What is the social structure of society?
The social structure of society refers to the organized patterns of relationships, roles, institutions, and hierarchies that shape human interactions within a given community or society. It provides a framework for understanding how individuals and groups are connected and how they function within a larger social context. Here are key aspects of the social structure of society and how it helps us understand human relationships:
Roles and Statuses: Social structure assigns individuals and groups specific roles, positions, and statuses. These roles define expectations, behaviors, and responsibilities. For example, in a family, there are roles for parents, children, and grandparents, each with its own set of expectations.
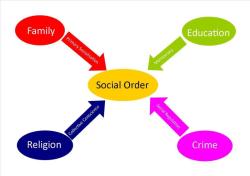
Social Institutions: Social structure includes various social institutions, such as family, education, religion, government, and the economy. These institutions serve specific functions in society and provide a framework for individuals to interact and fulfill their basic needs.
Hierarchy: Social structures often involve hierarchies that establish power and authority. For instance, governments have leaders and citizens, businesses have CEOs and employees, and schools have principals and students. Hierarchies can impact how resources, opportunities, and influence are distributed.
Social Groups: People in society form various social groups based on shared interests, values, or characteristics. These groups can include families, peer groups, clubs, and communities. Social structure helps define the roles and relationships within these groups.
Norms and Expectations: Social structures establish norms, which are culturally accepted standards of behavior. These norms guide individuals on how to act in various social situations. For example, politeness and respect are social norms that govern interactions in many societies.
Social Mobility: Social structure can influence an individual's social mobility, which refers to the ability to move up or down the social and economic hierarchy. In some societies, there are barriers that limit mobility, while others provide opportunities for upward mobility through education and hard work.
Cultural Values: Cultural values, beliefs, and traditions are integrated into the social structure and impact how people perceive themselves and their relationships with others. Cultural norms may influence the roles of men and women, family structures, and social expectations.
Social Networks: Social structure also includes the networks of relationships that individuals develop, both in person and online. These networks can be critical for social support, information sharing, and career opportunities.
Inequality and Stratification: Social structures can lead to social stratification, where individuals and groups are placed in different social classes based on factors like wealth, education, and social standing. Understanding social structure helps us examine and address issues of inequality and injustice.
Change and Evolution: Social structure is not static; it evolves over time in response to cultural, economic, and technological changes. Studying social structure can help us understand how societies adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
Understanding the social structure of society is essential for sociologists, anthropologists, and other social scientists as it provides insights into how societies function, how relationships are formed and maintained, and how individuals and groups are influenced by their social environment. It also helps individuals navigate the complexities of social life and make sense of their roles and responsibilities within their communities.