What are the examples of conflict theory?
Conflict theory, a sociological perspective that emphasizes the role of power, inequality, and competition in shaping society, can be observed in various aspects of life. Here are some examples of conflict theory in action:
Class Conflict: Karl Marx's theory of class struggle is a foundational concept within conflict theory. This can be observed in society through the tension between different social classes. For example, labor disputes and strikes are clear demonstrations of workers (proletariat) seeking better wages and working conditions from employers (bourgeoisie).
Income Inequality: The increasing income gap between the wealthy and the poor is a prominent example of conflict theory. It highlights the power imbalances and struggles over resources and opportunities, which can lead to social unrest and protests.
Racial and Ethnic Conflict: Discrimination, racial profiling, and disparities in education and employment opportunities can be seen as manifestations of conflict theory in the context of racial and ethnic relations. These disparities reflect the unequal distribution of power and resources in society.
Gender Inequality: Gender-based conflicts and inequalities are evident in the gender wage gap, unequal access to leadership positions, and issues like domestic violence. Feminist perspectives often draw on conflict theory to analyze and address these disparities.
Political Conflicts: Political conflicts often revolve around power struggles. For example, elections, political campaigns, and lobbying efforts can be seen as conflicts between different groups and individuals seeking to gain or maintain political power.
War and International Relations: Conflict theory can be applied to international relations, where countries compete for power, resources, and influence. Wars, disputes over resources, and global power dynamics are all examples of conflict theory at the international level.
Criminal Justice System: Conflict theory can be observed in the criminal justice system, where there is often a power struggle between law enforcement, the legal system, and marginalized communities. Issues like racial profiling, over-policing, and disparities in sentencing highlight these conflicts.
Labor Relations: Strikes, negotiations, and labor disputes are classic examples of how conflict theory plays out in the workplace. Labor unions often represent the interests of workers in conflicts with management over wages, benefits, and working conditions.
Education System: Inequalities in educational opportunities and outcomes can be analyzed through a conflict theory lens. Disparities in school funding, access to quality education, and the impact of standardized testing are all areas where conflicts over resources and power are evident.
Environmental Conflict: Disputes over environmental resources and the impacts of environmental degradation can be seen as conflicts over access to and control of natural resources. These conflicts involve various stakeholders, including government, corporations, and local communities.
These examples illustrate how conflict theory can help analyze and understand the power struggles, inequalities, and conflicts that exist in various social, economic, and political domains. Conflict theory provides a valuable perspective for examining the dynamics of society and advocating for social change to address these conflicts and disparities.
Exploring Conflict Theory: An Introduction to Social Sciences
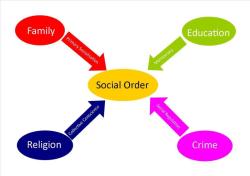
Conflict theory is a sociological perspective that views society as being in a state of perpetual conflict due to competition for limited resources. Conflict theorists argue that social order is maintained by domination and power, rather than by consensus and conformity.
Conflict theory is one of the three major theoretical perspectives in sociology, along with functionalism and symbolic interactionism. While conflict theory is often seen as being in opposition to functionalism, the two perspectives can be complementary. Functionalism focuses on how social institutions and structures contribute to the stability of society, while conflict theory focuses on the sources of conflict and change within society.
Key Concepts and Principles of Conflict Theory
Some of the key concepts and principles of conflict theory include:
- Social inequality: Conflict theorists argue that social inequality is the root cause of conflict in society. Social inequality can be based on factors such as class, race, gender, and ethnicity.
- Power: Power is another key concept in conflict theory. Conflict theorists argue that power is the ability to control others and to get what one wants. Power can be used to maintain social order, but it can also be used to oppress and exploit others.
- Change: Conflict theorists argue that conflict is a necessary part of social change. Conflict can challenge the status quo and lead to the creation of a more just and equitable society.
Conflict Theory in Sociology and Its Main Tenets
Conflict theory was first developed by Karl Marx, a German philosopher and sociologist. Marx's conflict theory is based on the idea that society is divided into two classes: the bourgeoisie (the owners of the means of production) and the proletariat (the working class). Marx argued that the bourgeoisie exploits the proletariat in order to generate profits. This conflict between the two classes is the driving force of social change.
Other notable conflict theorists include:
- Max Weber, who argued that conflict in society is not simply based on class, but also on other factors such as status and power.
- C. Wright Mills, who argued that power in society is concentrated in the hands of a small elite group.
- Ralph Dahrendorf, who argued that conflict in society is inevitable because of the different interests of different social groups.
Applications of Conflict Theory in Analyzing Social Issues
Conflict theory can be used to analyze a wide range of social issues, including:
- Crime and social disorder: Conflict theorists argue that crime and social disorder are caused by social inequality and the lack of opportunities for disadvantaged groups.
- Education: Conflict theorists argue that the education system is used to maintain social inequality by reproducing the dominant ideology and culture.
- Gender inequality: Conflict theorists argue that gender inequality is caused by the unequal distribution of power between men and women.
- Race and ethnicity: Conflict theorists argue that racism and ethnic discrimination are caused by the unequal distribution of power between different racial and ethnic groups.
Contemporary Relevance of Conflict Theory in Society
Conflict theory remains a relevant perspective for understanding and analyzing social issues today. Conflict theorists argue that the root causes of conflict in society, such as social inequality and power imbalances, have not changed significantly. As a result, conflict theory can help us to understand the challenges that we face in creating a more just and equitable society.
Conflict theory is also relevant to a number of emerging social issues, such as climate change and technological change. Conflict theorists argue that these issues are likely to exacerbate social inequality and conflict in the future.
Overall, conflict theory is a valuable perspective for understanding and analyzing social issues. It helps us to see that society is not a harmonious whole, but rather a complex arena of competing interests and power struggles.