What does ischemic heart disease mean?
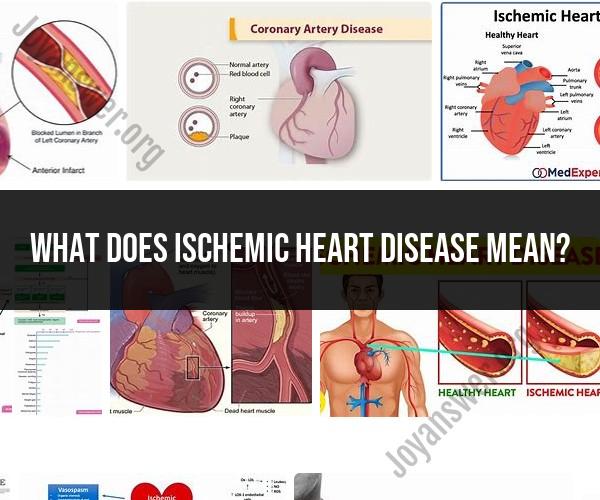
Ischemic heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease (CAD) or coronary heart disease (CHD), is a medical condition that occurs when there is a reduced blood supply to the heart muscle due to the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries are responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle (myocardium).
Ischemic heart disease typically develops over time as a result of the accumulation of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances (plaque) in the coronary arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis. This buildup of plaque can restrict blood flow to the heart, leading to various cardiac problems.
Key insights into ischemic heart disease include:
Causes: The primary cause of ischemic heart disease is atherosclerosis, which can be influenced by factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Genetic factors and family history can also play a role.
Symptoms: Common symptoms of ischemic heart disease include chest pain or discomfort (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and a feeling of pressure or squeezing in the chest. In some cases, it can lead to heart attacks (myocardial infarctions).
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examinations, imaging tests (e.g., angiography, stress tests), and blood tests to evaluate cardiac biomarkers.
Treatment: Treatment aims to relieve symptoms, improve blood flow to the heart, and reduce the risk of complications. Options may include lifestyle changes (e.g., diet, exercise), medications (e.g., statins, blood thinners), angioplasty and stent placement, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and lifestyle modifications.
Prevention: Preventive measures include adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors (e.g., controlling blood pressure, managing cholesterol levels, quitting smoking), and regular medical check-ups to monitor heart health.
Ischemic heart disease is a common and serious cardiovascular condition that can lead to significant health problems if left untreated. It is a leading cause of heart attacks and other cardiac events. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle changes can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications.
What is Ischemic Heart Disease?
Ischemic heart disease (IHD), also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), is a condition in which the blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced. This can happen when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked.
IHD is the most common type of heart disease and is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. It can affect people of all ages, but is more common in older adults, men, and people with other risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking.
Reduced Blood Flow and Oxygen in Ischemic Heart Disease
When the blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced, the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen. This can cause chest pain (angina) or, in severe cases, a heart attack. A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a section of the heart muscle is completely blocked, causing the heart muscle to die.
Angina and Heart Attacks in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Angina is a symptom of IHD that causes chest pain, tightness, or pressure. It is often described as a feeling of heaviness or squeezing in the chest. Angina can be triggered by exertion, stress, or cold weather. It usually goes away within a few minutes of rest.
A heart attack is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood flow to a section of the heart muscle is completely blocked. This causes the heart muscle to die. Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and sweating. If you think you or someone else is having a heart attack, call 911 immediately.
Treatment for Ischemic Heart Disease
The goal of treatment for IHD is to improve blood flow to the heart muscle and prevent heart attacks. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk of IHD and improve symptoms.
- Medications: Medications such as nitrates, statins, and beta blockers can help to improve blood flow to the heart muscle and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
- Medical procedures: Medical procedures such as angioplasty and stenting can be used to open blocked coronary arteries. In severe cases, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery may be necessary to reroute blood around blocked coronary arteries.
If you have IHD, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. By following your doctor's recommendations and making healthy lifestyle changes, you can reduce your risk of heart attacks and improve your quality of life.