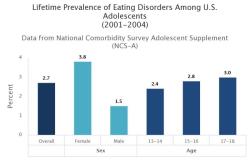
How to spot signs of anxiety in children?
Recognizing signs of anxiety in children can be challenging because children may not always express their feelings and emotions clearly. However, there are several common signs and behaviors that parents, caregivers, and teachers can look out for. Keep in mind that it's normal for children to experience occasional anxiety, but persistent and severe symptoms may indicate an anxiety disorder. Here are some signs to watch for:
Excessive Worry: Children with anxiety often worry excessively about various aspects of their lives, such as school, friends, family, health, or the future.
Restlessness: Restlessness and an inability to sit still can be a sign of anxiety. Children may fidget, tap their feet, or exhibit physical signs of tension.
Irritability: Anxiety can make children more irritable or easily frustrated. They may become more argumentative or have frequent meltdowns.
Physical Symptoms: Anxiety can manifest as physical symptoms in children, including stomachaches, headaches, muscle tension, nausea, and fatigue. These symptoms may not be linked to any underlying medical condition.
Avoidance: Children with anxiety may try to avoid situations or activities that trigger their anxiety. This could include avoiding school, social gatherings, or specific tasks.
Perfectionism: Anxious children may exhibit perfectionistic tendencies and become overly concerned about making mistakes or not meeting their own high standards.
Difficulty Sleeping: Anxiety can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing frequent nightmares.
Separation Anxiety: Younger children may experience separation anxiety, especially when being separated from parents or caregivers.
Social Anxiety: Some children may be excessively shy, anxious, or self-conscious in social situations. They may have trouble making friends or participating in group activities.
Academic Struggles: Anxiety can affect a child's ability to concentrate and perform well in school. It may lead to a decline in academic performance.
Excessive Seeking of Reassurance: Anxious children may repeatedly seek reassurance from parents or caregivers about their concerns and fears.
Emotional Changes: Changes in mood, such as increased sadness or tearfulness, can be indicative of anxiety.
Regression: In response to stress and anxiety, some children may exhibit regressive behaviors, such as bedwetting, thumb-sucking, or baby talk.
Avoidance of New Experiences: Children with anxiety may resist trying new things or taking on challenges due to fear of the unknown.
Complaints About School: Anxiety-related complaints about school can include reluctance to attend, frequent trips to the nurse's office, or a drop in enthusiasm for learning.
It's important to remember that children may display different signs of anxiety, and not all children will exhibit every symptom. Additionally, some signs may be subtle or easily attributed to other factors. If you suspect that a child is experiencing significant anxiety, it's advisable to seek guidance from a mental health professional who specializes in working with children and adolescents. Early intervention and support can help children better manage their anxiety and improve their overall well-being.
Recognizing Anxiety Signs in Children: A Comprehensive Guide
Anxiety is a normal emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. However, when anxiety becomes excessive or persistent, it can interfere with a child's daily life and may be a sign of an anxiety disorder.
Behavioral Signs of Anxiety in Children
Some common behavioral signs of anxiety in children include:
- Avoidance of certain situations or people
- Clinginess or separation anxiety
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fidgeting or restlessness
- Nail biting
- Perfectionism
- Temper tantrums
Emotional Signs of Anxiety in Children
Some common emotional signs of anxiety in children include:
- Excessive worry or fear
- Difficulty sleeping
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Stomachaches
- Headaches
- Feeling sad or blue
Observations to Make
If you are concerned that your child may be anxious, there are a few things you can observe to learn more:
- How does your child react to new situations?
- How does your child interact with other children?
- Does your child seem to be constantly worried?
- Does your child have trouble sleeping?
- Does your child have physical symptoms such as stomachaches or headaches?
If you notice any of the above signs or symptoms, it is important to talk to your child's doctor or a mental health professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve a child's prognosis and quality of life.
Here are some additional tips for recognizing anxiety signs in children:
- Pay attention to your child's overall behavior. Are there any changes in their mood, energy level, or sleep patterns?
- Talk to your child's teachers and coaches. They may be able to provide insights into your child's behavior at school or during activities.
- Trust your gut instinct. If you feel like something is wrong, it probably is.
Remember, you are not alone. There are many resources available to help children and families with anxiety disorders.