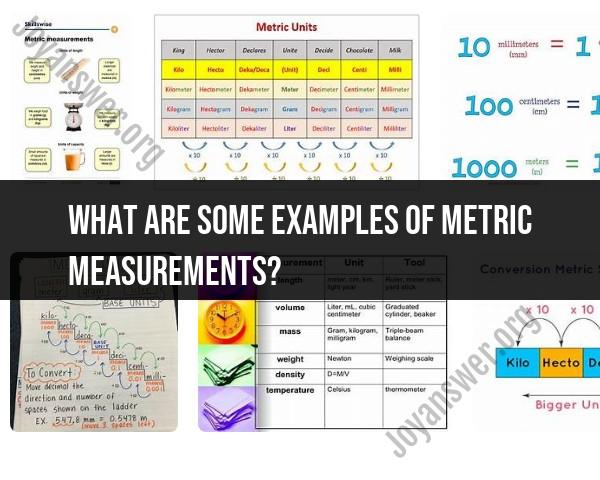
What are some examples of metric measurements?
Certainly! Metric measurements are widely used worldwide for their simplicity and consistency. Here are examples across various units:
Length:
- Millimeter (mm): The thickness of a credit card is about 0.76 mm.
- Centimeter (cm): A standard pencil is roughly 17.5 cm long.
- Meter (m): A dining table might be around 2 meters long.
- Kilometer (km): The distance between two cities might be 150 km.
Mass/Weight:
- Milligram (mg): A grain of salt might weigh about 0.05 mg.
- Gram (g): A medium-sized apple weighs approximately 150 grams.
- Kilogram (kg): A small bag of flour could be 2.5 kilograms.
- Metric Ton (t): A car's weight is typically around 1.5 metric tons.
Volume:
- Milliliter (mL): A small medicine cup holds about 5 mL of liquid.
- Centiliter (cL): A shot glass might contain 6 cL of liquid.
- Liter (L): A large bottle of soda is usually 2 liters.
- Cubic Meter (m³): The volume of a standard refrigerator might be 0.5 cubic meters.
Temperature:
- Celsius (°C): Water boils at 100°C and freezes at 0°C.
- Kelvin (K): Absolute zero is 0 Kelvin, equivalent to -273.15°C.
Area:
- Square Millimeter (mm²): The area of a postage stamp is about 25 mm².
- Square Meter (m²): A single-car parking space is approximately 12 m².
- Hectare (ha): A football field might be close to 1 hectare (10,000 m²).
Time:
- Second (s): A heartbeat takes about 0.8 seconds.
- Minute (min): A short phone call might last 5 minutes.
- Hour (h): A typical workday is around 8 hours long.
Speed:
- Meters per Second (m/s): Usain Bolt's top speed was about 12 m/s.
- Kilometers per Hour (km/h): The speed limit on highways might be 100 km/h.
These examples showcase how metric measurements cover various aspects of everyday life, providing a standardized system for measurements in science, industry, and everyday use.
Sure, here are some instances of measurements using the metric system:
- Body measurements:
- Height: Meters (m)
- Weight: Kilograms (kg)
- Temperature: Degrees Celsius (°C)
- Cooking and baking:
- Ingredients (volume): Milliliters (ml), liters (L)
- Ingredients (mass): Grams (g), kilograms (kg)
- Cooking times: Minutes (min), hours (h)
- Cooking temperatures: Degrees Celsius (°C)
- Household measurements:
- Length: Millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m)
- Area: Square meters (m²), square kilometers (km²)
- Volume: Liters (L), cubic meters (m³)
- Clothing and footwear:
- Clothing sizes: Numbers (based on metric measurements)
- Shoe sizes (Continental system): Centimeters (cm)
- Sports and fitness:
- Distances: Meters (m), kilometers (km)
- Speeds: Kilometers per hour (km/h), meters per second (m/s)
- Weights: Kilograms (kg)
- Times: Seconds (s), minutes (min), hours (h)
- Transportation:
- Speed limits: Kilometers per hour (km/h)
- Fuel consumption: Liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km)
- Vehicle dimensions: Meters (m)
- Science and engineering:
- Length: Millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), kilometers (km)
- Mass: Grams (g), kilograms (kg), tonnes (t)
- Volume: Milliliters (ml), liters (L), cubic meters (m³), cubic kilometers (km³)
- Temperature: Degrees Celsius (°C), Kelvin (K)
- Speed: Meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h)
- Force: Newtons (N)
- Pressure: Pascals (Pa)
These are just a few examples of the many ways in which the metric system is used in everyday life. The metric system is a widely adopted international standard for measurement, and it is used in a variety of contexts, including science, engineering, commerce, and everyday life.