What is an example of quality assurance?
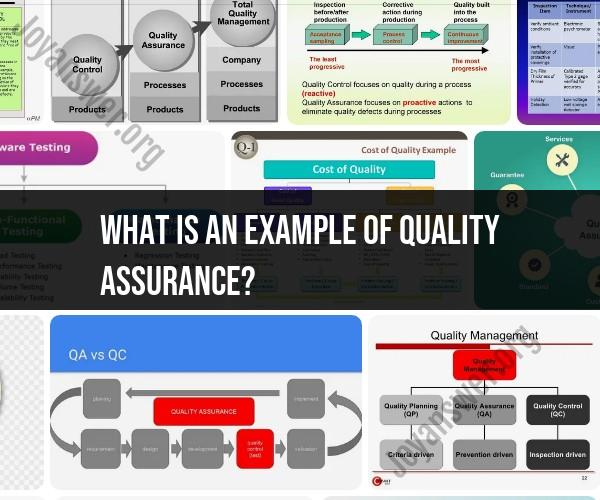
Quality assurance (QA) is a systematic process of ensuring that products, services, or processes meet established standards and expectations. It involves activities and techniques that focus on preventing defects and maintaining a high level of quality. Here are some examples of quality assurance in various industries:
Software Development:
- Code Reviews: Software developers review each other's code to identify and rectify errors, improve code quality, and ensure adherence to coding standards.
- Testing: QA engineers conduct various types of testing, such as functional, regression, and load testing, to identify and fix software defects.
Manufacturing:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Manufacturers use SPC techniques to monitor and control the production process, ensuring that products consistently meet quality standards.
- Inspection and Testing: Products are inspected at various stages of production to identify defects, and testing is performed to ensure they meet specifications.
Healthcare:
- Clinical Audits: Healthcare facilities conduct clinical audits to review patient records and processes to ensure compliance with healthcare standards and regulations.
- Medication Safety Checks: Pharmacists and nurses conduct medication safety checks to prevent medication errors and ensure patient safety.
Construction:
- Inspections and Codes: Building inspectors check construction sites to ensure compliance with building codes, safety regulations, and architectural plans.
- Material Quality Control: Construction companies may perform quality checks on construction materials like concrete and steel to ensure they meet specifications.
Education:
- Curriculum Alignment: Educational institutions align their curricula with educational standards and regularly review and update educational materials and methods.
- Assessment and Testing: Schools conduct assessments and standardized testing to measure student achievement and identify areas for improvement.
Aerospace and Aviation:
- Quality Management Systems (QMS): Aerospace companies implement QMS, such as AS9100, to ensure the highest standards of safety and reliability in aircraft production.
- Component Testing: Rigorous testing and inspection of aerospace components, such as engines and avionics, are conducted to ensure reliability and safety.
Food Industry:
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points): Food producers use HACCP to identify and control potential food safety hazards throughout the production process.
- Quality Audits: External and internal audits are conducted to ensure compliance with food safety and quality standards.
Pharmaceuticals:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Pharmaceutical companies adhere to GMP regulations to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of medications.
- Batch Testing: Each batch of pharmaceutical products undergoes extensive testing and quality checks before release.
Automotive Manufacturing:
- ISO/TS 16949: Automotive manufacturers follow ISO/TS 16949 standards for quality management to ensure product excellence.
- Durability Testing: Vehicles undergo rigorous testing for safety, performance, and durability before being released to the market.
Telecommunications:
- Network Monitoring: Telecommunication companies use network monitoring tools to ensure the quality and reliability of their communication networks.
- Customer Service Monitoring: Quality assurance teams review customer service interactions to ensure service excellence.
Quality assurance practices may vary between industries and organizations, but the overarching goal is to ensure that products, services, or processes consistently meet the specified standards and deliver high-quality results.
Quality Assurance in Action: Real-Life Examples
Quality assurance (QA) is the process of ensuring that a product or service meets or exceeds customer requirements. QA can be applied to any industry, from software development to manufacturing to healthcare.
Here are a few real-life examples of quality assurance in action:
- Software development: QA engineers test software applications to identify and fix bugs before the software is released to customers. They also work with developers to create and implement QA processes that help to prevent bugs from being introduced in the first place.
- Manufacturing: QA inspectors inspect manufactured products to ensure that they meet quality standards. They may also test products to ensure that they are safe and reliable.
- Healthcare: QA professionals in healthcare work to improve the quality and safety of patient care. They may develop and implement QA programs, conduct audits, and analyze data to identify and address quality issues.
Case Studies of Successful Quality Assurance Practices
Here are a few case studies of successful quality assurance practices:
- Toyota: Toyota is known for its high-quality vehicles and its commitment to quality assurance. Toyota uses a variety of QA practices, including lean manufacturing and Six Sigma, to ensure the quality of its products.
- Amazon: Amazon is another company that is known for its focus on quality assurance. Amazon uses a variety of QA practices, including customer feedback, data analysis, and machine learning, to ensure the quality of its products and services.
- Google: Google is known for its high-quality products and services, such as its search engine and Gmail. Google uses a variety of QA practices, including code reviews, automated testing, and user feedback, to ensure the quality of its products and services.
Quality Assurance Strategies for Different Industries
The specific QA strategies that are used will vary depending on the industry. However, there are some general QA principles that can be applied to any industry. These principles include:
- Planning: QA should be planned into the development or manufacturing process from the start. This includes developing QA plans and procedures, and identifying the resources that will be needed to implement the QA program.
- Execution: The QA plan should be executed effectively. This includes conducting inspections, tests, and audits to identify and fix quality issues.
- Monitoring: The QA program should be monitored regularly to ensure that it is effective and that it is meeting the needs of the organization.
Measuring Success through Quality Assurance Initiatives
There are a number of ways to measure the success of QA initiatives. Some common metrics include:
- Customer satisfaction: Customer satisfaction surveys can be used to measure how satisfied customers are with the quality of the products or services that they receive.
- Return rates: Return rates can be used to measure the number of products or services that are returned due to quality issues.
- Number of defects: The number of defects that are found in products or services can be used to measure the overall quality of the products or services.
- Cost of quality: The cost of quality can be used to measure the financial impact of quality issues. This includes the cost of fixing defects, the cost of returning products, and the cost of lost customers.
Ensuring Quality at Every Stage of Production
QA should be applied at every stage of the production process, from design to development to manufacturing to delivery. This helps to ensure that quality issues are caught early and prevented from reaching customers.
Here are some tips for ensuring quality at every stage of production:
- Design: QA should be involved in the design phase to help identify and mitigate potential quality risks.
- Development: QA should test and inspect products throughout the development process to identify and fix bugs and defects.
- Manufacturing: QA should inspect products during the manufacturing process to ensure that they meet quality standards.
- Delivery: QA should ensure that products are delivered to customers in good condition and that they meet customer expectations.
By following these tips, organizations can ensure that their products and services meet the highest quality standards.