What are exogenous variables in research?
What Are Exogenous Variables in Research?
In research (especially in statistics, econometrics, and social sciences), exogenous variables are variables that come from outside the system or model being studied.
They are not influenced by other variables within the model.
Instead, they influence or affect the dependent variable or other variables in the system.
Think of them as “external inputs” that help explain changes in the outcome, but remain independent of the system itself.
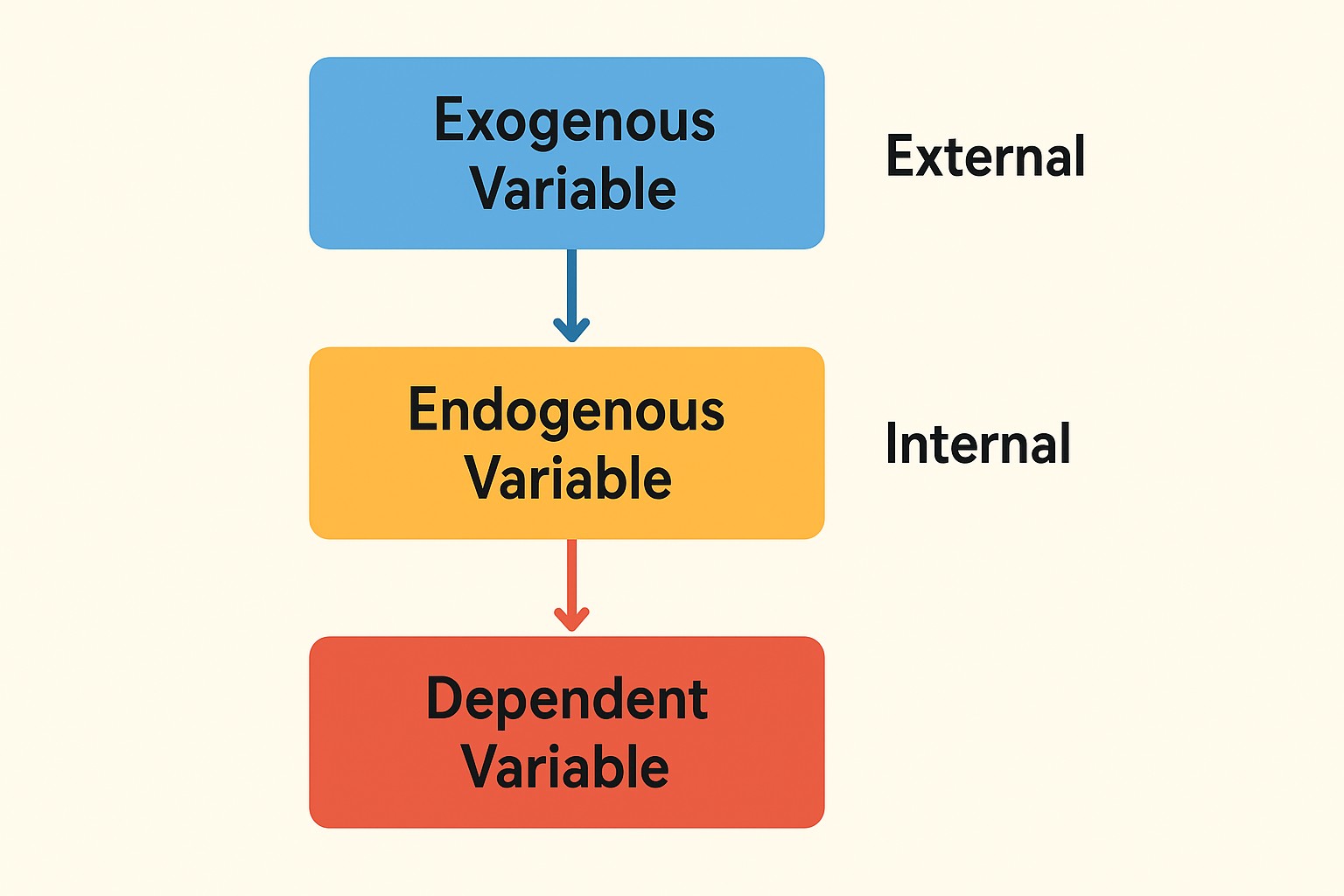
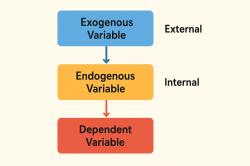
Exogenous vs. Endogenous Variables
Exogenous Variable → External, independent, not explained by the model.
Endogenous Variable → Internal, dependent, influenced by other variables in the model.
Example (Education & Income study):
Exogenous variable: Parents’ education level (not affected by the model’s variables).
Endogenous variable: Student’s income (depends on education, experience, etc.).
Examples of Exogenous Variables
Economics:
Government policies (tax rates, subsidies)
Weather conditions affecting agriculture
Global oil prices
Social Sciences:
Age, gender, ethnicity (cannot be changed by the model’s other factors)
Family background in educational studies
Medicine/Health Research:
Genetic traits
Environmental exposure (pollution, climate)
Why They Matter
Exogenous variables are crucial for causal inference.
Researchers must correctly identify them to avoid bias in models.
Misclassifying a variable (treating endogenous as exogenous) can lead to incorrect conclusions.
In short:
Exogenous variables are outside factors that influence outcomes in a research model but are not themselves influenced by the system being studied.
What Are Exogenous Variables in Research?
In any research model, variables are classified based on their relationship to the system being studied. An exogenous variable (also known as an independent or predictor variable) is a factor whose value is determined outside the model. It is not influenced by any other variables within the system you are analyzing. Instead, its value is taken as a given, and it is used to explain or predict the behavior of other variables.
Think of it as a "driver" of the model. For instance, in a study of crop yields, the amount of rainfall is an exogenous variable. It affects the crop yield, but the crop yield itself has no influence on the rainfall.
How to Identify Exogenous Variables in a Study?
Identifying exogenous variables is crucial for building a valid research model. A key test is to ask: "Does this variable's value change in response to anything else happening within my model?" If the answer is no, it's likely an exogenous variable. Here are some steps to help you identify them:
Look for external influences: Exogenous variables are often factors that are outside the control of the system or the researcher. These could be natural events (like weather), government policies, or broad economic conditions.
Check for a one-way causal relationship: The variable should have a causal effect on other variables in the model, but not be causally affected by them. For example, a company's advertising budget (set by a manager) can affect sales, but the sales figures don't typically determine the advertising budget for that same period.
Consider the context of the model: A variable that is exogenous in one model may be endogenous (determined within the model) in another. For example, in a simple model of consumer spending, income is often treated as exogenous. However, in a macroeconomic model, income is an endogenous variable, influenced by factors like investment and government spending.
Why Are Exogenous Variables Important in Research Design?
The correct identification and inclusion of exogenous variables are fundamental to a robust research design, particularly in fields like econometrics and social sciences.
Establishing Causality: By their nature, exogenous variables are essential for establishing a causal link between variables. Since they are not influenced by the system, any observed effect they have on an endogenous variable can be more confidently attributed to them.
Preventing Bias: A major problem in research is endogeneity, which occurs when a variable is correlated with the error term of a regression model. This can happen due to reverse causality, omitted variables, or measurement error. By correctly identifying and treating variables as exogenous, researchers can avoid this bias and ensure their results are more accurate.
Improving Model Accuracy: Including relevant exogenous variables helps to account for the variation in the dependent variable that is not explained by other factors in the model. This leads to more precise and reliable predictions.
How Do Exogenous Variables Affect Results?
The impact of an exogenous variable on research results can be direct and significant.
When an exogenous variable's value changes, it acts as an external "shock" to the system. This shock propagates through the model, influencing the values of the endogenous variables. For instance, if a government introduces a new tax policy (an exogenous variable), it can directly affect consumer prices and spending (endogenous variables) within an economic model. The results of the study will then show the predicted or actual magnitude of this effect.
The stability and predictability of exogenous variables are what allow researchers to model "what-if" scenarios and make forecasts. By observing how the endogenous variables respond to changes in the exogenous ones, we gain a deeper understanding of the system's dynamics.
What Are Examples of Exogenous Variables in Different Fields?
Economics:
Government Policies: A change in the central bank's interest rate or a new tax law are classic examples. They affect economic outcomes like inflation and unemployment but are not themselves determined by those outcomes within a given model.
Natural Disasters: An earthquake or a hurricane can disrupt production and supply chains, affecting a country's GDP, but the GDP does not influence the occurrence of the natural disaster.
Environmental Science:
Pollution Levels: The amount of industrial pollutants in a river might be treated as an exogenous variable when studying the health of a fish population. The health of the fish is affected by the pollution, but not the other way around.
Solar Radiation: The intensity of sunlight is an exogenous factor that affects plant growth in an agricultural model.
Medicine and Public Health:
Genetics: In a study on the effectiveness of a new medication, a patient's genetic predisposition to a certain disease can be considered an exogenous variable. It influences the outcome of the treatment but is not a result of it.
Patient Age and Gender: In many clinical trials, a patient's age or gender is a fixed characteristic that affects their response to a treatment but is not influenced by the treatment itself.