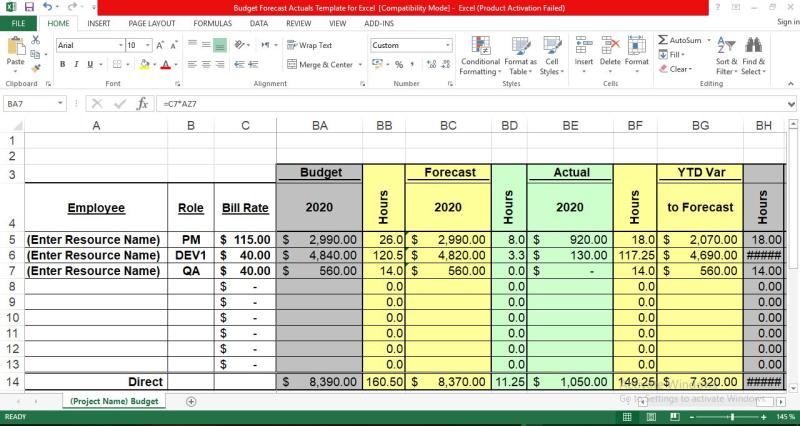
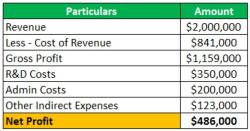
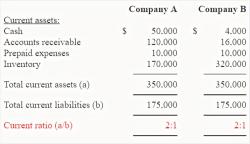
How to create a financial forecast?
Creating a financial forecast is a valuable exercise for businesses and individuals to plan for the future, make informed decisions, and set realistic financial goals. Here's a step-by-step process to help you create a financial forecast:
Step 1: Define the Scope and Purpose
Identify the Time Frame:
- Determine the period your financial forecast will cover, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Define the Purpose:
- Clearly articulate the purpose of your financial forecast. Are you planning for a new business venture, seeking funding, or simply managing personal finances?
Step 2: Gather Historical Data
Collect Past Financial Statements:
- Gather historical financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Review Trends:
- Analyze past trends in revenue, expenses, and other key financial metrics to identify patterns and potential factors influencing your financial performance.
Step 3: Project Sales and Revenue
Estimate Sales:
- Project future sales based on market research, historical performance, and any relevant factors affecting your industry.
Determine Pricing and Volume:
- Consider pricing changes or adjustments in sales volume that may impact your revenue.
Step 4: Plan Operating Expenses
Identify Fixed and Variable Costs:
- Categorize your operating expenses as fixed (e.g., rent, salaries) and variable (e.g., utilities, raw materials).
Forecast Operating Expenses:
- Estimate future operating expenses, considering any expected changes or cost-saving measures.
Step 5: Project Capital Expenditures
Plan for Capital Investments:
- Identify any major investments in assets, equipment, or technology that are planned during the forecast period.
Estimate Depreciation:
- If applicable, estimate the depreciation of capital assets over time.
Step 6: Factor in Financing
- Consider Debt and Equity:
- If your forecast involves business finances, consider the impact of debt repayment or new financing. Include interest payments.
Step 7: Account for Other Income and Expenses
Include Other Sources of Income:
- Account for any additional sources of income, such as interest, dividends, or other non-operating income.
Plan for Non-Operating Expenses:
- Consider any extraordinary expenses or one-time costs that may arise during the forecast period.
Step 8: Build Cash Flow Statement
- Construct Cash Flow Statement:
- Based on the revenue, expenses, and other factors, build a cash flow statement to project the inflow and outflow of cash during the forecast period.
Step 9: Review and Adjust
Conduct Sensitivity Analysis:
- Review your forecast under different scenarios to assess its sensitivity to changes in key variables.
Update Assumptions:
- Regularly revisit and update your assumptions as new information becomes available or circumstances change.
Step 10: Document and Communicate
Document Assumptions and Methodology:
- Clearly document the assumptions, methodologies, and sources of information used in your financial forecast.
Communicate the Forecast:
- Share your financial forecast with relevant stakeholders, such as business partners, investors, or your personal financial advisor.
Remember that a financial forecast is a dynamic tool that should be revisited and adjusted regularly as actual performance unfolds and new information becomes available. It's a planning tool that helps guide decision-making and provides a roadmap for achieving financial goals.
Charting your financial course: How to create a financial forecast?
A financial forecast is a prediction of a company's future financial performance. It is a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes, as it can help them to make informed decisions about their financial future.
There are a number of different ways to create a financial forecast. However, the most common approach is to use a spreadsheet to model the company's future income and expenses.
To create a financial forecast, you will need to gather the following information:
- Historical financial data, such as income statements and balance sheets.
- Assumptions about future economic conditions, such as GDP growth and interest rates.
- Assumptions about the company's future business performance, such as sales growth and market share.
Once you have gathered this information, you can begin to build your financial forecast. The following steps provide a general overview of the process:
- Start by creating a pro forma income statement. This will show the company's projected revenue and expenses for the forecast period.
- Next, create a pro forma balance sheet. This will show the company's projected assets, liabilities, and equity at the end of the forecast period.
- Finally, create a pro forma cash flow statement. This will show the company's projected cash inflows and outflows for the forecast period.
It is important to note that financial forecasts are estimates, and they should not be relied upon as exact predictions. However, they can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes to make informed decisions about their financial future.
Step-by-step guide to developing a reliable and actionable financial forecast
Here is a step-by-step guide to developing a reliable and actionable financial forecast:
- Set clear goals for your forecast. What do you want to achieve with your forecast? Are you using it to raise capital, plan for growth, or make budgeting decisions? Once you know your goals, you can tailor your forecast accordingly.
- Gather accurate data. Your forecast will only be as good as the data you input. Make sure to collect accurate historical financial data, economic data, and industry data.
- Use realistic assumptions. When making assumptions about your future performance, be realistic. Don't overestimate your sales or underestimate your costs.
- Be flexible. The world is constantly changing, so your forecast should be too. Be prepared to update your forecast as needed to reflect changes in the economy, your industry, or your business itself.
Tips for refining and updating financial forecasts to meet changing business needs
Here are some tips for refining and updating financial forecasts to meet changing business needs:
- Use a rolling forecast. A rolling forecast is a forecast that is updated on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly. This allows you to incorporate the latest information into your forecast and make sure that it is always accurate.
- Use scenario planning. Scenario planning is a technique for developing multiple forecasts based on different assumptions. This can help you to prepare for different possible outcomes and make informed decisions about your business.
- Use a forecasting tool. There are a number of forecasting tools available that can help you to develop more accurate and reliable forecasts. These tools can help you to automate the forecasting process and account for complex factors such as seasonality and economic trends.
By following these tips, you can develop and maintain a financial forecast that is reliable, actionable, and meets the changing needs of your business.