What are some examples of cognitive?
Cognitive processes are the mental activities that involve acquiring, processing, and using information. They play a crucial role in how individuals perceive, understand, remember, and respond to the world around them. Here are some examples of cognitive processes:
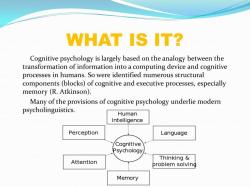
Perception: Perception involves the process of interpreting sensory information from the environment. This includes recognizing shapes, colors, sounds, and patterns. For example, seeing a red apple or hearing a familiar tune.
Attention: Attention is the ability to focus on specific stimuli while filtering out irrelevant information. For instance, concentrating on a lecture while ignoring background noise.
Memory: Memory includes various cognitive processes, such as encoding (receiving and processing information), storing (retaining information), and retrieving (recalling information). Examples include remembering a friend's birthday, a favorite childhood story, or a recent event.
Learning: Learning involves acquiring new knowledge, skills, or behaviors through cognitive processes like observation, practice, and instruction. Learning a new language, mastering a musical instrument, or acquiring a new technical skill are examples.
Problem-Solving: Problem-solving is the cognitive process of finding solutions to complex issues or challenges. For example, figuring out how to repair a malfunctioning appliance or solving a mathematical puzzle.
Decision-Making: Decision-making involves making choices from available options based on cognitive evaluation. Deciding where to go on vacation, what career to pursue, or what to eat for dinner are examples of decision-making.
Language Comprehension: Understanding spoken or written language involves cognitive processes like interpreting words, grammar, and context. For instance, comprehending a novel, following instructions, or engaging in a conversation.
Critical Thinking: Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and evaluate information or arguments to make reasoned judgments. This skill is used when assessing the credibility of sources, analyzing an essay's arguments, or solving ethical dilemmas.
Metacognition: Metacognition refers to the awareness and control of one's own cognitive processes. It includes the ability to monitor and regulate one's learning and thinking. For instance, students using strategies to improve their study habits or individuals reflecting on their decision-making process.
Creativity: Creativity involves the generation of novel and original ideas. It includes cognitive processes like divergent thinking, idea generation, and problem restructuring. Examples include artistic expression, inventing new products, or brainstorming creative solutions to a problem.
Emotion Regulation: Managing one's emotions involves cognitive processes such as recognizing emotional triggers, evaluating emotional responses, and employing strategies to modulate emotions. For example, practicing relaxation techniques to manage stress or reframing negative thoughts to enhance emotional well-being.
Spatial Reasoning: Spatial reasoning is the cognitive process of understanding and manipulating spatial relationships. This is used when reading maps, solving puzzles, or planning a room layout.
These are just a few examples of cognitive processes, and they represent the broad range of mental activities involved in how individuals perceive, think, and interact with the world. Cognitive processes are fundamental to human cognition and are essential for learning, problem-solving, decision-making, and daily functioning.
Examples of Cognitive Processes in Everyday Life
Cognitive processes are the mental operations that we use to think, learn, remember, and solve problems. They are essential for all aspects of our lives, from reading a book to driving a car to having a conversation with a friend.
Here are some examples of cognitive processes in everyday life:
- Paying attention to a conversation
- Remembering where you parked your car
- Making a decision about what to eat for dinner
- Solving a math problem
- Learning a new skill
- Planning a trip
- Navigating a new city
- Reading a book
- Writing an email
- Giving a presentation
- Playing a sport
- Creating a work of art
Cognitive Skills in Problem Solving and Decision Making
Problem-solving and decision-making are two important cognitive skills that we use every day. Problem-solving is the process of identifying and solving problems. Decision-making is the process of choosing between two or more options.
Cognitive skills such as attention, memory, and reasoning are essential for problem-solving and decision-making. For example, we need to be able to pay attention to the problem at hand, remember the information that is relevant to the problem, and reason about the different possible solutions in order to solve a problem effectively.
Memory as a Key Cognitive Function
Memory is a key cognitive function that is involved in all aspects of our lives. It allows us to store and retrieve information, which is essential for learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
There are three main types of memory: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory is the brief storage of sensory information. Short-term memory is the temporary storage of information that we are currently using. Long-term memory is the permanent storage of information.
Cognitive Development in Children and Adolescents
Cognitive development is the process by which children and adolescents acquire the cognitive skills and knowledge that they need to function in the world. Cognitive development occurs in a number of stages, and each stage is characterized by the development of new cognitive skills and abilities.
For example, in the early stages of cognitive development, children learn to pay attention to their surroundings and to remember information. As they get older, they develop more complex cognitive skills, such as problem-solving and decision-making skills.
Cognitive Abilities in Aging and Cognitive Decline
Cognitive abilities typically decline with age. This decline is often gradual, but it can also be sudden due to a stroke or other medical condition.
Cognitive decline can affect a variety of cognitive skills, including memory, attention, and reasoning. It can also lead to problems with communication, problem-solving, and decision-making.
There are a number of things that people can do to maintain their cognitive abilities as they age, such as staying active, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep. There are also a number of cognitive training programs that can help to improve cognitive function in older adults.