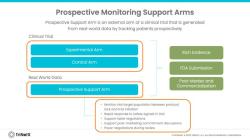
What is a comprehensive patient assessment?
A comprehensive patient assessment is a systematic and thorough evaluation of an individual's overall health and well-being. It is a fundamental process in healthcare that involves gathering detailed information about a patient's medical history, current health status, and various factors that may impact their health. The primary goal of a comprehensive patient assessment is to obtain a holistic understanding of the patient's health to inform diagnosis, treatment planning, and ongoing care. Here are key components and elements of a comprehensive patient assessment:
Medical History:
- Gathering information about the patient's past medical conditions, surgeries, allergies, medications, and family medical history. This helps healthcare providers understand the patient's medical background.
Chief Complaint:
- Identifying the primary reason for the patient's visit or hospitalization. Understanding the patient's main concern or symptoms is essential for diagnosis.
Present Illness:
- Detailed information about the current illness or condition, including the onset of symptoms, their progression, severity, and any factors that worsen or alleviate them.
Review of Systems:
- A comprehensive inquiry into the patient's various body systems (e.g., cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal) to identify any additional symptoms or issues that may not be part of the chief complaint.
Physical Examination:
- A thorough physical examination, including vital signs (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate, temperature), assessment of organ systems, and identification of physical abnormalities.
Psychosocial Assessment:
- Evaluating the patient's mental and emotional well-being, including factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, and social support systems.
Medication Review:
- Reviewing all current medications, including prescription, over-the-counter, and dietary supplements, to assess for potential interactions or side effects.
Lifestyle and Health Behaviors:
- Gathering information on the patient's lifestyle, including diet, exercise habits, alcohol and substance use, and tobacco use. Assessing these factors helps in promoting healthy behaviors.
Functional Assessment:
- Evaluating the patient's ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs), mobility, and any limitations in function, which may impact their overall well-being.
Cultural and Psychosocial Factors:
- Considering the patient's cultural background, beliefs, values, and socioeconomic factors that may influence their healthcare decisions and preferences.
Nutritional Assessment:
- Assessing the patient's nutritional status, dietary habits, and any specific dietary restrictions or needs.
Risk Assessment:
- Identifying potential health risks, such as exposure to environmental hazards, family history of specific diseases, or lifestyle factors that may contribute to health issues.
Diagnostic Testing:
- Ordering and interpreting diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, and screenings, to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Patient Goals and Preferences:
- Discussing the patient's healthcare goals, treatment preferences, and advance care planning, including decisions about end-of-life care.
A comprehensive patient assessment is an essential step in providing patient-centered care, enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to the individual's specific needs and circumstances. It also serves as a baseline for monitoring and evaluating the patient's progress over time. Effective communication and a patient-centered approach are critical during this process to ensure that patients are actively involved in their care and that their concerns and preferences are considered.