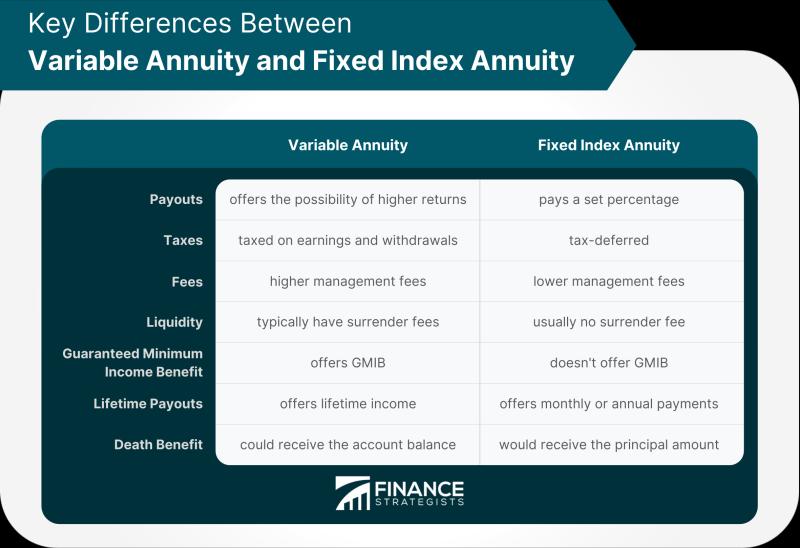
What are the differences between fixed and variable annuities?
Fixed and variable annuities are two distinct types of annuities, and they differ in several key ways, including how they accumulate value, provide income, and manage investment risk. Here are the main differences between fixed and variable annuities:
1. Investment and Returns:
Fixed Annuities: Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed interest rate, typically set at the time of purchase, that remains fixed for a specified period, such as one to ten years. The returns on a fixed annuity are stable and not tied to market performance.
Variable Annuities: Variable annuities allow you to allocate your premium payments into underlying investment options, often similar to mutual funds. The returns on a variable annuity are based on the performance of these investments. As a result, the value of a variable annuity can fluctuate with the financial markets.
2. Risk:
Fixed Annuities: Fixed annuities carry minimal investment risk. Your principal and the interest earned are typically guaranteed by the insurance company that issues the annuity. However, they may not keep pace with inflation, which can erode the purchasing power of your income over time.
Variable Annuities: Variable annuities involve market risk because your returns are directly tied to the performance of the underlying investments. If the investments perform poorly, the value of your annuity and the income it provides may decrease.
3. Income Stream:
Fixed Annuities: Fixed annuities provide a predictable and stable income stream, with payments that do not change over the life of the annuity. This can be suitable for those who seek guaranteed income in retirement.
Variable Annuities: Variable annuities offer the potential for higher income, but the payments can vary based on the performance of the underlying investments. Your income may fluctuate, and there is no guarantee of a specific payment amount.
4. Tax Treatment:
Fixed Annuities: The interest earned in a fixed annuity is tax-deferred. This means you won't pay taxes on the gains until you make withdrawals. This tax advantage can enhance the growth of your savings.
Variable Annuities: Variable annuities also provide tax-deferred growth, but you may incur capital gains taxes when you withdraw funds or annuitize the contract.
5. Flexibility:
Fixed Annuities: Fixed annuities are relatively inflexible. Once the interest rate is set, it remains fixed for the annuity's term, and there is limited opportunity to make investment choices.
Variable Annuities: Variable annuities offer greater flexibility in terms of investment choices. You can typically allocate your funds among a variety of investment options, allowing you to tailor your investment strategy to your risk tolerance and goals.
6. Costs and Fees:
Fixed Annuities: Fixed annuities typically have lower fees and charges compared to variable annuities. They may have modest administrative fees, but there are no expenses related to managing underlying investments.
Variable Annuities: Variable annuities often come with higher fees, including management fees, mortality and expense charges, and administrative fees. These fees can reduce the overall return on your investment.
When choosing between fixed and variable annuities, it's essential to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the level of guaranteed income you desire in retirement. Additionally, be sure to carefully review the terms, conditions, and fees associated with each type of annuity, and consider seeking guidance from a financial advisor to make an informed decision based on your unique circumstances.
Fixed vs. Variable Annuities: Key Differences and Considerations
Annuities are a popular investment option for individuals seeking retirement income and capital preservation. They offer a variety of features and benefits, but the two main types, fixed and variable annuities, differ significantly in their structure and potential returns.
Navigating the Annuity Market: Fixed vs. Variable Options
Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed interest rate for a predetermined period, ensuring a steady stream of income and shielding policyholders from market fluctuations. Variable annuities, on the other hand, offer the potential for higher returns but also carry more risk, as their value fluctuates based on market performance.
Choosing Between Fixed and Variable Annuities
The choice between fixed and variable annuities depends on individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and retirement income needs.
Fixed Annuities:
Pros: Guaranteed interest rates, predictable income, minimal risk.
Cons: Lower investment returns compared to other assets, potential surrender charges for early withdrawals.
Variable Annuities:
Pros: Potential for higher returns, participation in market growth.
Cons: Market-related risk, potential for losses, higher fees compared to fixed annuities.
Considerations for Choosing Between Fixed and Variable Annuities:
Risk tolerance: Fixed annuities are suitable for conservative investors seeking stability and predictability, while variable annuities are better suited for risk-tolerant investors seeking higher return potential.
Investment goals: Fixed annuities align well with goals of securing retirement income and preserving capital, while variable annuities are geared towards long-term growth objectives.
Retirement income needs: Fixed annuities provide a predictable income stream, while variable annuities may offer higher income potential but also carry more uncertainty.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consulting a financial advisor can help you assess your individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and retirement goals to determine the most suitable annuity type for your investment portfolio. They can explain the benefits, risks, and fees associated with each type of annuity and guide you towards making informed decisions that align with your long-term financial objectives.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between fixed and variable annuities is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Fixed annuities offer safety and predictability, while variable annuities provide the potential for higher returns but also carry more risk. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you navigate the annuity market and choose the type that best suits your individual needs and risk tolerance.