What is the principle of Economics?
Economics is a social science that studies how individuals, businesses, governments, and societies allocate their scarce resources to satisfy their unlimited wants and needs. The principles of economics are fundamental concepts that serve as the foundation for understanding economic behavior and decision-making. These principles are often divided into two main categories: microeconomics and macroeconomics.
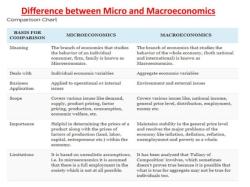
Microeconomics:
Scarcity and Choice: Resources are limited (scarce), and individuals, businesses, and governments must make choices about how to allocate these resources to meet their needs and wants.
Opportunity Cost: The value of the next best alternative forgone when a decision is made. Every choice involves giving up something else.
Supply and Demand: The interaction of supply and demand determines prices in a market economy. Sellers supply goods and services, and buyers demand them. Prices adjust to balance supply and demand.
Elasticity: The responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price. It helps to understand how sensitive consumers and producers are to price changes.
Market Structures: Different types of market structures (perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition) affect the behavior of firms and the efficiency of markets.
Macroeconomics:
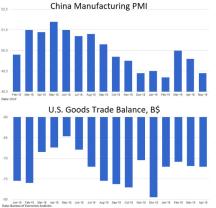
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The total value of all goods and services produced in an economy. It is a key indicator of economic health.
Unemployment: The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. It is an important measure of economic performance.
Inflation: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. Moderate inflation is generally considered normal in a growing economy.
Fiscal Policy: The use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. It includes measures such as budget deficits or surpluses.
Monetary Policy: The control of the money supply by a central bank to achieve economic goals. Interest rates and money supply are important tools.
International Trade: The study of trade between countries and the factors that influence trade, such as tariffs, exchange rates, and trade agreements.
The principles of economics help to analyze and understand how individuals and societies make choices, allocate resources, and respond to changes in economic conditions. These principles provide a framework for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to make informed decisions in the face of scarcity. Keep in mind that economic principles can vary and evolve, and different schools of economic thought may emphasize different aspects of economic analysis.
How is the principle of Economics defined or articulated?
Defining or articulating the principle of economics is not as straightforward as you might think! Economics, as a discipline, encompasses a vast array of theories, schools of thought, and approaches to understanding human behavior and resource allocation. Therefore, there's no single, universally accepted "principle" that encapsulates the entire field.
However, several core ideas underpin a significant portion of economic analysis:
Scarcity and Choice: Resources are limited, and individuals, households, and firms must make choices about how to allocate those resources to fulfill their needs and wants. This trade-off between different options lies at the heart of many economic models.
Incentives and Optimization: People respond to incentives, and their actions are often driven by the desire to maximize their own benefit (utility) given the resources and constraints they face. Understanding how incentives shape behavior is crucial for predicting economic outcomes.
Markets and Exchange: Markets provide a mechanism for exchange and interaction between buyers and sellers, leading to the allocation of resources based on supply and demand. Analyzing market forces and their impact on prices, production, and consumption is a major pillar of economic theory.
Efficiency and Trade: Specialization and trade can increase overall efficiency and welfare by allowing individuals and economies to focus on their comparative advantages and exchange goods and services at mutually beneficial terms.
Growth and Development: Understanding the factors that drive economic growth and development, such as technological advancements, institutional factors, and human capital, is a key area of focus for economists.
These are just some of the central principles that are frequently invoked in various economic schools of thought. It's important to remember that different theorists may place varying emphasis on these principles and even challenge them through alternative perspectives.
Here are some additional points to consider:
- Some argue that focusing on just one "principle" misses the richness and complexity of economic phenomena.
- The definition of "economic principle" itself can be debated, with some advocating for a broader view that encompasses social and ethical considerations in addition to purely economic ones.
- The choice of which principles to emphasize depends on the specific economic problem or issue being studied.
Ultimately, understanding the diverse spectrum of ideas and assumptions under the umbrella of economics can provide a more nuanced and comprehensive perspective than relying on a single, oversimplified definition.
I hope this helps clarify the multifaceted nature of "principles" in economics! Feel free to ask further questions if you'd like to delve deeper into specific aspects.