What is the diagnostic test for myocardial infarction?
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is often diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessment, patient history, and various diagnostic tests. Key diagnostic tests for myocardial infarction include:
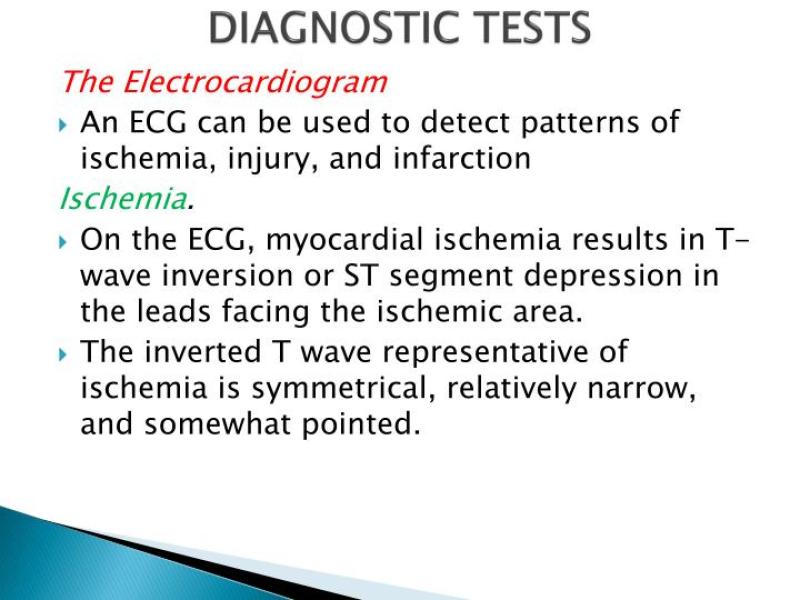
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG):
- An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart. It can show changes in the heart's rhythm and identify abnormalities that may suggest a myocardial infarction. Specific patterns, such as ST-segment elevation or depression, are indicative of myocardial damage.
Blood Tests:
- Cardiac Biomarkers: Blood tests measure cardiac biomarkers, such as troponin, creatine kinase (CK), and CK-MB. Elevated levels of these markers indicate damage to the heart muscle.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test provides information about the number of blood cells and can help identify conditions that may affect the heart.
Chest X-ray:
- A chest X-ray can help rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms and may show signs of heart failure or other complications associated with a heart attack.
Echocardiogram:
- An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create an image of the heart. It can assess the pumping function of the heart, detect structural abnormalities, and identify areas of reduced blood flow.
Coronary Angiography:
- This invasive procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the coronary arteries, followed by X-ray imaging. It helps visualize the blood vessels and identify any blockages or narrowed areas that may be causing reduced blood flow to the heart.
Computed Tomography (CT) Angiography:
- CT angiography uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the heart and blood vessels. It can help identify coronary artery disease and assess blood flow.
Stress Tests:
- Stress tests assess the heart's response to physical stress. This can be done through exercise or medication that simulates the effects of exercise. Abnormalities in the heart's response may indicate coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction.
It's important to note that the combination of these tests is often used for a comprehensive evaluation. The choice of diagnostic tests depends on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and the clinical judgment of healthcare providers. If someone is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with myocardial infarction.
Understanding Diagnostic Tests for Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to a portion of the heart is blocked, depriving heart muscle tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for minimizing heart damage and improving patient outcomes. Various diagnostic tests play a critical role in confirming myocardial infarction and guiding treatment decisions.
1. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG), also known as an EKG, is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It provides valuable information about the heart's rhythm, conduction, and overall health. Changes in the ECG pattern can indicate myocardial infarction, such as ST-segment elevation or T-wave inversion.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for detecting elevated levels of cardiac biomarkers, which are proteins released into the bloodstream in response to heart muscle damage. Troponin is the most specific and sensitive biomarker for myocardial infarction. Elevated troponin levels indicate heart muscle damage and support the diagnosis of a heart attack.
3. Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques provide detailed visualization of the heart and its structures, allowing for the assessment of heart damage and the identification of blockages in coronary arteries. Common imaging techniques used for myocardial infarction include:
Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart's structure and function. It can assess the extent of heart muscle damage and identify any abnormalities in heart valve function.
Chest X-ray: While not as specific for myocardial infarction as ECG or blood tests, a chest X-ray can provide valuable information about the overall condition of the heart and lungs. It can detect signs of heart enlargement, fluid buildup in the lungs, or other abnormalities that may be associated with a heart attack.
Cardiac CT Angiography (CTA): Cardiac CTA is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays and contrast dye to create detailed images of the coronary arteries. It can identify blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries, which are the main blood vessels supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle.
Interpreting Test Results
The interpretation of diagnostic test results for myocardial infarction involves a comprehensive assessment of the clinical presentation, ECG findings, blood test results, and imaging findings. Each test provides a piece of the puzzle, and the combined interpretation allows for a more definitive diagnosis.
Implications for Treatment Decisions
The results of diagnostic tests play a crucial role in guiding treatment decisions for myocardial infarction. Prompt treatment is essential to restore blood flow to the affected heart muscle and minimize damage. Treatment options may include:
Medications: Medications such as aspirin, clopidogrel, and statins are used to prevent blood clots, reduce cholesterol levels, and protect the heart from further damage.
Angioplasty and Stenting: Angioplasty involves inserting a thin tube with a balloon or stent into the blocked coronary artery to open it up and restore blood flow.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): CABG involves grafting a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to bypass the blocked coronary artery and restore blood flow to the heart muscle.
Importance of Prompt Diagnosis and Timely Intervention
The timeliness of diagnosis and intervention is critical for improving outcomes in myocardial infarction. Early treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and subsequent heart attacks. Delaying treatment can lead to irreversible heart muscle damage and worsen the prognosis.
In conclusion, a comprehensive approach to diagnosing myocardial infarction involves a combination of clinical presentation, ECG findings, blood tests, and imaging techniques. The interpretation of test results guides treatment decisions and underscores the importance of prompt diagnosis and timely intervention for improving patient outcomes.