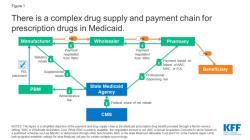
What is agrammatic aphasia?
Agrammatic aphasia, also known as agrammatism, is a type of language disorder that affects a person's ability to form grammatically correct sentences and convey ideas through speech or writing. This condition is typically caused by damage to specific areas of the brain, most commonly in the left hemisphere, which is responsible for language processing in most right-handed individuals and many left-handed individuals.
Here are some key characteristics, symptoms, and potential causes of agrammatic aphasia:
Characteristics and Symptoms of Agrammatic Aphasia:
Impaired Grammar: One of the hallmark features of agrammatic aphasia is difficulty with grammatical structures. People with this condition may omit or misuse grammatical elements, such as articles (e.g., "the" or "a"), verb tense, subject-verb agreement, and word order.
Telegraphic Speech: Agrammatic speech often resembles telegraphic speech, where individuals produce short, fragmented phrases that convey the main idea but lack grammatical completeness. For example, instead of saying "I am going to the store," a person with agrammatic aphasia might say, "Go store."
Difficulty with Function Words: Function words, such as prepositions (e.g., "in," "on"), conjunctions (e.g., "and," "but"), and auxiliary verbs (e.g., "is," "have"), are frequently omitted or used incorrectly.
Content Words Preserved: While grammar is disrupted, the ability to produce content words (nouns, verbs, adjectives) is often less affected. This means that individuals can typically convey the main ideas or content of their messages despite grammatical errors.
Comprehension Generally Intact: People with agrammatic aphasia often have relatively preserved language comprehension abilities. They can typically understand spoken and written language reasonably well, even if their expressive language is impaired.
Potential Causes of Agrammatic Aphasia:
Agrammatic aphasia is primarily caused by damage to specific language areas in the brain. The most common cause is stroke, but it can also result from other conditions such as:
Broca's Area Damage: Agrammatic aphasia is often associated with damage to Broca's area, a region in the left frontal lobe of the brain that plays a crucial role in language production and grammatical processing.
Brain Tumors: Tumors in or near language areas of the brain can cause language disorders, including agrammatic aphasia.
Head Trauma: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) or other types of head trauma can lead to language deficits, including agrammatism, if the areas responsible for language processing are affected.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Progressive neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease or primary progressive aphasia, can also cause agrammatic aphasia as they impact various aspects of language function over time.
Treatment for agrammatic aphasia often involves speech-language therapy, where individuals work with speech-language pathologists to improve their language skills. Therapy may focus on building grammatical skills, improving word retrieval, and developing strategies to compensate for language deficits. The specific treatment plan may vary depending on the individual's needs and the underlying cause of their aphasia.
Understanding Agrammatic Aphasia: Symptoms and Communication Challenges
Agrammatic aphasia is a type of aphasia that affects the ability to produce and understand grammatically correct language. People with agrammatic aphasia may have difficulty using function words (such as articles, prepositions, and conjunctions), constructing complex sentences, and following the rules of grammar.
Symptoms of agrammatic aphasia may include:
- Difficulty using function words (e.g., "the," "a," "in," "on," "and," "but")
- Difficulty constructing complex sentences
- Difficulty following the rules of grammar
- Difficulty understanding grammatically complex sentences
- Difficulty with word order
- Difficulty with verb conjugations
- Difficulty with noun declensions
Communication challenges for people with agrammatic aphasia may include:
- Difficulty expressing their thoughts and feelings clearly
- Difficulty understanding what others are saying, especially in complex or noisy environments
- Difficulty following conversations
- Difficulty participating in social interactions
Agrammatic Aphasia Explained: Insights into Language Impairment
Agrammatic aphasia is caused by damage to the Broca's area, a region of the brain that is responsible for language production. Broca's area is involved in planning and executing speech, as well as in understanding the grammatical structure of language.
When Broca's area is damaged, it can affect the ability to use and understand grammar. This can lead to a variety of communication challenges, including difficulty speaking fluently, difficulty understanding complex language, and difficulty participating in social interactions.
Navigating Agrammatic Aphasia: Approaches to Support and Treatment
There is no cure for agrammatic aphasia, but there are a number of approaches that can help people with this condition to improve their communication skills. Speech-language therapy is the primary treatment for agrammatic aphasia. Speech-language therapists can help people with agrammatic aphasia to:
- Improve their grammar skills
- Develop strategies for communicating more effectively
- Use alternative communication methods, such as gestures, pictures, and writing
In addition to speech-language therapy, there are a number of other things that can be done to support people with agrammatic aphasia, including:
- Providing them with opportunities to communicate and practice their language skills
- Being patient and understanding
- Using simple language and short sentences
- Breaking down complex tasks into smaller steps
- Providing visual and auditory cues
- Encouraging them to participate in social activities
With the right support and treatment, people with agrammatic aphasia can learn to communicate effectively and live fulfilling lives.