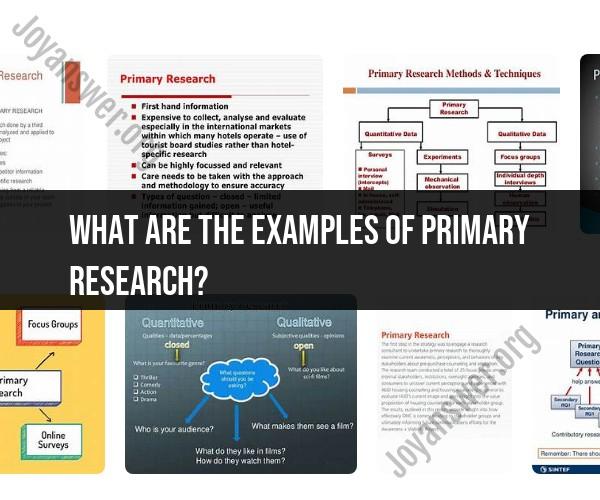
What are the examples of primary research?
Primary research refers to the collection of original data or information directly from individuals, groups, or sources. It is a fundamental research method used in various disciplines to gather firsthand data and draw conclusions based on new or previously unknown information. Here are examples of primary research across different academic disciplines:
Social Sciences:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Researchers in sociology or psychology may conduct surveys or questionnaires to collect data on attitudes, behaviors, or opinions of individuals.
- Observational Studies: Anthropologists may engage in participant observation to study cultural practices and behaviors in specific communities.
- Interviews: Political scientists may conduct interviews with political leaders and stakeholders to understand policy decisions.
Natural Sciences:
- Laboratory Experiments: Chemists might conduct experiments to analyze the chemical reactions and properties of substances.
- Field Research: Biologists may conduct field research to study ecosystems, animal behavior, or plant biology.
- Surveys: Environmental scientists may use surveys to collect data on public perception of environmental issues.
Health Sciences:
- Clinical Trials: Medical researchers perform clinical trials to test the safety and efficacy of new drugs or medical treatments.
- Patient Surveys: Healthcare professionals may use patient surveys to gather information on the quality of healthcare services.
- Observational Studies: Epidemiologists might conduct observational studies to investigate the spread of diseases in populations.
Humanities:
- Archival Research: Historians explore primary sources like historical documents, letters, and diaries to reconstruct historical events.
- Oral History Interviews: Cultural anthropologists or historians may conduct oral history interviews to capture personal narratives and experiences.
- Textual Analysis: Literary scholars analyze primary texts, such as novels or poems, to study literary movements or authorship.
Business and Economics:
- Market Research Surveys: Marketing professionals use surveys and focus groups to understand consumer preferences and market trends.
- Financial Data Analysis: Economists analyze financial reports, market data, and economic indicators to assess economic conditions.
Engineering and Technology:
- Prototype Testing: Engineers build and test prototypes to evaluate the performance and functionality of new products or technologies.
- User Testing: User experience (UX) designers gather feedback through user testing to improve the usability of software or products.
Education:
- Classroom Observations: Educators may observe classroom dynamics and teaching methods to improve pedagogy.
- Standardized Testing: Educational researchers use standardized tests to assess students' academic performance.
Communication and Media Studies:
- Content Analysis: Media researchers analyze news articles or television broadcasts to study media framing or representation.
- Audience Surveys: Communication scholars may conduct surveys to understand audience preferences and media consumption habits.
Law and Criminal Justice:
- Legal Case Analysis: Legal scholars examine court cases, statutes, and legal documents to analyze legal precedents.
- Criminal Justice Surveys: Criminologists use surveys to gather data on crime rates and public perceptions of law enforcement.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of primary research methods across academic disciplines. Researchers use primary research to generate new knowledge, test hypotheses, and contribute to the advancement of their respective fields. The specific methods and techniques employed vary depending on the research questions and goals of each discipline.