Which are fundamental principles of Economics?
The fundamental principles of economics form the core concepts that help explain how individuals, businesses, and societies make decisions about resource allocation. While the number of essential principles may vary depending on the perspective or context, here are some foundational principles in economics:
Scarcity:
- Resources are limited, and human wants are virtually unlimited. Scarcity is the fundamental economic problem, requiring individuals and societies to make choices about how to allocate scarce resources.
Choice and Opportunity Cost:
- Choices must be made due to scarcity, and each choice involves an opportunity cost—the value of the next best alternative foregone. Individuals weigh the benefits and costs of different options when making decisions.
Supply and Demand:
- The interaction of supply and demand determines prices in a market economy. The law of supply states that as prices rise, producers are willing to supply more, while the law of demand states that as prices rise, consumers are willing to buy less.
Incentives:
- Individuals and firms respond to incentives. Positive incentives, such as rewards, and negative incentives, such as penalties, influence decision-making and behavior.
Trade and Comparative Advantage:
- Trade allows individuals and nations to specialize in what they do best and exchange goods and services. Comparative advantage, where one entity has a lower opportunity cost in producing a good or service, is a key driver of trade.
Marginal Analysis:
- Rational decision-makers compare marginal benefits and marginal costs when making choices. Marginal analysis involves evaluating the additional benefit or cost of a small change in decision-making.
Markets and Prices:
- Markets, where buyers and sellers interact, are a powerful mechanism for coordinating economic activity. Prices serve as signals that guide individuals and firms in their decision-making.
Property Rights and Rule of Law:
- Clear property rights and the rule of law are essential for a functioning market economy. They provide individuals and businesses with the security to make investments, trade, and engage in economic activities.
Efficiency and Equity:
- Economic efficiency refers to the optimal use of resources to maximize overall well-being. Equity concerns the fairness of the distribution of resources and income. Achieving a balance between efficiency and equity is often a goal in economic policy.
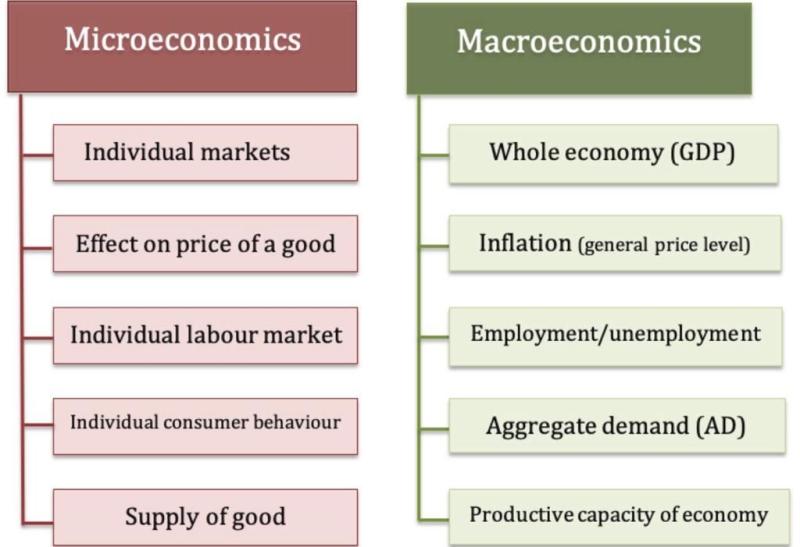
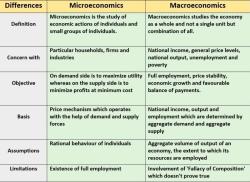
Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced in an economy. It is a key indicator of economic performance and is used to assess the standard of living and economic growth.
Inflation and Unemployment:
- Inflation is the general increase in the overall price level of goods and services, and unemployment refers to the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. These two factors are crucial indicators in macroeconomic analysis.
Role of Government:
- The government plays a role in enforcing property rights, addressing market failures, providing public goods, and ensuring a legal and regulatory framework that supports economic activity.
These principles provide a foundation for understanding economic behavior, decision-making, and the functioning of market economies. Keep in mind that economics is a diverse field with various schools of thought, and the application of these principles can vary in different economic contexts and theories.
What are the essential principles defining Economics?
Defining the "essential principles" of economics is tricky because the discipline encompasses diverse schools of thought and approaches. There's no single, universally accepted set of rules! However, several core ideas frequently reappear and underpin a significant portion of economic analysis:
1. Scarcity and Choice: Resources are limited, forcing individuals, households, and firms to make choices about how to allocate them to fulfill needs and wants. This fundamental reality necessitates trade-offs between different options, forming the basis of many economic models.
2. Incentives and Optimization: People respond to incentives, seeking to maximize their own benefit (utility) within their resource constraints. Understanding how incentives shape behavior is crucial for predicting economic outcomes, such as market responses to price changes or individual investment decisions.
3. Markets and Exchange: Markets provide a platform for exchange and interaction between buyers and sellers, influencing resource allocation through supply and demand. Analyzing market forces and their impact on prices, production, and consumption is a major pillar of economic theory.
4. Efficiency and Trade: Specialization and trade can increase overall efficiency and welfare by allowing individuals and economies to focus on their comparative advantages and exchange goods and services at mutually beneficial terms. This principle highlights the potential gains from international trade and economic cooperation.
5. Growth and Development: Understanding the factors that drive economic growth and development, such as technological advancements, institutional factors, and human capital, is a key area of focus for economists. Analyzing these elements helps formulate policies and strategies aimed at improving living standards and economic well-being.
These are just some of the essential principles. You'll encounter others as you delve deeper into specific economic theories and schools of thought. Additionally, some argue that focusing solely on principles misses the richness and complexity of economic phenomena, advocating for broader perspectives that encompass social, ethical, and historical considerations.
Ultimately, understanding the diversity of ideas and assumptions within economics can provide a more nuanced and comprehensive perspective than relying on a limited set of principles. Feel free to ask about specific economic concepts or delve deeper into any of the principles mentioned above!