What are financial ratios used for?
Financial ratios are used to evaluate and analyze a company's financial performance and its overall financial health. They provide a way to assess different aspects of a company's operations and can be valuable for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and analysts. Here are some key purposes and uses of financial ratios:
Performance Assessment: Financial ratios help in assessing how well a company is performing. They provide a snapshot of a company's financial performance over time.
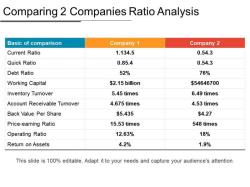
Comparative Analysis: Ratios enable comparisons between companies in the same industry or sector. This helps in benchmarking and understanding how a company stacks up against its peers.
Trend Analysis: By calculating ratios over multiple periods, you can identify trends and changes in a company's financial performance, which can be crucial for making strategic decisions.
Credit Risk Evaluation: Creditors, such as banks and bondholders, use financial ratios to assess a company's creditworthiness and determine the risk associated with lending money to the company.
Investment Decisions: Investors use financial ratios to evaluate the potential of an investment. Ratios like price-to-earnings (P/E) and dividend yield are common indicators for investors.
Management Decision-Making: Company management uses financial ratios to monitor their performance, identify areas of improvement, and make strategic decisions. For example, return on investment (ROI) can help in capital allocation decisions.
Forecasting and Planning: Ratios can be used to forecast future financial performance and help in the development of financial plans and budgets.
Liquidity Analysis: Ratios like the current ratio and quick ratio are used to assess a company's ability to meet its short-term financial obligations.
Profitability Assessment: Ratios like gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin help in understanding how efficiently a company generates profits.
Efficiency Analysis: Efficiency ratios, such as inventory turnover and accounts receivable turnover, provide insights into how well a company manages its assets and liabilities.
Common financial ratios include:
- Liquidity Ratios: Current ratio, quick ratio.
- Profitability Ratios: Gross margin, operating margin, net profit margin.
- Solvency Ratios: Debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio.
- Efficiency Ratios: Inventory turnover, accounts receivable turnover.
- Valuation Ratios: Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-book (P/B) ratio.
Different stakeholders may focus on different ratios depending on their interests and objectives. It's important to use a combination of ratios to get a comprehensive view of a company's financial health and performance.
The Purpose and Significance of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are a set of metrics that are used to analyze a company's financial performance. They are calculated using data from the company's financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Financial ratios are significant because they provide insights into a company's financial health, profitability, efficiency, and solvency. This information can be used by investors, creditors, and managers to make informed decisions.
Common Financial Ratios for Performance Assessment
There are many different financial ratios that can be used to assess a company's performance. Some of the most common ratios include:
- Liquidity ratios: These ratios measure a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations. Some common liquidity ratios include the current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio.
- Profitability ratios: These ratios measure a company's ability to generate profits. Some common profitability ratios include the net profit margin, operating profit margin, and return on equity.
- Efficiency ratios: These ratios measure how well a company is using its resources. Some common efficiency ratios include the inventory turnover ratio, accounts receivable turnover ratio, and total asset turnover ratio.
- Solvency ratios: These ratios measure a company's ability to meet its long-term obligations. Some common solvency ratios include the debt-to-equity ratio and the times interest earned ratio.
Interpreting Ratios in the Context of Financial Analysis
When interpreting financial ratios, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Industry averages: Some financial ratios vary widely by industry. For example, a high inventory turnover ratio may be considered good for a retail company, but it may be considered bad for a manufacturing company.
- Trend analysis: It is often more informative to track a company's financial ratios over time than to compare them to industry averages at a single point in time. This can help to identify trends in the company's performance and to identify potential problems early on.
- Qualitative factors: Financial ratios should not be used in isolation. It is also important to consider qualitative factors, such as the company's management team, its competitive landscape, and its industry outlook.
Utilizing Ratios for Investment and Business Decisions
Financial ratios can be used to make a variety of investment and business decisions. For example, investors may use financial ratios to screen for potential investment opportunities and to evaluate the performance of their existing investments. Creditors may use financial ratios to assess a company's creditworthiness before lending money. And managers may use financial ratios to track the company's performance and to identify areas where improvement is needed.
Calculating and Applying Financial Ratios Effectively
To calculate financial ratios effectively, it is important to have a good understanding of the underlying financial statements. Once you have calculated the ratios, it is important to interpret them in the context of the factors discussed above.
Here are some tips for applying financial ratios effectively:
- Use a combination of ratios: No single ratio can provide a complete picture of a company's financial health. It is important to use a combination of ratios to get a more comprehensive view.
- Compare ratios to industry averages: Comparing a company's ratios to industry averages can help you to identify areas where the company is performing better or worse than its peers.
- Track ratios over time: Tracking a company's ratios over time can help you to identify trends in the company's performance and to identify potential problems early on.
- Consider qualitative factors: Financial ratios should not be used in isolation. It is also important to consider qualitative factors, such as the company's management team, its competitive landscape, and its industry outlook.
Financial ratios are a powerful tool that can be used to analyze a company's financial health, profitability, efficiency, and solvency. By understanding and applying financial ratios effectively, investors, creditors, and managers can make more informed decisions.