What is the meaning of structural functionalism?
Structural functionalism is a sociological perspective and theoretical framework that seeks to understand society by examining its various parts and how they work together to maintain social stability and equilibrium. This theory views society as a complex system composed of interrelated parts, each of which plays a specific role in maintaining the overall function and stability of the society.
Key elements and concepts of structural functionalism include:
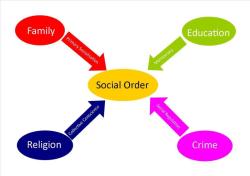
Social Structure: Structural functionalism emphasizes the idea that society has a structure or organization. This structure comprises various institutions, such as family, education, religion, and government, as well as norms, values, and roles that guide individuals' behavior within these institutions.
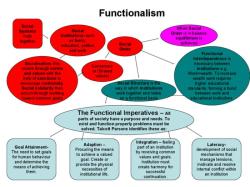
Functionalism: The theory posits that each element or part of society has a function or purpose. These functions can be manifest (intended and recognized) or latent (unintended and not always recognized). Functions contribute to the overall stability and cohesion of society.
Interconnectedness: Structural functionalism highlights the interconnectedness of social institutions and parts. It suggests that changes or disruptions in one part of society can have ripple effects throughout the entire system. For example, changes in the family structure may impact education and employment patterns.
Equilibrium and Stability: The theory assumes that society tends to maintain a state of equilibrium or stability. It suggests that social institutions and norms work together to balance conflicting interests and maintain social order.
Integration and Consensus: Structural functionalism emphasizes the importance of social integration and consensus. It suggests that shared values and norms help to create a sense of solidarity and unity among members of society.
Critique of Social Change: Critics argue that structural functionalism can be conservative and resistant to change. Since it focuses on stability and equilibrium, it may not adequately address issues of social inequality, conflict, and social change.
Prominent sociologists associated with structural functionalism include Emile Durkheim and Talcott Parsons. Durkheim's work on suicide, religion, and social integration contributed to the development of this perspective. Parsons expanded on these ideas and developed a comprehensive framework for understanding the functions of various social institutions.
While structural functionalism has been influential in sociology, it has also faced criticism for its limited attention to social conflict and inequalities. As a result, contemporary sociological theories, such as conflict theory and symbolic interactionism, have emerged to provide alternative perspectives on society that focus on power dynamics, inequality, and the role of symbols and interactions in shaping social reality.
Understanding Structural Functionalism: An Overview of the Theory
Structural functionalism is a sociological theory that views society as a complex system made up of interrelated parts. Each part of society, or social structure, plays a specific role in maintaining the stability and functioning of the whole system.
Structural functionalists believe that society is like a living organism, with each part playing a vital role in its survival. For example, the family is a social structure that plays a vital role in socializing children and providing emotional support to its members. The economy is a social structure that plays a vital role in providing goods and services to society.
The Core Tenets of Structural Functionalism in Sociology
The core tenets of structural functionalism in sociology include:
- Society is a system: Structural functionalists view society as a complex system made up of interrelated parts. Each part of society plays a specific role in maintaining the stability and functioning of the whole system.
- Social structures are functional: Structural functionalists believe that social structures exist because they serve a useful function for society. For example, the family socializes children and provides emotional support to its members. The economy provides goods and services to society.
- Social change is gradual and evolutionary: Structural functionalists believe that social change is gradual and evolutionary. They believe that social structures are resistant to change because they serve important functions for society.
Applying Structural Functionalism: Analyzing Social Structures and Functions
Structural functionalism can be used to analyze social structures and functions in a variety of ways. For example, a structural functionalist might analyze the social structure of the family to understand its role in socializing children and providing emotional support to its members. A structural functionalist might also analyze the social structure of the economy to understand its role in providing goods and services to society.
Here are some examples of how structural functionalism can be applied to analyze social structures and functions:
- The family: The family is a social structure that plays a vital role in socializing children and providing emotional support to its members. Structural functionalists would argue that the family is necessary for the functioning of society because it provides children with the skills and values they need to become productive members of society.
- The economy: The economy is a social structure that plays a vital role in providing goods and services to society. Structural functionalists would argue that the economy is necessary for the functioning of society because it provides people with the goods and services they need to survive and thrive.
- Education: The education system is a social structure that plays a vital role in preparing children for adulthood. Structural functionalists would argue that the education system is necessary for the functioning of society because it provides children with the knowledge and skills they need to be successful in the workforce.
Structural functionalism is a valuable theory for understanding social structures and functions. It can help us to understand how society works and why things are the way they are. However, it is important to note that structural functionalism has been criticized for being too conservative and for ignoring the role of conflict and inequality in society.