How do you write a proposal for a research paper?
Writing a research paper proposal involves outlining the key elements of your planned research, demonstrating its significance, and providing a roadmap for how you intend to conduct the study. Here are guidelines to help you craft a research paper proposal:
1. Title:
- Provide a clear and concise title that reflects the main focus of your research. The title should be engaging and informative.
2. Introduction:
Background and Context:
- Introduce the general topic and provide background information to contextualize your research. Explain the significance of the problem or issue you are addressing.
Problem Statement:
- Clearly state the problem or research question that your study aims to address. Define the scope of the problem and why it is important to investigate.
Objectives or Hypotheses:
- Outline the specific objectives or hypotheses of your research. What do you aim to achieve or prove through your study?
3. Literature Review:
Review of Previous Studies:
- Summarize relevant literature that provides context for your research. Identify gaps, controversies, or areas where further research is needed.
Theoretical Framework:
- If applicable, discuss the theoretical framework that will guide your study. Explain how existing theories inform your research.
4. Research Design and Methods:
Research Design:
- Describe the overall research design (e.g., experimental, observational, qualitative, quantitative). Justify why this design is appropriate for your research.
Sampling:
- Specify your target population and describe your sampling method. Explain how you will select participants or sources for your study.
Data Collection Methods:
- Detail the methods you will use to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments). Discuss why these methods are suitable for your research.
Data Analysis:
- Outline the techniques you will use to analyze the collected data. Explain how the analysis will address your research questions or test your hypotheses.
5. Significance and Contribution:
Significance of the Study:
- Clearly articulate why your research is important and how it contributes to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
Expected Contribution:
- Explain the potential contributions of your study. How will your research advance understanding, inform practice, or contribute to policy?
6. Timeline:
- Provide a realistic timeline for the completion of different stages of your research. Include milestones, such as literature review completion, data collection, analysis, and writing.
7. Budget (if applicable):
- If your research requires funding, provide a brief budget outline. Include estimated costs for materials, participant compensation, travel, or any other relevant expenses.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss ethical considerations associated with your research, including participant consent, confidentiality, and any potential risks. Explain how you plan to address ethical concerns.
9. References:
- Include a list of references cited in your proposal. Ensure that your citations follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
10. Formatting and Style:
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your institution or the publication you are submitting the proposal to. Pay attention to font, spacing, and other formatting details.
11. Review and Revise:
- Review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and completeness. Seek feedback from mentors or peers and be prepared to revise based on their suggestions.
12. Appendices:
- Include any necessary appendices, such as survey instruments, interview guides, or additional supporting documents.
13. Submission Instructions:
- If submitting the proposal for approval or publication, adhere to any specific submission instructions provided by the relevant institution, committee, or journal.
14. Presentation:
- If required, be prepared to present your proposal orally to an audience. Create slides or materials that effectively communicate the key points of your research.
Remember that the specific requirements for a research paper proposal may vary depending on the academic or institutional context. Always refer to the guidelines provided by your instructor, department, or the publication you are submitting to.
Crafting a Compelling Research Proposal: Essential Elements and Structure
A compelling research proposal serves as a roadmap for your research project, outlining the problem you aim to address, the methods you intend to employ, and the expected outcomes. To craft a persuasive proposal, consider these essential elements and structure:
1. Introduction
- Background: Briefly introduce the research area and the context of your study.
- Problem Statement: Clearly articulate the specific problem or question your research aims to address.
- Significance: Highlight the importance of your research and its potential contribution to the field.
2. Literature Review
- Demonstrate Expertise: Demonstrate your understanding of the existing body of knowledge in your field.
- Identify Gaps: Identify gaps in the literature that your research seeks to fill.
- Position Your Research: Position your research within the context of existing literature.
3. Research Methodology
- Research Design: Clearly state the research design, whether experimental, observational, or qualitative.
- Data Collection: Describe the methods you will use to collect data, including sampling techniques and data collection instruments.
- Data Analysis: Explain how you will analyze the data collected to address your research question.
4. Expected Outcomes
- Anticipated Findings: Discuss the anticipated findings of your research and their potential impact.
- Contributions: Highlight the potential contributions of your research to the field of study.
- Dissemination Plan: Outline your plan for disseminating your research findings to the broader community.
5. Conclusion
- Reiterate Significance: Reemphasize the importance and significance of your research.
- Call to Action: Conclude with a call to action, encouraging support for your research project.
Formulating a Clear and Concise Research Question or Hypothesis
A well-formulated research question or hypothesis is the cornerstone of a compelling research proposal. It guides your investigation and provides a clear framework for interpreting your findings.
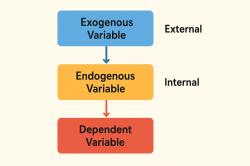
Research Question: A research question poses a specific inquiry that your research seeks to answer. It should be focused, clear, and researchable.
Hypothesis: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables. It should be testable, falsifiable, and specific.
Characteristics of a Good Research Question or Hypothesis:
- Focus: Clearly identifies the specific problem or relationship you are investigating.
- Clarity: Easily understandable and unambiguous.
- Researchability: Can be addressed using available methods and data.
- Falsifiability: Can be proven true or false based on empirical evidence.
- Specificity: Narrowly defined and focused on a specific aspect of the research problem.
Conducting a Thorough Literature Review to Support Your Research Proposal
A comprehensive literature review demonstrates your understanding of the existing body of knowledge in your research area and positions your project within the context of previous studies.
Steps for Conducting a Thorough Literature Review:
Identify Relevant Sources: Utilize academic databases, journals, and books to locate relevant scholarly literature.
Evaluate Sources: Critically evaluate the credibility, relevance, and timeliness of each source.
Summarize and Synthesize Findings: Summarize and synthesize the key findings of relevant studies, identifying patterns, trends, and gaps in the literature.
Cite Sources Properly: Use proper citation styles, such as APA or MLA, to acknowledge the work of others.
Integrate Findings: Integrate the findings of your literature review into your research proposal, supporting your research question or hypothesis.