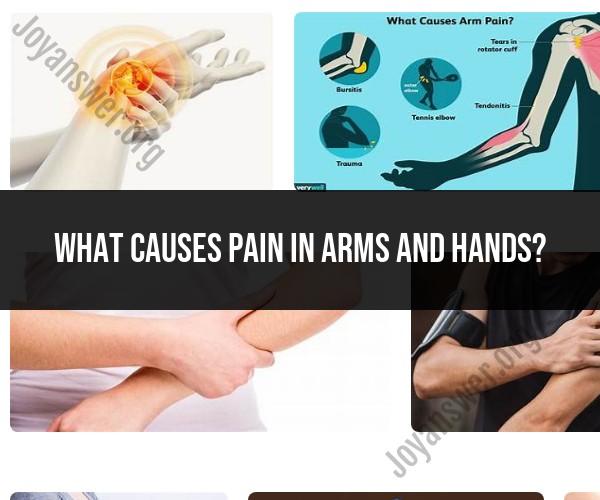
What causes pain in arms and hands?
Pain in the arms and hands can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, medical conditions, overuse, and lifestyle factors. Identifying the specific cause of arm and hand pain may require a medical evaluation, but here are some common causes:
Muscle Strain or Overuse: Overexertion or repetitive movements can lead to muscle strains in the arms and hands. This type of pain is often localized and can be a result of activities like lifting heavy objects, typing for extended periods, or playing sports.
Nerve Compression or Pinched Nerves:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: This condition is characterized by the compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand and fingers.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: It involves compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, leading to pain, tingling, and weakness in the forearm, hand, and fingers.
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome: This involves compression of the radial nerve, causing pain on the top of the forearm and into the back of the hand and wrist.
Tennis or Golfer's Elbow: These are types of tendinitis that affect the tendons of the forearm. Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) causes pain on the outside of the elbow, while golfer's elbow (medial epicondylitis) causes pain on the inside of the elbow.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints in the arms and hands, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
Cervical Radiculopathy: Nerve compression in the cervical spine (neck) can result in pain that radiates down the arms and into the hands. This condition is often associated with conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This occurs when nerves or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet (area between the neck and the shoulder) are compressed, leading to pain, tingling, and numbness in the arms and hands.
Injuries: Traumatic injuries, such as fractures, dislocations, or sprains in the arms or hands, can cause acute pain. Soft tissue injuries like bruises and contusions can also lead to pain.
Peripheral Neuropathy: Conditions like diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, and certain medications can damage peripheral nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or tingling in the hands and feet.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This is a condition where nerves or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet (the area between the neck and shoulder) are compressed, leading to symptoms like pain, numbness, and tingling in the arms and hands.
Repetitive Stress Injuries: Prolonged and repetitive movements, such as using a computer mouse or keyboard for long hours, can cause pain and discomfort in the arms and hands.
Autoimmune Conditions: Conditions like lupus or multiple sclerosis can affect the nervous system, potentially leading to pain and numbness in the extremities.
Vascular Conditions: Blood circulation problems, such as blood clots or peripheral artery disease, can cause pain and discomfort in the arms and hands.
It's essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent or severe arm and hand pain, especially if it is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. A proper diagnosis is critical to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Exploring the Causes of Pain in Arms and Hands
Pain in the arms and hands can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Injuries, such as fractures, sprains, and strains
- Overuse syndromes, such as tennis elbow and carpal tunnel syndrome
- Inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis and bursitis
- Nerve conditions, such as pinched nerves and neuropathy
- Circulatory problems, such as peripheral artery disease
- Infections
- Tumors
Common Factors and Conditions That Contribute to Arm Pain
Some of the most common factors and conditions that contribute to arm pain include:
- Age: Arm pain is more common in older adults. This is because the tendons and ligaments in the arms and hands tend to weaken with age.
- Occupation: Certain occupations, such as those that require repetitive movements of the arms and hands, can increase the risk of arm pain.
- Sports: Certain sports, such as tennis, golf, and baseball, can also increase the risk of arm pain.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, arthritis, and thyroid disease, can also increase the risk of arm pain.
Diagnosing and Managing Arm and Hand Pain
To diagnose the cause of arm pain, your doctor will ask you about your medical history and symptoms. They will also perform a physical exam. In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to get a better look at the bones and soft tissues in your arms and hands.
Once your doctor has diagnosed the cause of your arm pain, they will recommend a treatment plan. Treatment may include:
- Rest: Resting the affected arm or hand is often the first step in treatment.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles and improve the range of motion in the affected arm or hand.
- Corticosteroid injections: Corticosteroid injections can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary in some cases, such as when there is a pinched nerve or a tear in a tendon or ligament.
Prevention and Self-Care Strategies for Arm Pain
There are a number of things you can do to prevent arm pain and to manage it at home, including:
- Use good posture: Maintain good posture when sitting, standing, and walking. Avoid slouching and hunching over.
- Take breaks: Take breaks when doing activities that require repetitive movements of the arms and hands.
- Warm up before exercise: Warm up before engaging in physical activity. This will help to prepare your muscles for exercise and reduce the risk of injury.
- Stretch: Stretch your arms and hands regularly. This will help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness.
- Apply ice or heat: Applying ice or heat to the affected area can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Use over-the-counter pain medications: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help to relieve pain and inflammation.
Real Stories of Coping with and Overcoming Arm Pain
Here are a few real stories of coping with and overcoming arm pain:
- "I'm a tennis player and I developed tennis elbow a few years ago. The pain was so bad that I couldn't even hold a tennis racket. I went to the doctor and he prescribed physical therapy. After a few weeks of physical therapy, I was able to start playing tennis again." - John, 35-year-old male
- "I'm a computer programmer and I sit at a desk all day. I started to develop pain in my wrist and hand from all the typing. I went to the doctor and he diagnosed me with carpal tunnel syndrome. He recommended that I take breaks throughout the day and that I wear a wrist brace at night. After following the doctor's orders, my pain started to improve." - Sarah, 25-year-old female
- "I'm a construction worker and I injured my shoulder on the job. I had to have surgery to repair the damage. After surgery, I went to physical therapy. It took a few months, but I was eventually able to regain full use of my shoulder." - Mike, 40-year-old male
If you are experiencing arm pain, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions. Once the cause of your arm pain has been diagnosed, your doctor can recommend a treatment plan and self-care strategies to help you manage your pain and improve your function.