal and external stakeholders
- Work independently and as part of a team
- Solve problems and think critically
- Maintain ethical and professional standards
Key Competencies for Success in Accounting Roles
In addition to the general functional competencies listed above, there are a few key competencies that are particularly important for success in accounting roles. These include:
- Data analysis and interpretation: Accountants need to be able to collect, analyze, and interpret large amounts of data in order to identify trends and patterns, and to make informed recommendations.
- Risk assessment and management: Accountants need to be able to identify and assess financial risks, and to develop and implement strategies to mitigate those risks.
- Technology proficiency: Accountants need to be proficient in the use of accounting software and other technologies in order to perform their jobs efficiently and effectively.
- Business acumen: Accountants need to have a good understanding of business operations and financial markets in order to provide valuable insights to stakeholders.
Developing and Enhancing Functional Competencies in Accounting
There are a number of ways to develop and enhance functional competencies in accounting. Some of the most effective methods include:
- Formal education: Accounting degree programs teach students the essential technical and professional competencies needed for success in accounting roles.
- Continuing professional education (CPE): CPAs and other accounting professionals are required to complete CPE credits on a regular basis in order to maintain their certifications and licenses. CPE courses can be a valuable way to stay up-to-date on the latest accounting trends and developments, and to learn new skills.
- On-the-job training: Many accounting professionals develop and enhance their skills through on-the-job training. This can involve working on complex accounting projects, mentoring junior staff, and attending industry events.
Career Advancement and Growth through Competency Development
By developing and enhancing their functional competencies in accounting, professionals can position themselves for career advancement and growth. Accountants with strong functional competencies are in high demand, and they often have the opportunity to move into senior management positions and to earn higher salaries.
Recognizing and Measuring Functional Competencies in the Accounting Field
There are a number of ways to recognize and measure functional competencies in the accounting field. Some of the most common methods include:
- Performance reviews: Employers typically conduct regular performance reviews of their accounting staff. During these reviews, they assess the employee's performance against a set of competency-based criteria.
- Professional certifications: Professional certifications, such as the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation, demonstrate that an accountant has met certain standards of competence.
- Skill assessments: Employers may also use skill assessments to evaluate the functional competencies of potential and current employees. These assessments can be in the form of written tests, interviews, or practical exercises.
By recognizing and measuring functional competencies in accounting, employers can ensure that they have the skilled and qualified staff they need to succeed.