What did Emile Durkheim believe about society?
Émile Durkheim (1858-1917) was a pioneering French sociologist who made significant contributions to the field of sociology. His work laid the foundation for the study of sociology as a scientific discipline, and he had several key beliefs about society, which are summarized below:
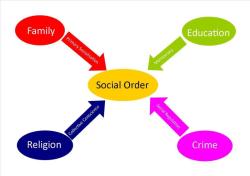
Social Solidarity: Durkheim believed that social solidarity, or the bonds that hold society together, is essential for social order. He identified two types of social solidarity:
- Mechanical Solidarity: In traditional, pre-industrial societies, people share similar values, norms, and beliefs. Social cohesion is based on the similarity of individuals.
- Organic Solidarity: In modern, industrial societies, social cohesion is based on the interdependence of individuals. People have specialized roles and depend on each other for the functioning of society.
Anomie: Durkheim introduced the concept of "anomie" to describe a state of normlessness and breakdown in social order. He argued that rapid social change and disintegration of traditional norms could lead to anomie, which might result in deviant behavior and increased suicide rates.
Division of Labor: Durkheim was interested in how the division of labor in society affects social integration. He believed that as societies become more complex and industrialized, the division of labor increases, leading to organic solidarity. However, an excessive division of labor without a sense of connection can result in social problems.
Religion: Durkheim examined the role of religion in society. He believed that religion served as a way to create and reinforce social cohesion. He distinguished between the sacred (things set apart and revered) and the profane (ordinary, everyday things). Religious rituals and symbols, according to Durkheim, helped to bind individuals to the collective conscience of society.
Social Facts: Durkheim emphasized the importance of studying "social facts," which are external, objective forces that shape individual behavior. These include norms, values, institutions, and social structures. Durkheim believed that sociologists should study these social facts to understand and explain social phenomena.
Suicide: Durkheim's pioneering study on suicide is a classic in sociology. He explored the social causes of suicide, highlighting how different types of suicides (egoistic, altruistic, anomic) were related to the level of integration of individuals in society.
Crime and Deviance: Durkheim studied crime and deviance and argued that they are normal and necessary parts of society. They help to define and reinforce societal norms and boundaries.
In summary, Durkheim believed that society was more than just the sum of its individual parts; it had its own properties and functions. His work emphasized the importance of social order, integration, and the role of social forces in shaping human behavior. Durkheim's ideas have had a profound influence on the field of sociology and continue to be relevant for understanding the dynamics of contemporary society.
Emile Durkheim's Beliefs About Society: An Overview
Emile Durkheim was a French sociologist who is considered to be one of the founding fathers of sociology. He believed that society is more than just the sum of its individual parts, and that it has its own unique properties and characteristics.
Durkheim was particularly interested in the role of social institutions, such as religion and morality, in promoting social order and cohesion. He argued that these institutions provide individuals with a sense of shared identity and purpose, and that they help to regulate social behavior.
Durkheim's Contributions to Sociology and Social Theory
Durkheim made a number of significant contributions to sociology and social theory. He was one of the first sociologists to develop a systematic method for studying society, and he pioneered the use of quantitative data in social research.
Durkheim also developed a number of important concepts, such as social facts, anomie, and collective consciousness. These concepts have been widely adopted by sociologists, and they continue to be used in social research today.
The Concept of "Anomie" and Its Relevance in Modern Society
One of Durkheim's most important concepts is anomie, which he defined as a state of social normlessness. Anomie occurs when traditional social norms and values break down, and individuals are left feeling lost and directionless.
Durkheim argued that anomie is a major cause of social problems, such as suicide and crime. He also believed that anomie is a particular problem in modern societies, which are characterized by rapid social change and a high degree of individualization.
The concept of anomie is still relevant today. For example, many experts believe that the rising rates of suicide and drug addiction in the United States are partly due to anomie.
Durkheim's Influence on the Study of Suicide and Social Pathology
Durkheim's work on suicide is particularly influential. In his book Suicide: A Study in Sociology, Durkheim argued that suicide is not simply the result of individual psychological factors. Instead, he argued that suicide is a social phenomenon that is influenced by social factors, such as social class, religion, and family life.
Durkheim's work on suicide helped to lay the foundation for the study of social pathology, which is a branch of sociology that examines the causes and consequences of social problems.
Contemporary Relevance of Durkheim's Sociological Ideas
Durkheim's sociological ideas remain relevant today. For example, his work on social institutions can help us to understand how these institutions promote social order and cohesion. His work on anomie can help us to understand the root causes of social problems, such as suicide and crime. And his work on suicide can help us to develop effective prevention strategies.
Overall, Durkheim's work is essential reading for anyone who is interested in society and how it works. His ideas continue to shape our understanding of social phenomena and to inform our efforts to address social problems.