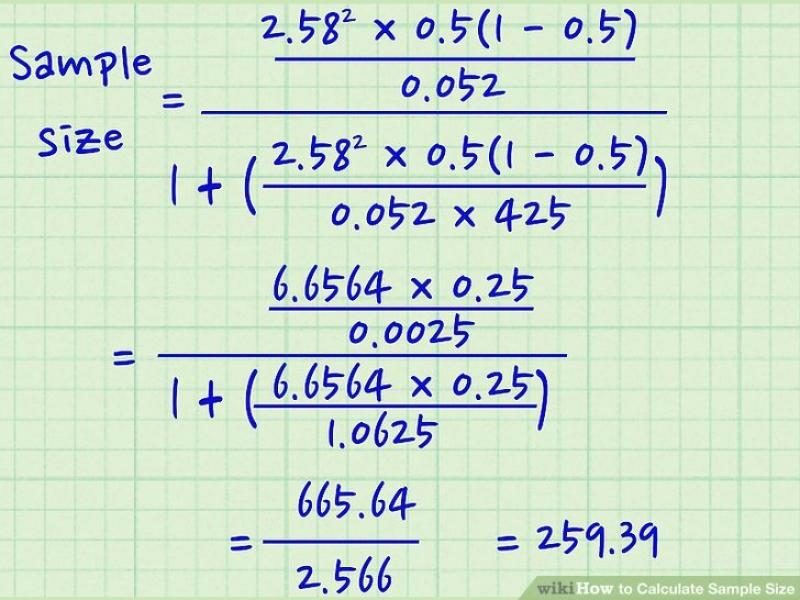How do you calculate Sample Size for a survey?
Calculating the sample size for a survey is a crucial step in the survey research process. It involves determining the number of respondents you need to obtain statistically significant and reliable results. The sample size depends on several factors, including the desired level of confidence, the margin of error, and the size of the population you are studying. Here's a guide on how to calculate the sample size for a survey:
Define Your Parameters:
- Population Size (N): Determine the total number of individuals in the population you want to study. If your population is very large (e.g., over 100,000), you can assume it to be infinite (often called "infinite population correction" or "large population size correction").
- Confidence Level (Z): Choose the desired level of confidence, typically expressed as a percentage. Common values include 95% or 99%, corresponding to Z-scores of 1.96 and 2.58, respectively. You can find these values in standard normal distribution tables.
- Margin of Error (E): Decide on the maximum acceptable margin of error. The margin of error represents the maximum difference between the sample estimate and the true population parameter.
- Variance or Proportion (P): Estimate the variance (for quantitative data) or proportion (for categorical data) of the characteristic you're studying. If you're unsure, you can use a conservative estimate, such as 0.5 for proportion.
Calculate the Sample Size (n): The formula for calculating the sample size is as follows:
For estimating a population proportion (categorical data):
For estimating a population mean (quantitative data):
Where:
- = Required sample size
- = Z-score corresponding to the chosen confidence level
- = Estimated population proportion (for proportion estimation)
- = Estimated population variance (for mean estimation)
- = Margin of error
Adjust for Finite Population (if applicable): If your population size is small (not infinite), you should use the finite population correction (FPC) to adjust the sample size formula. The adjusted formula is:Where:
- = Sample size with finite population correction
- = Sample size calculated from the formula without correction
- = Population size
Round Up: Once you've calculated the sample size, it's a good practice to round up to the nearest whole number to ensure that your sample size is sufficient.
Consider Non-Response and Data Quality: Keep in mind that not all respondents may participate or provide usable data. To account for non-response, you might need to increase the sample size further.
Collect Data and Analyze: After determining your sample size, proceed with collecting survey data and analyze the results using appropriate statistical techniques.
Calculating the sample size accurately is essential to ensure that your survey results are representative of the population and that the estimates are reliable. Keep in mind that sample size requirements can vary depending on the specific goals and characteristics of your survey.
Calculating Sample Size for a Survey: Methods and Formulas
Determining the appropriate sample size for a survey is crucial for obtaining statistically significant and reliable results. Several factors influence the sample size, including the desired confidence level, margin of error, population size, and the expected variability within the population.
Methods for Sample Size Calculation:
Confidence Level: The confidence level represents the probability that the sample results accurately reflect the true values in the population. A higher confidence level requires a larger sample size.
Margin of Error: The margin of error represents the maximum amount of error that is tolerable in the sample results. A smaller margin of error requires a larger sample size.
Population Size: The population size refers to the total number of individuals in the group you want to study. Generally, a larger population requires a smaller sample size, as there is more variation within the population.
Expected Variability: The expected variability within the population affects the sample size. If the population is expected to be more homogenous, a smaller sample size may suffice.
Formula for Sample Size Calculation:
The most common formula for calculating sample size is:
n = (Z^2 * p * q) / (e^2)
Where:
n is the desired sample size
Z is the z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level (e.g., 1.96 for 95% confidence)
p is the estimated proportion of the population with the characteristic of interest
q is 1 - p
e is the margin of error
Determining the Ideal Sample Size for Survey Research
The ideal sample size for survey research depends on the specific research objectives, the complexity of the survey questions, and the available resources. However, some general guidelines can be followed:
For exploratory research: A smaller sample size may be sufficient to gather preliminary data and identify trends.
For descriptive research: A larger sample size is often necessary to accurately describe the characteristics and attitudes of the population.
For causal research: A very large sample size may be required to establish a strong causal relationship between variables.
Survey Sample Size Estimation: A Practical Approach
In practice, estimating the ideal sample size often involves a balance between statistical rigor and practical considerations. Researchers typically consider factors such as budget limitations, time constraints, and the accessibility of the target population.
Tips for Practical Sample Size Estimation:
Consult with experts: Seek guidance from statisticians or experienced researchers to determine a suitable sample size for your specific research project.
Use sample size calculators: Utilize online sample size calculators or statistical software to estimate the sample size based on your research parameters.
Consider stratified sampling: Divide the population into subgroups (strata) and draw samples from each stratum to ensure a representative sample.
Pilot testing: Conduct a pilot test with a small sample to assess the effectiveness of the survey questions and identify potential issues before proceeding with the full-scale survey.
Remember, the ideal sample size is not always a fixed number. It may be necessary to adjust the sample size during the research process based on emerging findings or unexpected challenges.