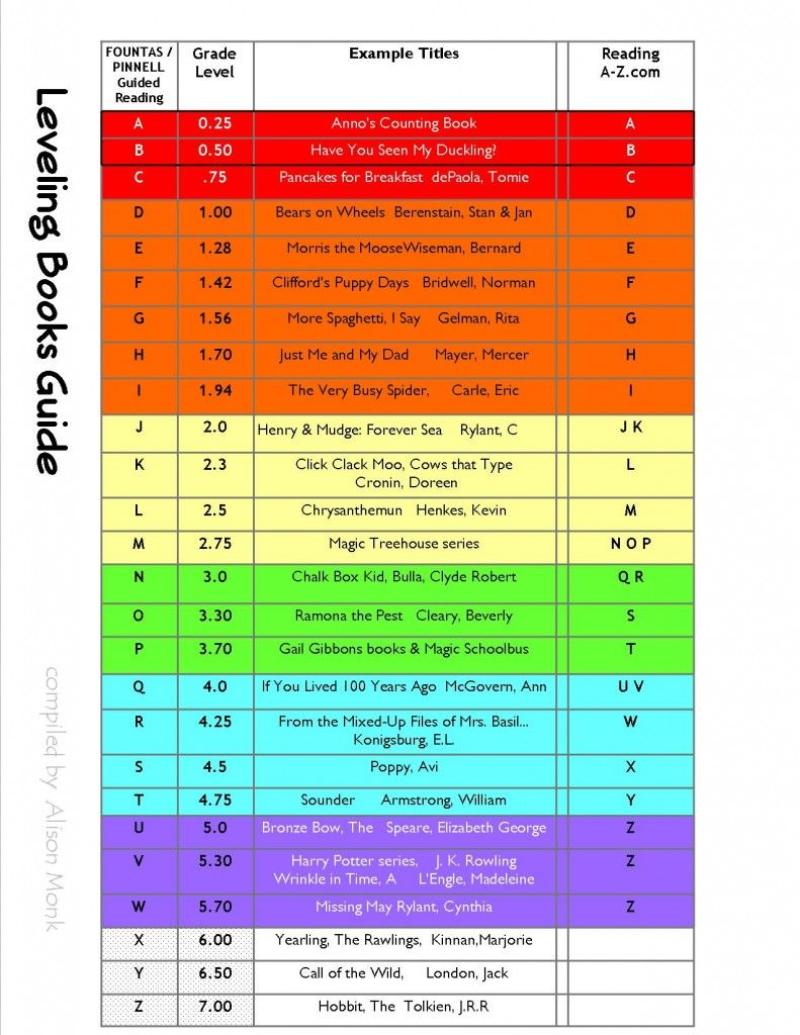
What are the reading levels for second grade?
Reading levels for second grade can vary, and different educational systems and publishers may use different methods to assess and classify reading proficiency. However, a common tool used in the United States to determine reading levels is the Guided Reading (GR) system, often associated with letter levels (e.g., Level C, Level M) or numerical levels (e.g., Level 3, Level 20). These levels are part of a broader framework that helps educators match students with appropriate books based on their reading abilities.
As a general guide, here are approximate reading levels for second grade in the Guided Reading system:
Early Second Grade (Beginning of Year):
- Guided Reading Level: C-D
- Lexile Level: 150-250
Mid Second Grade:
- Guided Reading Level: J-K
- Lexile Level: 450-550
End of Second Grade:
- Guided Reading Level: M-N
- Lexile Level: 600-700
Please note that these are general guidelines, and individual students may progress at different rates. It's essential for teachers to use a combination of assessment tools, including observations, running records, and comprehension checks, to determine each student's specific reading level accurately.
Additionally, other reading level systems, such as the Fountas and Pinnell Text Level Gradient, may be used in different educational settings. Teachers often assess students using multiple measures to gain a comprehensive understanding of their reading abilities and to guide appropriate instruction.
If you're specifically interested in a particular school district or educational program, it's recommended to check with local educators or the curriculum guidelines provided by the relevant educational authority, as reading level expectations may vary.
Sure, here are the answers to your questions:
What are the typical reading levels expected for second-grade students?
Second-grade students typically have a reading level of DRA 28-38. This means that they are able to read and understand books that are written in a level 2 range. Level 2 books are typically characterized by:
- Simple sentences with 4-7 words per sentence
- High-frequency vocabulary words
- Familiar topics and concepts
- Predictable patterns and repetition
By the end of second grade, students should be able to read and understand a variety of genres, including fiction, nonfiction, and poetry.
How do educators assess and determine reading levels for second-grade students?
Educators use a variety of methods to assess and determine reading levels for second-grade students. These methods include:
Observational assessments: Educators observe students reading aloud and silently to get a sense of their fluency, comprehension, and decoding skills.
Formal assessments: Educators may also administer standardized tests, such as the Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) or the Fountas and Pinnell Benchmark Reading Assessment, to measure students' reading levels.
Running records: Educators may also use running records to track students' progress in reading. Running records are informal assessments that involve recording a student reading a passage of text and noting their accuracy, fluency, and comprehension.
What are the benchmarks or standards for second-grade reading proficiency?
The benchmarks or standards for second-grade reading proficiency vary from state to state. However, most states have adopted the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts. The CCSS for second-grade reading include the following:
- Read with sufficient fluency to support comprehension.
- Recognize words on sight and decode unfamiliar words.
- Understand the literal meaning of what is read.
- Distinguish between literal and figurative language.
- Retell the main idea and important details of what is read.
- Use context clues to figure out the meaning of unfamiliar words.
- Read a variety of genres, including fiction, nonfiction, and poetry.
Are there effective strategies to improve reading levels in second-grade students?
Yes, there are many effective strategies to improve reading levels in second-grade students. These strategies include:
Provide students with plenty of opportunities to read. Students should be encouraged to read both for pleasure and for information.
Make sure students have access to a variety of books at their reading level.
Teach students effective reading strategies, such as decoding, fluency, and comprehension.
Provide opportunities for students to practice reading aloud.
Encourage parents to read to their children at home.
Work with students individually or in small groups to provide targeted instruction.
How do reading levels at the second-grade level impact future academic success?
Reading levels at the second-grade level have a significant impact on future academic success. Students who are able to read fluently and with comprehension by the end of second grade are more likely to succeed in all of their academic subjects. They are also more likely to graduate from high school and college.
There are a number of reasons why reading levels are so important for future academic success. Reading is the foundation for all learning, and students who are able to read well are able to access and understand the information they need to succeed in school. Reading also helps students develop their critical thinking skills, vocabulary, and communication skills.
If you are concerned about your child's reading level, please talk to their teacher. There are many resources available to help students improve their reading skills, and early intervention can make a big difference.