How do you calculate the angle of deflection?
The angle of deflection can be calculated in various contexts, such as physics, engineering, and structural analysis. The method and formula for calculating the angle of deflection depend on the specific scenario and the type of deflection you are dealing with. Here, I'll provide a general overview of how to calculate the angle of deflection in a few common scenarios:
Bending of Beams:
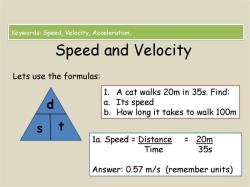
The angle of deflection in a beam, such as a cantilever or simply supported beam, can be calculated using the following formula:
Where:
- is the angle of deflection in radians.
- is the applied load (force).
- is the length of the beam.
- is the modulus of elasticity of the material.
- is the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area.
Torsion of Shafts:
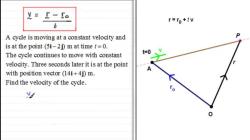
In the case of a shaft undergoing torsional (twisting) deformation, the angle of deflection can be calculated using the following formula:
Where:
- is the angle of deflection in radians.
- is the applied torque (twisting moment).
- is the length of the shaft.
- is the shear modulus of elasticity.
- is the polar moment of inertia of the shaft's cross-sectional area.
Truss Structures:
- When analyzing deflection in truss structures, you often use methods like the method of joints or method of sections to determine forces in the members. Once you have the forces in the members, you can calculate deflection angles using trigonometric relationships based on the geometry of the truss.
Other Mechanical Systems:
- For other mechanical systems and components, such as gears, linkages, or mechanical link systems, the angle of deflection may be calculated using geometry, trigonometry, or specialized formulas relevant to the specific system.
Electrostatic Deflection (Physics):
- In the context of physics, such as in the deflection of charged particles in an electric or magnetic field, you would use principles from electromagnetism and particle physics to calculate the angle of deflection.
It's important to note that the specific formulas and methods for calculating deflection can vary widely depending on the structural or mechanical system being analyzed. Additionally, the units of measurement for angles of deflection can be in radians or degrees, so be sure to use the appropriate units in your calculations.
Calculating Angle of Deflection: Methods and Formulas
The angle of deflection is the angle between the original direction of a beam or light ray and its final direction after it has been deflected by an object or force field. The angle of deflection can be calculated using a variety of methods and formulas, depending on the specific situation.
One common method for calculating the angle of deflection is to use the formula:
θ = 2 * arcsin(d / 2L)
where:
- θ is the angle of deflection in radians
- d is the distance between the point of deflection and the center of the object or force field
- L is the length of the beam or light ray
Another common method for calculating the angle of deflection is to use the formula:
θ = F * d / (2 * T)
where:
- θ is the angle of deflection in radians
- F is the force applied to the beam or light ray
- d is the distance between the point of deflection and the point where the force is applied
- T is the tension in the beam or light ray
The angle of deflection can also be calculated using a variety of software programs, such as ray tracing software.
Deflection Angle Calculation: A Step-by-Step Guide
To calculate the angle of deflection using the formula θ = 2 * arcsin(d / 2L), follow these steps:
- Determine the distance between the point of deflection and the center of the object or force field.
- Divide the distance by 2 to get the radius.
- Calculate the angle of deflection using the formula θ = 2 * arcsin(d / 2L).
Example:
A beam of light is deflected by a mirror. The distance between the point of deflection and the center of the mirror is 10 cm. The length of the beam of light is 20 cm.
To calculate the angle of deflection, we would first divide the distance by 2 to get the radius:
r = d / 2 = 10 cm / 2 = 5 cm
Then, we would calculate the angle of deflection using the formula:
θ = 2 * arcsin(r / L) = 2 * arcsin(5 cm / 20 cm) = 53.1 degrees
Therefore, the angle of deflection is 53.1 degrees.
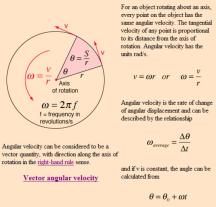
Understanding Angular Deflection: How to Compute It
To compute the angular deflection of a beam or light ray, we need to know the following:
- The initial direction of the beam or light ray
- The final direction of the beam or light ray
- The distance between the point of deflection and the center of the object or force field
Once we have this information, we can use one of the formulas above to calculate the angle of deflection.
The angle of deflection is an important concept in many different fields, including physics, engineering, and optics. It can be used to calculate the trajectories of beams of light, the trajectories of projectiles, and the forces acting on objects.