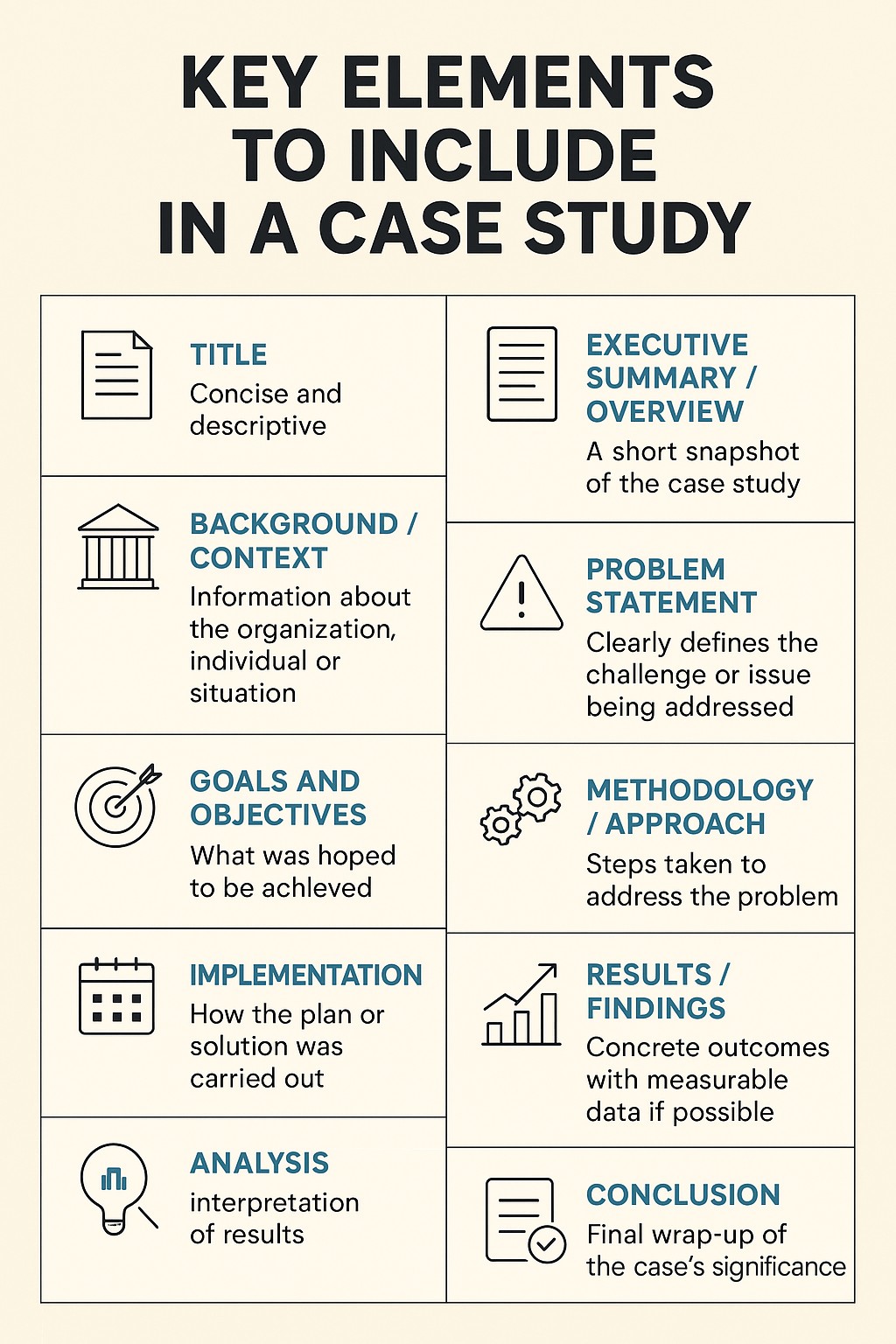
What should be included in a case study?
A well-written case study should be clear, structured, and detailed enough to help readers understand the context, actions taken, and outcomes. Here are the key elements you should include:
1. Title
Concise and descriptive.
Reflects the main topic, challenge, or result.
2. Executive Summary / Overview
A short snapshot of the case study.
Summarizes the problem, solution, and results.
Helps readers quickly decide if the case is relevant.
3. Background / Context
Information about the organization, individual, or situation.
Relevant history, size, industry, or other setting-specific details.
Sets the stage for why the case is important.
4. Problem Statement
Clearly defines the challenge or issue being addressed.
Explains its significance and impact.
May include contributing factors or constraints.
5. Goals and Objectives
What was hoped to be achieved.
Specific, measurable targets if available.
6. Methodology / Approach
Steps taken to address the problem.
Tools, strategies, or frameworks used.
Rationale for choosing the approach.
7. Implementation
How the plan or solution was carried out.
Timeline of actions.
Resources used (personnel, technology, funding, etc.).
8. Results / Findings
Concrete outcomes with measurable data if possible.
Before-and-after comparisons.
Charts, graphs, or visuals to support results.
9. Analysis
Interpretation of results.
What worked well, what didn’t, and why.
Any unexpected outcomes.
10. Lessons Learned
Insights or takeaways from the experience.
Practical advice for similar situations.
11. Conclusion
Final wrap-up of the case’s significance.
Restates how the goals were met (or why they weren’t).
12. References & Appendices
Citations for any data or sources.
Extra materials like surveys, interview transcripts, or detailed data tables.
What Should Be Included in a Case Study?
A comprehensive case study should include a detailed description of the subject, the problem or challenge they faced, the actions taken to address it, and the outcomes or results. It's a deep dive into a specific situation, designed to provide insights and lessons. You should also include a clear introduction setting the context, a methodology section explaining how data was gathered, and a conclusion that summarizes the findings and offers recommendations.
How to Collect Relevant Case Information?
To collect relevant case information, you'll need a mix of primary and secondary sources. Primary data comes directly from the case subject through interviews, surveys, and direct observation. You'll want to ask open-ended questions to get rich, descriptive answers. Secondary data can be gathered from existing documents, reports, company websites, and public records. A good case study uses both types of data to create a well-rounded and credible narrative.
What Are the Different Sections of a Case Study?
A typical case study is structured into several key sections to ensure a logical flow and comprehensive analysis:
Introduction/Executive Summary: A concise overview of the case, its purpose, and the main findings.
Background: Provides context about the subject, industry, and the situation.
Problem Statement: Clearly defines the central issue or challenge being addressed.
Methodology: Explains the research methods used to collect data.
Analysis/Findings: Presents the key data, observations, and insights gathered from the research.
Discussion: Interprets the findings, connecting them back to the problem statement and broader theories.
Recommendations: Offers actionable solutions or strategies based on the analysis.
Conclusion: Summarizes the entire study, restating the key takeaways and implications.
Appendices: Includes supplementary materials like interview transcripts or data tables.
How to Analyze and Interpret Case Data?
Analyzing case data involves more than just presenting facts; it requires you to synthesize information and draw meaningful conclusions. You should look for patterns, trends, and connections within the data. Use qualitative analysis to interpret interviews and observations, and quantitative analysis to make sense of numerical data. The goal is to explain why certain events happened and what their implications are. You can use frameworks or models (like a SWOT analysis or a PESTLE analysis) to structure your interpretation and provide a more robust understanding.
How to Present Recommendations Clearly?
To present recommendations clearly, they should be specific, actionable, and directly tied to your analysis. Avoid vague suggestions. For each recommendation, explain what should be done, why it's necessary (linking back to a specific finding), and how it can be implemented. You can use a numbered list or bullet points to make them easy to read. Prioritize the recommendations, starting with the most critical or impactful ones. Your goal is to provide a practical and persuasive roadmap for solving the problem identified in the case study.