What is the probability of event A given event B?
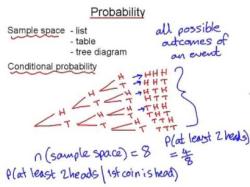
The probability of event A occurring given that event B has already occurred is denoted as P(A|B), which is read as "the probability of A given B." Conditional probability is used to assess the likelihood of one event happening, taking into account the knowledge that another event has already occurred.
Mathematically, conditional probability is calculated using the following formula:
Where:
- P(A|B) is the conditional probability of A given B.
- P(A and B) is the probability of both events A and B happening.
- P(B) is the probability of event B happening.
To calculate P(A|B), you need to know both P(A and B) and P(B). If you have this information, you can use the formula to find the conditional probability.
Here's an example to illustrate:
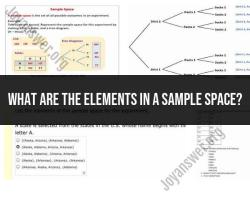
Let's say you have a deck of playing cards, and you want to find the probability of drawing a red card (event A) given that you've already drawn a spade card (event B).
- P(A): Probability of drawing a red card = 26/52 (there are 26 red cards out of 52 cards in a deck).
- P(B): Probability of drawing a spade card = 13/52 (there are 13 spade cards out of 52).
Now, let's say you've drawn a spade card, so event B has occurred. To find P(A|B), we use the formula:
In this case, P(A and B) is the probability of drawing a red spade card, which is 0 (there are no red spade cards in the deck).
So,
Therefore, the probability of drawing a red card given that you've already drawn a spade card is 0. This makes sense because there are no red spade cards in the deck, so event A cannot occur once event B has occurred.
Here are a few examples to illustrate conditional probability:
Example 1 - Coin Toss:
- Suppose you have a fair coin. Event A could be "getting heads" on a coin toss, and event B could be "getting heads on the second toss." If you already know that the second toss resulted in heads (event B), then the conditional probability of getting heads on the first toss (event A) is 1, because the outcome of the first toss is guaranteed to be heads.
Example 2 - Weather Forecast:
- Event A might represent "rain tomorrow," and event B could be "overcast skies today." The conditional probability of rain tomorrow (event A) given overcast skies today (event B) can be calculated based on historical data.
Example 3 - Medical Testing:
- In medical testing, event A might be "testing positive for a disease," and event B could be "having certain symptoms." The conditional probability of testing positive (event A) given the presence of specific symptoms (event B) can help assess the accuracy of the test.
Conditional probability is a fundamental concept in probability theory and is widely used in various fields, including statistics, machine learning, and decision-making, to model and analyze situations where outcomes are influenced by specific conditions or prior information.