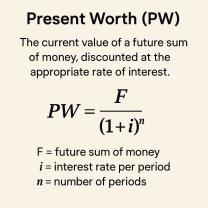
How to calculate fixed weight-price index?
A fixed-weight price index, also known as a Laspeyres index, is a type of price index used in economics to measure the relative change in the cost of a fixed basket of goods and services over time. This index keeps the quantities of goods and services constant, unlike a quantity-weighted index (Paasche index) that adjusts for changes in consumption patterns. To calculate a fixed-weight price index, you can follow these steps:
Select a Base Year:
- Choose a specific year as the "base year." The prices and quantities of goods and services in this year will serve as the reference point.
Define the Basket of Goods and Services:
- Create a list of items (goods and services) that represent a typical consumer's purchases. This basket remains constant over time.
Gather Price Data:
- Obtain the prices of each item in the basket for both the base year and the current year (or other relevant years). Prices should be collected consistently (e.g., monthly or annually).
Calculate the Cost in the Base Year:
- For each item in the basket, multiply the quantity purchased in the base year by the price in the base year.
- Cost in Base Year = Quantity in Base Year x Price in Base Year
Calculate the Cost in the Current Year:
- For each item in the basket, multiply the quantity purchased in the current year by the price in the current year.
- Cost in Current Year = Quantity in Current Year x Price in Current Year
Compute the Fixed-Weight Price Index:
The formula for the fixed-weight price index is:
- Fixed-Weight Price Index = (Cost in Current Year / Cost in Base Year) x 100
This formula calculates the percentage change in the cost of the fixed basket of goods and services from the base year to the current year.
Interpret the Result:
- The fixed-weight price index provides a measure of price inflation or deflation for the selected basket of goods and services. A value greater than 100 indicates an increase in the cost of the basket (inflation), while a value less than 100 suggests a decrease (deflation).
Repeat for Subsequent Years (Optional):
- You can calculate the fixed-weight price index for multiple years to track price changes over time, always using the base year's basket as the reference.
It's important to note that the fixed-weight price index has limitations, particularly because it does not account for changes in consumer behavior or shifts in consumption patterns. For a more comprehensive analysis, economists often use the quantity-weighted (Paasche) index, which adjusts the basket of goods and services to account for changing consumption patterns.
Understanding the Basics of Fixed Weight-Price Index Calculation
A fixed weight-price index is a measure of inflation that uses a fixed basket of goods and services to calculate price changes over time. This means that the same goods and services are used in each period to calculate the index, regardless of whether their importance in the consumer basket has changed.
Fixed weight-price indexes are calculated by dividing the current price of the basket of goods and services by the base year price of the basket and multiplying by 100. The base year is a period of time that is used as a benchmark for comparison.
Steps to Calculate Fixed Weight-Price Index
To calculate a fixed weight-price index, follow these steps:
- Select a basket of goods and services that represent the typical consumption habits of consumers.
- Collect price data for the basket of goods and services in the base year.
- Calculate the weight of each item in the basket by dividing its price by the total price of the basket.
- Calculate the current price of the basket of goods and services.
- Calculate the fixed weight-price index by dividing the current price of the basket of goods and services by the base year price of the basket and multiplying by 100.
Interpreting Fixed Weight-Price Index Trends
Fixed weight-price indexes can be used to track inflation over time and to compare inflation rates between different countries or regions.
If the fixed weight-price index is increasing, then this indicates that inflation is occurring. If the fixed weight-price index is decreasing, then this indicates that deflation is occurring.
Fixed weight-price indexes can also be used to compare the cost of living in different places. For example, if the fixed weight-price index for a city is higher than the fixed weight-price index for another city, then this indicates that the cost of living is higher in the first city.
Limitations of Fixed Weight-Price Indexes
Fixed weight-price indexes have some limitations. One limitation is that they do not account for changes in consumer spending habits over time. For example, if consumers start to spend more money on new goods and services that are not included in the basket of goods and services used to calculate the index, then this can bias the index upwards.
Another limitation is that fixed weight-price indexes do not account for quality changes. For example, if the quality of a good or service improves over time, then this can bias the index downwards.
Despite their limitations, fixed weight-price indexes are widely used to measure inflation and to compare the cost of living in different places.