How can I improve my expressive aphasia?
Improving expressive aphasia involves targeted strategies and consistent practice to enhance communication skills. It's important to note that progress can vary from person to person, and improvement may be gradual. Here are some strategies to help improve expressive aphasia:
Speech-Language Therapy:
- Work with a speech-language pathologist (SLP) who specializes in aphasia. They can assess your specific challenges and design a personalized therapy plan to address expressive language difficulties.
Practice Regularly:
- Consistent practice is crucial for improvement. Set aside dedicated time each day for language exercises, conversations, and other language-related activities.
Use Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC):
- Explore AAC devices, communication boards, or other tools that can assist in communication. These tools can provide alternative ways to express thoughts and ideas.
Word-Finding Strategies:
- Practice word-finding strategies such as visualizing the word, breaking it down into syllables, or using related words to help recall the target word.
Chunk Information:
- Break down information into smaller, more manageable chunks. This can make it easier to process and express thoughts.
Use Gestures and Facial Expressions:
- Incorporate gestures and facial expressions to enhance communication. Non-verbal cues can often complement verbal communication and help convey meaning.
Practice Reading Aloud:
- Reading aloud can help improve speech fluency and pronunciation. Start with short passages and gradually progress to more complex materials.
Sing or Recite Familiar Songs or Poems:
- Singing or reciting familiar songs and poems engages different areas of the brain and may facilitate language production. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with non-fluent aphasia.
Engage in Conversations:
- Actively participate in conversations with family, friends, or support groups. Regular social interaction provides opportunities to practice communication skills in a supportive environment.
Use Technology:
- Explore speech therapy apps and tools designed to target specific aspects of expressive language. These may include exercises for word retrieval, sentence formation, and pronunciation.
Record and Listen:
- Record yourself speaking and listen to the recordings. This can help you identify areas for improvement, track progress, and gain awareness of your speech patterns.
Join Aphasia Support Groups:
- Connecting with others who have aphasia can provide a supportive community for sharing experiences and practicing communication skills in a non-judgmental setting.
Visual Aids:
- Use visual aids such as pictures, drawings, or written cues to assist in expressing ideas. These aids can serve as prompts during conversations.
Take Breaks:
- If you find yourself struggling with expressive language, take breaks when needed. Stress and fatigue can impact communication abilities, so it's important to manage energy levels.
Set Realistic Goals:
- Establish realistic and achievable goals for yourself. Celebrate small victories and progress, and recognize that improvement may take time.
It's crucial to collaborate closely with your speech-language pathologist, as they can provide guidance, monitor progress, and make adjustments to the therapy plan as needed. Patience, persistence, and a positive attitude are key elements in the journey to improving expressive aphasia.
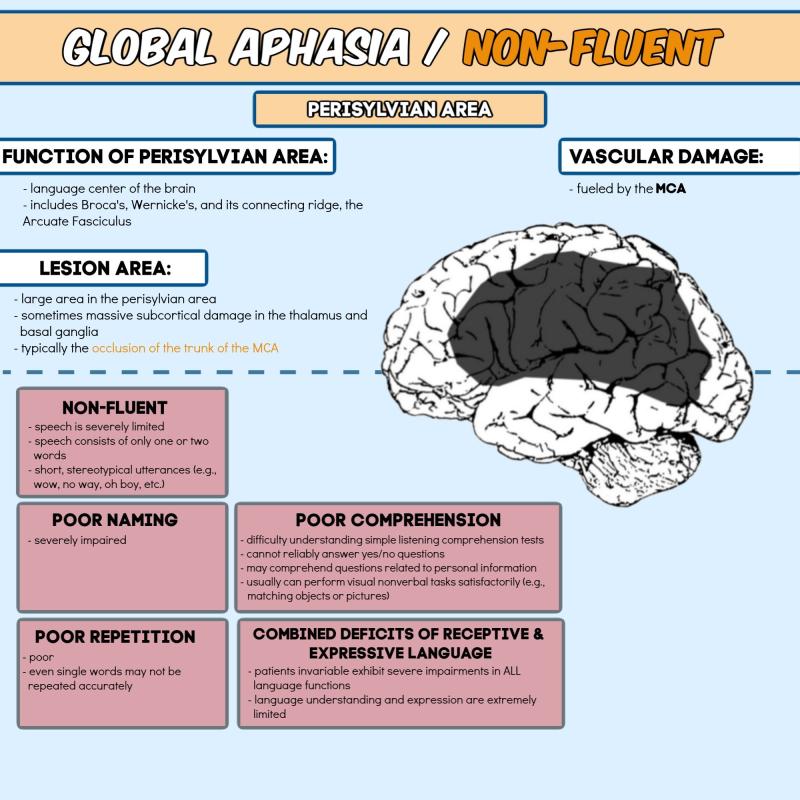
Understanding Expressive Aphasia and its Impact on Communication
Expressive aphasia, also known as Broca's aphasia, is a type of aphasia characterized by difficulty with language production. Individuals with expressive aphasia may struggle to find the right words, speak fluently, or construct grammatically correct sentences. However, their comprehension of spoken language typically remains intact.
The impact of expressive aphasia on communication can be significant, affecting an individual's ability to:
Express their thoughts, ideas, and feelings
Engage in conversations and social interactions
Request help or express their needs
Participate in work, school, or other activities that require verbal communication
Utilizing Speech Therapy and Communication Strategies for Expressive Aphasia
Speech therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for expressive aphasia. Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) work with individuals to improve their language production skills through various techniques, including:
Naming therapy: This therapy helps individuals with word retrieval difficulties, practicing naming objects, pictures, and actions.
Melodic intonation therapy (MIT): MIT uses a melodic and rhythmic approach to improve speech production and intonation.
Constraint-induced aphasia therapy (CIAT): CIAT involves focusing on the impaired language modality (speaking) while restricting the use of the unaffected modality (writing) to promote recovery.
Articulation therapy: This therapy focuses on improving speech articulation, such as producing sounds correctly and clearly.
Grammar and syntax therapy: This therapy addresses grammatical errors and sentence structure issues.
In addition to speech therapy, various communication strategies can help individuals with expressive aphasia:
Simplification: Using simple language, avoiding complex vocabulary and sentence structures.
Slowing down: Speaking slowly and clearly, allowing time for the individual to process and respond.
Visual aids: Using pictures, symbols, or written words to supplement spoken communication.
Gesture and facial expressions: Utilizing gestures, facial expressions, and body language to enhance communication.
Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC): Using AAC tools, such as picture boards, speech-generating devices, or writing aids, to provide alternative communication methods.
Supporting and Encouraging Individuals with Expressive Aphasia
Supporting and encouraging individuals with expressive aphasia is crucial for their emotional well-being and communication progress. Here are some ways to provide support:
Be patient and understanding: Recognize that communication may take time and effort for individuals with expressive aphasia.
Provide opportunities for communication: Engage in conversations, ask questions, and listen attentively.
Use clear and concise language: Avoid using jargon or complex language that may be difficult to understand.
Offer praise and encouragement: Acknowledge their efforts and celebrate their progress.
Seek professional support: Encourage them to attend speech therapy sessions and participate in support groups.
Remember, expressive aphasia can be a challenging condition, but with proper support, individuals can make significant progress in improving their communication skills and regaining their independence.