What does marginal analysis mean?
Marginal analysis is a fundamental concept in economics that involves examining the incremental changes in various aspects of a decision, such as cost, benefit, or revenue, as a result of making small adjustments to that decision. It helps individuals, businesses, and policymakers make informed choices by evaluating the additional or marginal effects of each decision.
Key components of marginal analysis include:
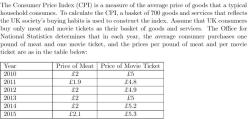
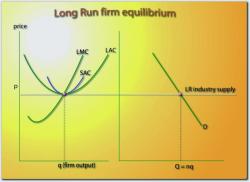
Marginal Cost (MC): This represents the additional cost incurred when producing one more unit of a good or service. It helps determine the cost-effectiveness of increasing production.
Marginal Benefit (MB): This refers to the additional benefit or utility gained from consuming or producing one more unit of a good or service. It helps assess the value of each additional unit.
Marginal Revenue (MR): In a business context, this is the additional revenue generated by selling one more unit of a product. It's essential for profit maximization and pricing decisions.
Marginal Utility (MU): In consumer theory, this represents the additional satisfaction or happiness gained from consuming one more unit of a product. It helps individuals make choices about consumption.
The core principle of marginal analysis is that rational decision-makers will continue to engage in an activity (such as producing, consuming, or investing) as long as the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost. When MB is greater than MC, it indicates that increasing the activity is beneficial. Conversely, when MC exceeds MB, it suggests that reducing the activity may be more economically efficient.
Marginal analysis is applied in various economic contexts, including production, pricing, resource allocation, consumption choices, and public policy decisions. It helps individuals and organizations optimize their decisions by considering the additional consequences of each incremental change. By comparing marginal costs and benefits, economic actors can make choices that maximize their overall well-being, profits, or utility.