What is a gastrocnemius recession?
Gastrocnemius recession, also known as gastrocnemius lengthening or Strayer procedure, is a surgical procedure performed on the gastrocnemius muscle, which is one of the two major muscles of the calf. The purpose of this procedure is to address tightness or contracture of the gastrocnemius muscle, which can contribute to various foot and ankle conditions.
The gastrocnemius muscle has two heads and forms the bulk of the calf muscles. When this muscle becomes excessively tight, it can lead to issues such as equinus deformity, where there is limited ankle joint dorsiflexion (the ability to bring the foot upward toward the shin). Equinus deformity can contribute to conditions like Achilles tendonitis, foot ulcers, and altered gait.
Here is an overview of the gastrocnemius recession surgical procedure:
Indications:Gastrocnemius recession is considered in cases where conservative treatments, such as physical therapy and stretching exercises, have not effectively addressed the tightness in the gastrocnemius muscle. It is often performed to improve ankle joint dorsiflexion and relieve symptoms associated with equinus deformity.
Procedure:
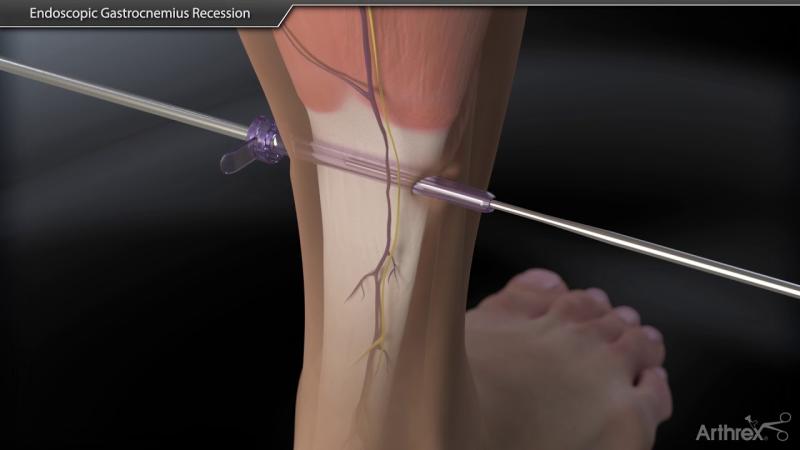
Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the back of the lower leg, typically just above the ankle joint.
Identification of Gastrocnemius Muscle: The gastrocnemius muscle is identified and isolated.
Lengthening of the Muscle: The surgeon performs a lengthening of the gastrocnemius muscle. This can be achieved through various techniques, such as releasing a portion of the muscle or detaching and reattaching it at a longer length.
Closure: After the desired lengthening is achieved, the incision is closed with sutures.
Recovery:
- Patients generally need to follow a structured rehabilitation program that includes physical therapy to regain strength and range of motion.
- Weight-bearing and return to regular activities are typically gradual and guided by the surgeon based on the individual's progress.
Risks and Complications:As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with gastrocnemius recession. These can include infection, scarring, nerve injury, and the possibility of over-lengthening the muscle.
Follow-Up:Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process and adjust the rehabilitation plan as needed. It's crucial for patients to communicate any concerns or changes in symptoms during the recovery period.
Individuals considering gastrocnemius recession should consult with an orthopedic surgeon or a specialist in foot and ankle disorders. The decision to undergo surgery is based on a thorough evaluation of the patient's condition, symptoms, and response to conservative treatments.
Sure, here is an overview of the gastrocnemius recession procedure, its effectiveness, risks and benefits, recovery, and alternative treatments:
What is involved in a gastrocnemius recession procedure?
A gastrocnemius recession is a surgical procedure that lengthens the gastrocnemius muscle, a large muscle at the back of the calf. This procedure is typically performed to treat tightness or contracture of the gastrocnemius muscle, which can cause conditions such as equinus (commonly called toe walking) and Achilles tendonitis.
During a gastrocnemius recession, the surgeon makes an incision in the back of the calf and then releases the tight portion of the gastrocnemius muscle. This lengthening of the muscle allows the heel to shift downward into a more natural position, improving range of motion and reducing pain.
How does a gastrocnemius recession alleviate certain conditions?
A gastrocnemius recession can alleviate certain conditions by addressing the underlying cause of the problem. By lengthening the gastrocnemius muscle, the procedure helps to:
Improve range of motion in the ankle joint, allowing the heel to touch the ground more fully when walking
Reduce pain and discomfort caused by muscle tightness and contracture
Prevent further damage to the Achilles tendon, which can occur due to excessive tension
What are the risks and benefits associated with gastrocnemius recession surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks associated with gastrocnemius recession surgery. These risks include:
Bleeding
Infection
Nerve damage
Overcorrection (excessive lengthening of the muscle), which can lead to weakness and instability in the ankle joint
The benefits of gastrocnemius recession surgery typically outweigh the risks for patients who experience significant pain, limited mobility, and an increased risk of Achilles tendon injury due to tight gastrocnemius muscles.
How is recovery managed after undergoing a gastrocnemius recession?
The recovery process after a gastrocnemius recession typically involves:
A period of rest and elevation of the foot and ankle to reduce swelling and promote healing
Physical therapy to gradually regain range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the ankle
Use of a walking cast or boot to protect the ankle during initial healing and rehabilitation
Most patients can return to their normal activities within a few weeks. However, it may take several months for the full benefits of the procedure to be realized.
Are there alternative treatments to gastrocnemius recession for related conditions?
In some cases, alternative treatments may be considered before recommending gastrocnemius recession surgery. These alternatives may include:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
Physical therapy to stretch the gastrocnemius muscle and improve range of motion
Night splints to keep the ankle in a plantarflexed position (heel down) while sleeping, which can gradually lengthen the gastrocnemius muscle
Botox injections to temporarily weaken the gastrocnemius muscle, providing relief from pain and stiffness
If these non-surgical treatments are not effective or if the condition is severe, gastrocnemius recession surgery may be recommended.