How is wind energy turned into usable energy?
Wind energy is converted into usable power through a series of steps that involve harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind and transforming it into electrical energy. Here's the process of how wind energy is turned into usable power:
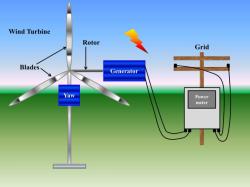
Wind Capture:
- Wind turbines are strategically placed in locations with consistent and sufficient wind speeds. The kinetic energy of the moving air (wind) is the initial energy source.
Rotor Blades:
- The rotor blades of the wind turbine are designed to capture the kinetic energy from the wind. These blades are aerodynamically shaped to efficiently interact with the wind.
Rotation of Rotor Blades:
- As the wind blows against the rotor blades, they begin to rotate. This rotation represents the conversion of kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy in the form of rotational motion.
Main Shaft:
- The rotor blades are connected to the main shaft of the wind turbine. As the blades rotate, they transfer their mechanical energy to the main shaft, causing it to spin.
Generator:
- The main shaft is linked to a generator, typically located inside the nacelle, the housing at the top of the wind turbine tower. The mechanical energy of the spinning shaft is transferred to the generator.
Electromagnetic Induction:
- Inside the generator, mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through the principle of electromagnetic induction. The generator contains a rotor (rotating part) and a stator (stationary part). As the rotor spins, it creates a changing magnetic field, which induces an electric current in coils of wire in the stator.
Generation of Electrical Energy:
- The electrical energy produced in the generator is typically in the form of alternating current (AC). This electrical energy is the primary product of the wind energy conversion process within the turbine.
Conversion and Conditioning:
- The electrical energy generated may go through transformers and other electrical equipment to adjust its voltage and frequency to match the electrical grid or the specific application.
Grid Connection:
- The electrical energy is then transmitted through power lines and connected to the electrical grid. It becomes part of the larger electricity supply and can be distributed and used to power homes, businesses, and industries.
Energy Storage (Optional):
- In some cases, excess energy generated by the wind turbine can be stored in batteries or other energy storage systems for use when the wind is not blowing.
Inverter (if needed):
- In cases where the wind turbine generates direct current (DC) but the grid or application requires alternating current (AC), an inverter may be used to convert the energy from DC to AC.
In summary, the process of turning wind energy into usable power involves capturing the kinetic energy of the wind, converting it into mechanical energy, and then transforming it into electrical energy. This electrical energy can be integrated into the electrical grid or used directly to provide clean and renewable power for various applications. Wind energy plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and providing a sustainable source of electricity.
How is wind energy harnessed and converted into electricity?
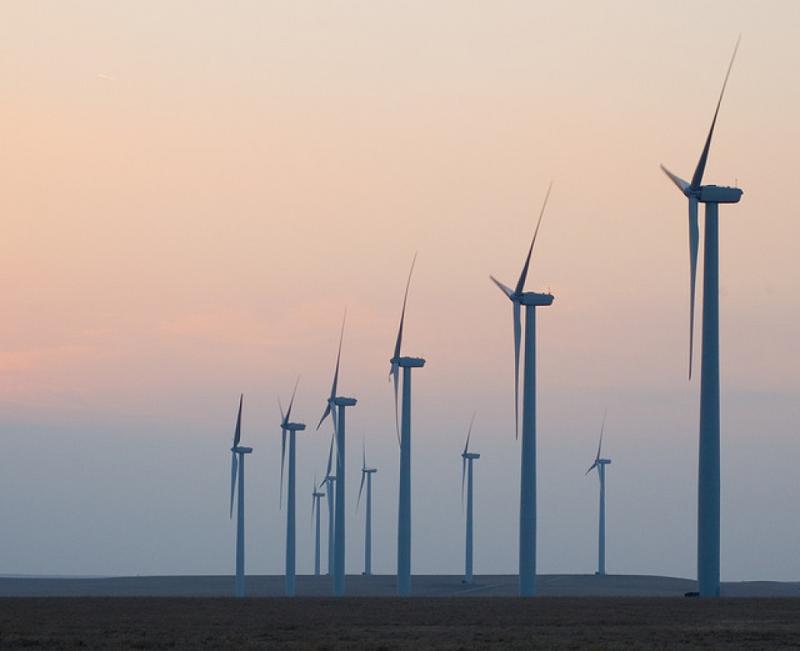
Wind energy is a clean, renewable, and sustainable source of energy that has the potential to play a significant role in meeting our growing energy needs. Wind turbines, the towering structures that dot landscapes across the globe, are the key players in harnessing the power of the wind and converting it into usable electricity.
The Journey of Wind Energy to Electricity
The transformation of wind energy into electricity involves a fascinating interplay of aerodynamic principles, mechanical motion, and electrical induction. Let's delve into the intricacies of this process and uncover how wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into usable electrical power.
1. Capturing Wind Energy
The journey of wind energy to electricity begins with the interaction of wind blades with the moving air. As wind flows over the blades, it creates lift, similar to the force that keeps airplanes airborne. This lift force, acting on the blades, causes them to rotate, and this rotational motion is the key to generating electricity.
2. Transforming Rotational Motion
The rotating blades, collectively known as the rotor, form the heart of a wind turbine. The rotor is typically mounted on a tall tower to capture wind at higher speeds, where the energy density is greater. As the wind turns the rotor, the rotational motion is transferred to a central shaft, which acts as the conduit for energy transfer.
3. Converting Mechanical Energy to Electrical Power
At the core of the wind turbine lies the generator, the electrical counterpart to the rotor's mechanical energy. The generator is a device that converts rotational motion into electrical energy through a process called electromagnetic induction.
Inside the generator, coils of wire are arranged in a specific pattern within a magnetic field. When the rotor turns, it causes the coils to rotate within the magnetic field. This movement of the coils relative to the magnetic field induces an electrical current in the wires.
4. Transmission and Distribution
The electrical energy generated by the wind turbine is not directly usable in homes or businesses. It first needs to be transformed and transmitted to the power grid, which acts as a network of interconnected power lines that distribute electricity to consumers.
Transformers are used to step up the voltage of the generated electricity, making it suitable for long-distance transmission through high-voltage power lines. These power lines carry the electricity from wind farms to substations, where it is further transformed and distributed to homes and businesses.
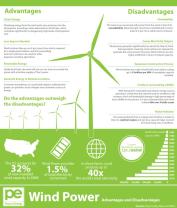
Environmental Benefits of Wind Energy
The use of wind energy for electricity generation offers several environmental benefits compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power plants:
1. Reduces greenhouse gas emissions: Wind energy does not produce any greenhouse gases, which are the main cause of climate change. Fossil fuels, on the other hand, are the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Improves air quality: Wind energy does not emit any air pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and other health problems.
3. Protects water resources: Wind energy does not require water for cooling, unlike traditional power plants that use water from rivers, lakes, and other sources. This can help to conserve water resources and protect aquatic ecosystems.
4. Preserves land: Wind energy requires less land than traditional power plants, such as coal-fired and nuclear plants. This can help to preserve natural habitats and open space.
In conclusion, wind energy is a clean, renewable, sustainable, and affordable source of energy that has many environmental benefits. As the technology continues to develop, wind energy is expected to play an increasingly important role in the global energy mix.