What is an example of structural functionalism?
Structural functionalism is a sociological perspective that views society as a complex system with various parts and institutions that work together to maintain stability and order. According to this perspective, each part of society has a function that contributes to the overall functioning and stability of the whole. Here's an example of structural functionalism in sociology:
Education System:One classic example of structural functionalism is the analysis of the education system within society. In this perspective:
Function of Socialization: The education system serves the function of socializing individuals into the norms, values, and roles of society. It teaches children not only academic subjects but also social skills and cultural knowledge.
Function of Sorting and Stratification: Another function of education is to sort individuals based on their abilities and qualifications. This helps society allocate individuals to different roles and positions according to their talents and skills. For example, the education system identifies individuals who are suitable for various professions, from doctors and engineers to artists and teachers.
Function of Social Order: The education system also contributes to social order by instilling discipline, punctuality, and respect for authority in students. This helps maintain a stable and orderly society.
Function of Economic Productivity: Education prepares individuals for the workforce, which is vital for the functioning of the economy. It provides the knowledge and skills needed for various jobs and professions, thus contributing to economic productivity.
Function of Social Change: While education reinforces existing norms and values, it can also serve as a mechanism for social change. For instance, through education, societies can introduce new ideas, values, and perspectives that challenge the status quo and lead to social change.
In this example, structural functionalism suggests that the education system is a vital institution in society, as it performs various functions that contribute to the overall stability and functioning of the social system. This perspective emphasizes the interconnectedness of different parts of society and how they work together to maintain equilibrium. However, it's worth noting that structural functionalism has been criticized for overlooking issues of inequality and conflict within society, which other sociological perspectives, such as conflict theory and symbolic interactionism, address more directly.
An Example of Structural Functionalism in Society
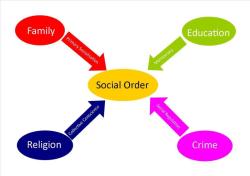
One example of structural functionalism in society is the family. The family is a social institution that serves a number of important functions, such as:
- Socialization: The family is the primary agent of socialization, teaching children the basic norms and values of society.
- Emotional support: The family provides its members with emotional support and love.
- Economic support: The family provides its members with economic support, such as food, clothing, and shelter.
The family institution is also interconnected with other social institutions, such as the education system and the economy. For example, parents are responsible for sending their children to school, and children need to be educated in order to get good jobs and support their families.
Applying Structural Functionalism to Analyze Social Institutions
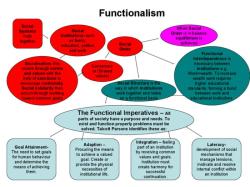
Structural functionalism can be applied to analyze any social institution, such as the government, the economy, or religion. To analyze a social institution using structural functionalism, you would need to identify:
- The structure of the institution: What are the different parts of the institution and how do they work together?
- The functions of the institution: What needs does the institution meet for society?
- The interconnectedness of the institution with other social institutions: How does the institution interact with other parts of society?
For example, to analyze the government using structural functionalism, you would need to identify the different branches of government (legislative, executive, and judicial), how they interact with each other, and the functions that they serve for society (e.g., making laws, enforcing laws, and interpreting laws). You would also need to consider how the government is interconnected with other social institutions, such as the economy and the education system.
Case Study: Understanding Society Through the Lens of Structural Functionalism
One way to understand society through the lens of structural functionalism is to examine how social institutions work together to meet the needs of society. For example, the family, the education system, and the economy all play a role in preparing young people for adulthood and productive employment.
The family provides children with the socialization and emotional support they need to develop into healthy and well-adjusted adults. The education system provides children with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in the workforce. And the economy provides jobs and opportunities for adults to support themselves and their families.
By understanding how social institutions work together to meet the needs of society, we can gain a better understanding of how society functions as a whole.
Limitations of Structural Functionalism
Structural functionalism has been criticized for a number of reasons, including:
- It is a conservative theory that tends to view the status quo as desirable.
- It does not take into account conflict or social change.
- It focuses on the functions of social institutions, but it does not adequately explain how social institutions came to be or how they change over time.
Despite these limitations, structural functionalism remains an important theoretical framework for understanding society. It provides a useful way to think about how social institutions work together to meet the needs of society.