What factors determine the foreign exchange rate of a currency?
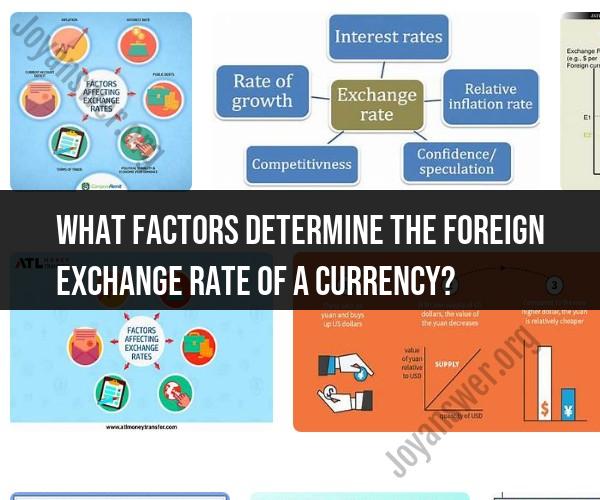
Foreign exchange rates are determined by a complex interplay of various factors, including economic, financial, political, and psychological influences. Here are some of the key determinants that affect the foreign exchange rates of a currency:
Interest Rates: Central banks' monetary policies, including changes in interest rates, play a significant role in influencing exchange rates. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign capital, increasing demand for the domestic currency and strengthening its value.
Economic Indicators: Various economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, employment data, and trade balances can impact exchange rates. Strong economic performance tends to attract foreign investment, leading to currency appreciation.
Inflation Rate: A country with lower inflation rates typically sees an appreciation in its currency's value because its purchasing power increases compared to countries with higher inflation.
Political Stability: Political stability and good governance can contribute to a strong and stable currency. Political uncertainty or instability can lead to currency depreciation.
Market Sentiment: Traders' perceptions and market sentiment can have a short-term impact on exchange rates. News, events, and speculative trading can lead to rapid and temporary fluctuations.
Supply and Demand: The basic economic principle of supply and demand applies to foreign exchange markets. If there is high demand for a particular currency, its value will typically increase. Conversely, increased supply can lead to depreciation.
Central Bank Interventions: Central banks may engage in foreign exchange interventions by buying or selling their own currency to influence its value. These interventions can be aimed at stabilizing or manipulating exchange rates.
Trade Balance: A country's trade balance, which is the difference between its exports and imports, can affect its currency's value. A trade surplus (more exports than imports) can strengthen the currency, while a trade deficit can weaken it.
Speculation: Currency traders and investors often speculate on future exchange rate movements. Their actions can influence short-term fluctuations in exchange rates.
Global Economic and Political Events: Events such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and global economic crises can significantly impact exchange rates, leading to safe-haven flows or risk aversion.
Government Policies: Government policies, including trade policies, taxation, and regulatory changes, can influence exchange rates. For instance, tariffs and trade restrictions can impact currency values.
Market Liquidity: The foreign exchange market is the most liquid financial market in the world. Liquidity can affect exchange rates, with more liquid currencies often being more stable.
Market Speculation: Traders and investors often make bets on future exchange rate movements, which can lead to short-term fluctuations in currency values.
Relative Strength of Other Currencies: Exchange rates are relative. The value of one currency is determined in relation to another. Therefore, changes in the strength of other major currencies also influence exchange rates.
It's important to note that these determinants are interconnected, and exchange rates are influenced by a combination of these factors. Moreover, exchange rates can be influenced by both short-term and long-term considerations, which makes predicting currency movements a complex endeavor. Forex markets are highly volatile, and many factors can impact exchange rates on a daily basis. Traders, businesses, and investors often closely monitor these determinants when dealing with foreign exchange.
Factors Determining Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are determined by a variety of factors, including economic, political, and social factors. Some of the most important factors include:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, which can lead to an appreciation of the currency.
- Inflation: Inflation is the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. A higher inflation rate can lead to a depreciation of the currency, as foreign investors will be less likely to invest in a country with a high inflation rate.
- Economic growth: A strong economy is typically associated with a strong currency. A country with a growing economy is more likely to attract foreign investment, which can lead to an appreciation of the currency.
- Political stability: Political instability can lead to a depreciation of the currency, as foreign investors are less likely to invest in a country with an unstable political environment.
- Trade balance: A trade balance is the difference between a country's exports and imports. A trade deficit (more imports than exports) can lead to a depreciation of the currency, as the country will need to sell its currency to buy foreign goods and services.
Economic and Political Forces Impacting Exchange Rates
Economic and political forces can have a significant impact on exchange rates. For example, a recession in one country can lead to a depreciation of that country's currency, as foreign investors will be less likely to invest in a country with a weak economy. Political instability, such as a war or coup, can also lead to a depreciation of the currency.
Central Banks and Their Role in Currency Valuation
Central banks play an important role in currency valuation by setting interest rates and conducting foreign exchange interventions. Central banks can raise interest rates to attract foreign investment and support the currency. They can also sell foreign currency reserves to buy their own currency and support the value of the currency.
Speculation and Market Sentiment in Exchange Rates
Speculation and market sentiment can also play a role in exchange rate fluctuations. Speculators buy and sell currencies in the hope of making a profit from changes in exchange rates. Market sentiment refers to the overall mood of the market, which can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as economic data, news events, and political developments.
Analyzing Exchange Rate Fluctuations in a Global Context
Exchange rate fluctuations can have a significant impact on the global economy. For example, a depreciation of the US dollar can make US exports cheaper for foreign buyers, which can boost US exports and economic growth. However, a depreciation of the US dollar can also make imports more expensive for US consumers, which can lead to inflation.
It is important to analyze exchange rate fluctuations in a global context to understand their impact on the global economy. For example, if the US dollar is depreciating against all major currencies, this suggests that there is a global shortage of US dollars. This can lead to higher interest rates and slower economic growth in the United States.
Exchange rates are complex and are influenced by a variety of factors. It is important to understand the different factors that can impact exchange rates in order to make informed decisions about foreign exchange transactions.