What are the main features of Managerial Economics?
Managerial Economics is a branch of economics that applies economic theories and principles to decision-making in business management. It combines economic concepts with business practices to help managers make rational and informed decisions. The main features of Managerial Economics include:
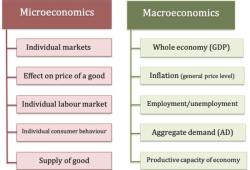
Microeconomic Focus:
- Managerial Economics is primarily concerned with microeconomic principles, focusing on individual firms or organizations rather than the overall economy.
Decision-Making Orientation:
- The central focus of Managerial Economics is to assist managers in making decisions that contribute to the effective and efficient use of resources to achieve organizational goals.
Integration of Economic Theory:
- It integrates economic theories and concepts, drawing from microeconomics, macroeconomics, and decision sciences to analyze and solve business problems.
Applied Nature:
- Managerial Economics is highly applied, emphasizing the practical application of economic theories to real-world business scenarios and decision-making.
Optimization Principle:
- The goal of managerial decision-making is often optimization, where managers seek to allocate resources in a way that maximizes the organization's objectives, such as profit maximization.
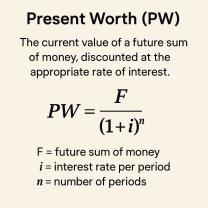
Use of Quantitative Methods:
- Managerial Economics often employs quantitative methods and tools, including statistical analysis, mathematical modeling, and optimization techniques, to support decision-making.
Focus on Demand and Supply:
- Analysis of demand and supply is a key component of Managerial Economics. Managers need to understand market demand for their products or services and how supply factors influence production and pricing decisions.
Cost and Production Analysis:
- It involves the analysis of production costs, cost structures, and cost functions. Understanding cost relationships is crucial for making informed decisions about production levels and pricing strategies.
Market Structure Analysis:
- Managerial Economics examines different market structures, such as perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition, to understand the impact on pricing and strategic decision-making.
Risk and Uncertainty Considerations:
- Managers often make decisions under conditions of risk and uncertainty. Managerial Economics addresses decision-making in situations where outcomes are uncertain and involves risk assessment.
Strategic Decision-Making:
- Managerial Economics is instrumental in strategic decision-making, including market positioning, product differentiation, and long-term planning.
Government and Business Interaction:
- It considers the role of government in business operations, examining regulatory environments, antitrust policies, and legal constraints that can affect managerial decisions.
International Perspective:
- With globalization, Managerial Economics often includes an international perspective, considering factors such as global markets, exchange rates, and international trade in decision-making.
Ethical Considerations:
- Managerial Economics recognizes the importance of ethical considerations in decision-making. Managers need to consider the social responsibility of their actions and the impact on stakeholders.
Continuous Adaptation:
- Managerial Economics is dynamic and continuously adapts to changing economic conditions, market trends, and technological advancements.
These features collectively make Managerial Economics a valuable tool for managers, enabling them to make informed decisions in a dynamic business environment.
Key attributes defining Managerial Economics?
Managerial Economics is a distinct field of study that bridges the gap between theoretical economics and practical business applications. Several key attributes define this field:
1. Microeconomic Character:
Managerial Economics primarily focuses on microeconomic principles and applies them to the decision-making processes within individual firms or businesses. It analyzes economic concepts like demand and supply, cost analysis, market structures, and competition to inform business strategies and optimize resource allocation.
2. Goal-Oriented:
Managerial Economics is not simply theoretical exploration; it has a practical and goal-oriented approach. It emphasizes the application of economic tools and techniques to solve real-world business problems. This includes making informed decisions about pricing, production, marketing, investment, and other crucial aspects of business operations.
3. Conceptual and Metrical:
Managerial Economics combines both conceptual understanding and quantitative analysis. It utilizes theoretical frameworks like economic models and statistical methods to analyze data, forecast trends, and evaluate different alternatives. This blend of theory and data-driven insights allows for informed and effective decision-making.
4. Pragmatic and Practical:
Managerial Economics is not about abstract academic discussions; it focuses on solving practical business problems. It provides managers with the necessary tools and frameworks to make decisions that are not only theoretically sound but also practical and feasible in the real world business environment.
5. Normative:
Managerial Economics goes beyond simply describing economic phenomena; it also aims to prescribe optimal solutions for business decisions. It provides guidance on how to allocate resources efficiently, maximize profits, and achieve organizational goals through strategic economic analysis.
6. Interdisciplinary:
Managerial Economics draws upon knowledge from various disciplines, including economics, accounting, finance, marketing, and statistics. This interdisciplinary approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of business problems and facilitates the development of effective solutions.
7. Dynamic:
Managerial Economics is a dynamic field that constantly evolves to reflect changes in the business environment, economic trends, and technological advancements. It requires continuous learning and adaptation to remain effective in managing businesses in a dynamic and complex world.
8. Multilevel Application:
Managerial Economics is applicable at various levels within an organization, from individual decision-making to strategic planning. It can be used by entrepreneurs, managers, executives, and other stakeholders to make informed choices about resource allocation, pricing, production, and other critical business functions.
9. Mathematical and Quantitative Tools:
Managerial Economics utilizes various mathematical and quantitative tools, including regression analysis, optimization techniques, and simulation models. These tools help analyze complex data, forecast future trends, and evaluate different business scenarios to make informed and data-driven decisions.
10. Continuous Research and Development:
Managerial Economics is a field with ongoing research and development activities. New economic theories, analytical methods, and decision-making tools are continuously being developed to enhance its effectiveness and applicability in the ever-changing business landscape.
In conclusion, these key attributes collectively define Managerial Economics as a distinct field of study that equips businesses with the necessary knowledge, tools, and frameworks to make informed decisions, solve real-world problems, and achieve their organizational goals.