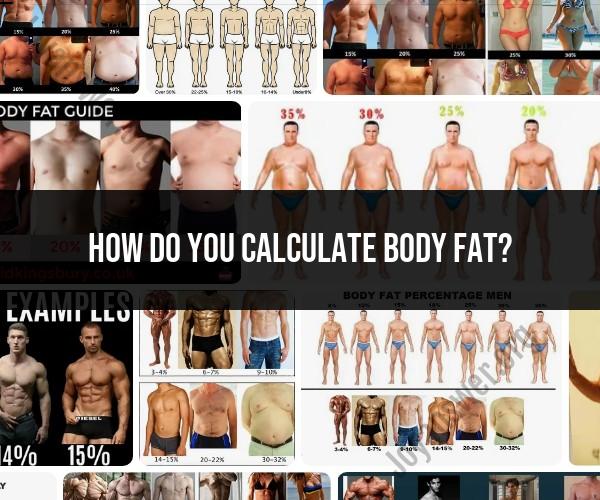
How do you calculate body fat?
There are several methods for calculating body fat, each with its own level of accuracy and complexity. Here are some common methods used to estimate or measure body fat:
1. Body Mass Index (BMI):
- BMI is a simple and widely used method that calculates body fat based on height and weight. While it provides a general indication of body fat, it doesn't differentiate between muscle and fat.
2. Skinfold Calipers:
- This method involves using calipers to measure the thickness of skinfolds at specific sites on the body. These measurements are then used in equations to estimate body fat percentage.
3. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA):
- BIA measures the resistance of electrical flow through the body. The principle is that lean tissue conducts electrical impulses better than fat tissue. BIA devices are available for home use, but their accuracy can be influenced by factors like hydration levels.
4. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA):
- DEXA is a precise method that uses X-rays to measure bone density, lean mass, and fat mass. It is commonly used in research and clinical settings but is more expensive and involves radiation exposure.
5. Hydrostatic Weighing:
- Also known as underwater weighing, this method measures body density by weighing a person underwater. It is based on the principle that fat is less dense than lean tissue. While accurate, it requires specialized equipment.
6. Air Displacement Plethysmography (Bod Pod):
- Similar to hydrostatic weighing, the Bod Pod measures body volume and density using air displacement. It is considered less invasive than underwater weighing.
7. Infrared Interactance:
- This method uses infrared light to estimate body fat based on the absorption of light by subcutaneous fat. While it's non-invasive, its accuracy may be influenced by factors like skin pigmentation.
8. 3D Body Scanners:
- Advanced 3D body scanners create a digital model of the body, allowing for a precise analysis of body composition. These scanners are becoming more accessible and provide detailed information.
9. Waist-to-Hip Ratio:
- This is a simple anthropometric measurement that assesses fat distribution. A higher ratio may indicate a higher risk of certain health conditions.
Important Considerations:
Accuracy: No method is perfect, and results can vary. Factors like hydration, time of day, and individual variability can affect measurements.
Professional Guidance: For more accurate assessments, it's advisable to consult with healthcare professionals, fitness trainers, or nutritionists who are experienced in body composition analysis.
Consistency: When using a specific method, it's crucial to be consistent with the conditions under which measurements are taken (e.g., time of day, hydration level) for more reliable comparisons.
Common Methods for Calculating Body Fat:
There are several methods for estimating body fat percentage, each with its own advantages and limitations:
1. Skinfold calipers: This portable and inexpensive method uses calipers to pinch and measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat at specific body sites. The measurements are then used to calculate an estimated body fat percentage using formulas or reference charts. While convenient, accuracy can be affected by user technique and body composition variations.
2. Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA): This method uses a low-level electrical current to measure the body's resistance to electricity. Fat and muscle have different electrical properties, allowing the device to estimate body fat percentage. BIA devices are readily available and user-friendly, but accuracy can be influenced by hydration levels and recent food intake.
3. Hydrostatic weighing: This is considered the gold standard for measuring body fat. It involves underwater weighing to compare body density to the density of fat-free mass. This method is highly accurate but requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, making it less accessible.
4. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA): This advanced imaging technique uses low-dose radiation to measure body composition, including bone mineral density, fat mass, and lean mass. DEXA provides highly accurate and detailed results but is expensive and not widely accessible.
5. Air displacement plethysmography (ADP): Similar to DEXA, this method uses air pressure to measure body volume and composition. ADP is considered highly accurate but requires specific equipment and trained personnel.
Accuracy of Technology:
Technology can play a significant role in measuring body fat percentage, with varying degrees of accuracy depending on the chosen method:
- Skinfold calipers and BIA devices: These are readily available but offer moderate accuracy, often within a 3-5% margin of error.
- Hydrostatic weighing and DEXA scans: These are considered gold standards, offering high accuracy within 1-2% margin of error.
- Biometric devices: Smart scales and other wearable devices are becoming increasingly popular, but their accuracy can vary depending on the technology used and calibration.
It's important to note that no method is perfect. Individual factors, such as body composition, hydration levels, and recent activity, can influence the accuracy of any measurement.
Choosing the right method depends on your individual needs and priorities. Consider the desired level of accuracy, accessibility, and cost when selecting a method for measuring your body fat percentage.