Do high levels of dopamine cause schizophrenia?
The relationship between dopamine levels and schizophrenia is complex and involves more than just the absolute levels of dopamine. Schizophrenia is a multifactorial disorder with genetic, environmental, and neurobiological factors contributing to its development. However, there is a longstanding theory, known as the dopamine hypothesis, that suggests dysregulation of dopamine neurotransmission plays a role in the manifestation of schizophrenia symptoms.
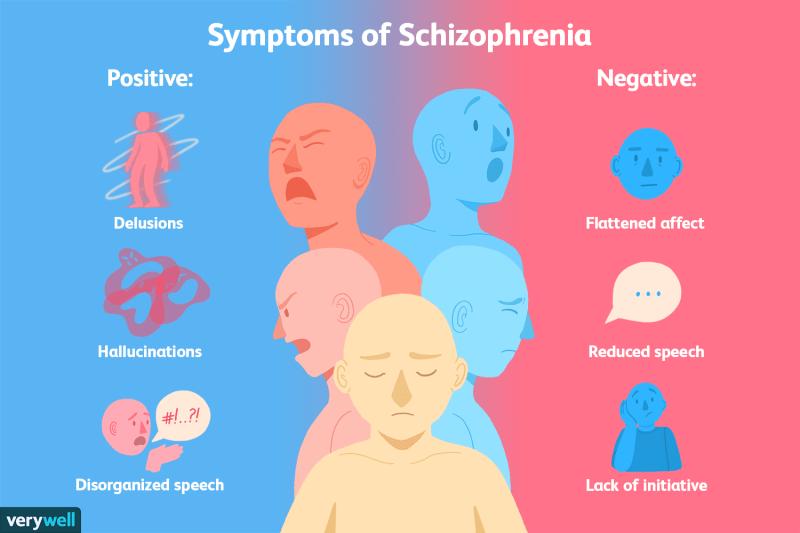
The dopamine hypothesis posits that an overactivity of dopamine transmission, particularly in certain brain circuits, is associated with the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Positive symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorders. While the dopamine hypothesis has provided valuable insights, it's essential to recognize that it doesn't explain all aspects of schizophrenia, and the role of other neurotransmitters and brain circuits is also implicated in the disorder.
Here are some key points regarding dopamine and schizophrenia:
Mesolimbic Pathway:
- The mesolimbic pathway is a dopamine pathway in the brain associated with the reward system. It is believed that overactivity of dopamine transmission in this pathway may contribute to positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications, which are often used to treat schizophrenia, primarily target dopamine receptors in this pathway.
Mesocortical Pathway:
- The mesocortical pathway is another dopamine pathway involved in cognitive functions. Hypoactivity in this pathway is associated with cognitive deficits observed in schizophrenia. The balance between mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways is thought to be disrupted in individuals with schizophrenia.
Dopamine Receptor Sensitivity:
- Studies have suggested that individuals with schizophrenia may have increased sensitivity to dopamine or an increased number of dopamine receptors, particularly the D2 receptors. This heightened sensitivity may contribute to the dysregulation of dopamine signaling in the brain.
Role of Other Neurotransmitters:
- While dopamine dysregulation is a key aspect, other neurotransmitters such as glutamate and serotonin are also implicated in schizophrenia. The interaction and balance of these neurotransmitters contribute to the complexity of the disorder.
Genetic Factors:
- Genetic factors play a role in the susceptibility to schizophrenia, and certain genetic variations may affect dopamine function. However, the genetics of schizophrenia are complex, involving multiple genes and interactions with environmental factors.
It's important to note that the relationship between dopamine and schizophrenia is not a simple cause-and-effect scenario. While medications that block dopamine receptors (antipsychotics) are effective in alleviating some symptoms of schizophrenia, they do not provide a cure, and their exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
Research into the neurobiology of schizophrenia is ongoing, and the understanding of the disorder continues to evolve. The dopamine hypothesis remains a useful framework for understanding certain aspects of schizophrenia, but it is likely that future research will provide a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of the disorder's underlying mechanisms.
Dopamine dynamics: Exploring the link between dopamine and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex mental health condition that is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and social withdrawal. While the exact causes of schizophrenia are still unknown, scientists believe that dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in motivation, reward, and learning, plays a significant role in the development and progression of the disorder.
The neuroscience perspective: How dopamine levels impact mental health
Dopamine is released in the brain when we experience something pleasurable, such as eating a delicious meal, spending time with loved ones, or achieving a goal. This release of dopamine reinforces the behavior and makes us more likely to do it again.
However, in people with schizophrenia, dopamine levels are often elevated in certain areas of the brain. This can lead to a number of symptoms, including:
- Delusions: Delusions are false beliefs that are held despite clear evidence to the contrary. For example, a person with schizophrenia may have the delusion that they are being persecuted by the government or that they have special powers.
- Hallucinations: Hallucinations are sensory experiences that occur in the absence of any real external stimuli. For example, a person with schizophrenia may hear voices, see things that aren't there, or feel sensations on their body that aren't real.
- Disorganized thinking: People with schizophrenia may have difficulty thinking clearly and logically. They may have trouble following conversations, making decisions, and completing tasks.
- Social withdrawal: People with schizophrenia may withdraw from social activities and relationships. They may feel isolated and alone, and they may have difficulty trusting others.
Research insights: Studies on the correlation between dopamine and schizophrenia
A number of studies have shown a correlation between elevated dopamine levels and schizophrenia. For example, a study published in the journal Schizophrenia Bulletin found that people with schizophrenia had higher levels of dopamine in the striatum, a region of the brain that is involved in reward and motivation.
Another study, published in the journal Nature Neuroscience, found that people with schizophrenia had higher levels of dopamine receptors in the prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain that is involved in cognitive function and decision-making.
Treatment considerations: Addressing dopamine levels in schizophrenia therapy
Current treatments for schizophrenia often focus on reducing dopamine levels in the brain. This can be done using a variety of medications, such as antipsychotics. Antipsychotics work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which helps to reduce the symptoms of schizophrenia.
In addition to medication, there are a number of other therapies that can be helpful for people with schizophrenia, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and social skills training. CBT can help people to identify and challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs, while social skills training can help them to develop better communication and relationship skills.
The bigger picture: Understanding the multifaceted causes of schizophrenia
It is important to note that dopamine is just one of many factors that contribute to the development of schizophrenia. Other factors, such as genetics, brain development, and environmental factors, also play a role.
As a result, there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for schizophrenia. The best treatment approach for each individual will depend on a variety of factors, including their specific symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle.
If you or someone you know is struggling with schizophrenia, it is important to seek professional help. A psychiatrist or other mental health professional can assess your needs and develop a treatment plan that is right for you.