Are employers required to withhold federal income tax?
Yes, employers in the United States are generally required to withhold federal income tax from their employees' wages. The federal income tax withholding system is a key component of the U.S. tax system and is administered by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Employers play a crucial role in collecting and remitting federal income taxes on behalf of their employees.
Here are the key points regarding employers' responsibilities for withholding federal income tax:
Employee's W-4 Form:
- When an employee is hired, they are required to fill out a Form W-4, Employee's Withholding Certificate. This form provides information about the employee's filing status, dependents, and any additional amount they want to withhold.
Withholding Allowances:
- The W-4 form includes information about withholding allowances. Employees with more allowances may have less federal income tax withheld from their paychecks, while those with fewer allowances may have more tax withheld.
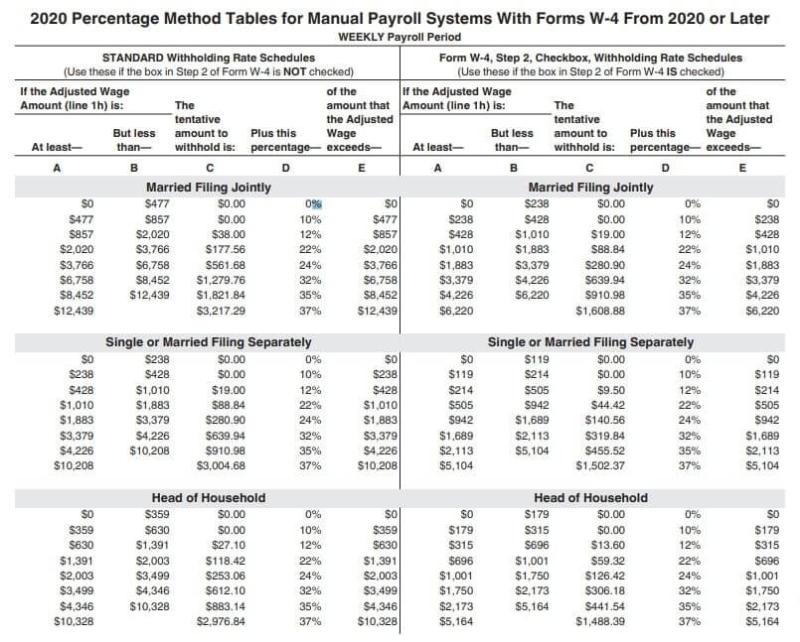
IRS Withholding Tables:
- Employers use the information provided on the W-4 form, along with the IRS withholding tables, to calculate the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from each paycheck.
Frequency of Withholding:
- Federal income tax withholding is typically done on each paycheck. The amount withheld is based on the employee's taxable wages and the information provided on the W-4 form.
Remittance to the IRS:
- Employers are responsible for collecting the withheld federal income taxes and remitting them to the IRS on a regular basis. The specific schedule for remitting these taxes depends on the size of the employer.
Reporting to Employees:
- Employers must provide employees with an annual statement, Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement, which details the employee's total wages and the amounts withheld for federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare.
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
- Employers who fail to withhold the correct amount of federal income tax or fail to remit the withheld taxes to the IRS may be subject to penalties.
It's important for both employers and employees to understand these processes to ensure accurate and compliant withholding. Employers should stay informed about updates to tax laws and IRS guidelines to remain in compliance with their responsibilities regarding federal income tax withholding. Employees can review their paystubs and annual W-2 forms to verify the accuracy of tax withholding. If adjustments are needed, employees can update their W-4 forms with their employers.
Federal laws and regulations mandating employers to withhold federal income tax from employees' paychecks
Federal income tax withholding is a system by which employers are required to deduct a portion of their employees' paychecks and send it to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) on behalf of the employees. This process ensures that employees pay their taxes throughout the year, rather than in a lump sum at the end of the year when they file their tax returns.
The primary legislation mandating federal income tax withholding is the Internal Revenue Code (IRC), specifically Section 3402. The IRC outlines the general rules for withholding, including the applicable tax rates, the frequency of withholding, and the employer's responsibilities.
In addition to the IRC, there are various regulations and guidelines issued by the IRS that provide more detailed instructions for employers on how to implement withholding procedures. These regulations are published in Title 26 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR).
Exceptions to the general rule of mandatory federal income tax withholding
There are a few exceptions to the general rule that employers must withhold federal income tax from employees' paychecks. These exceptions include:
Employees who claim exemption from withholding on Form W-4: Employees who anticipate owing no or minimal federal income tax may claim exemption from withholding by completing Form W-4 and submitting it to their employer.
Employees with nonresident alien status: Nonresident alien employees may be exempt from withholding if they meet certain criteria, such as being a student or a teacher on a temporary visa.
Employees with certain religious beliefs: Employees who hold certain religious beliefs may file Form 4026 with the IRS to claim exemption from withholding.
Employer responsibilities in withholding federal income tax, including accuracy, timeliness, and reporting
Employers have several responsibilities related to federal income tax withholding, including:
Accurately determining the amount of withholding: Employers must use the correct tax tables and formulas to determine the appropriate amount of withholding based on the employee's wages, filing status, and adjustments claimed on Form W-4.
Withholding tax in a timely manner: Employers must withhold tax from each paycheck and deposit it with the IRS on a regular schedule, typically quarterly or monthly.
Reporting withholding to the IRS and employees: Employers must file Form 941 with the IRS to report the total amount of tax withheld and deposited each quarter or month. They must also provide Form W-2 to employees annually, which summarizes the employee's wages and withholding amounts for the tax year.
The role of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in overseeing federal income tax withholding
The IRS plays a crucial role in overseeing federal income tax withholding by:
Issuing tax tables, formulas, and guidelines for employers: The IRS provides employers with the necessary resources to calculate and withhold tax accurately.
Monitoring employer compliance: The IRS conducts audits and investigations to ensure that employers are withholding tax correctly and fulfilling their reporting obligations.
Providing guidance and assistance to employers: The IRS offers various resources, such as publications, online tools, and telephone support, to assist employers with withholding procedures.
Implications of employer noncompliance with federal income tax withholding requirements
Failing to withhold federal income tax or failing to do so accurately can have serious consequences for employers. These consequences may include:
Penalties and interest: Employers may be subject to penalties and interest for late or inaccurate withholding deposits.
Civil liability for employee tax liabilities: In some cases, employers may be held liable for unpaid taxes owed by their employees if they failed to withhold the correct amount.
Criminal charges: In severe cases, employers may face criminal charges for intentionally failing to withhold tax or engaging in fraudulent withholding practices.