How bad is OCD?
The severity of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can vary significantly from person to person. OCD is typically categorized into different levels of severity, ranging from mild to severe, based on the impact it has on an individual's daily life. Here's a general overview of the levels of OCD severity:
Mild OCD:
- Individuals with mild OCD may experience occasional obsessions and compulsions that are relatively easy to manage.
- Symptoms might not significantly interfere with daily life and functioning.
- They may be able to maintain relationships and hold down a job or attend school with minimal disruption.
Moderate OCD:
- Moderate OCD typically involves more frequent and distressing obsessions and compulsions.
- Symptoms may interfere with daily routines and activities to a noticeable extent.
- Social and occupational functioning may be compromised, and it can be more challenging to maintain relationships or employment or attend school.
Severe OCD:
- Severe OCD is characterized by intense and frequent obsessions and compulsions that can consume a significant portion of a person's day.
- Daily life is often disrupted to a severe degree, making it difficult to hold a job, attend school, or maintain relationships.
- Individuals with severe OCD may require more intensive treatment and support.
Extreme OCD:
- Extreme cases of OCD are marked by severe and debilitating symptoms that can dominate an individual's life.
- Daily functioning may be severely impaired, and individuals may struggle to maintain even the most basic activities of daily living.
- In extreme cases, individuals may require extensive treatment and support, including hospitalization in some instances.
It's important to note that the severity of OCD does not necessarily correlate with the type or nature of obsessions and compulsions. Even seemingly "mild" obsessions and compulsions can be distressing and disruptive if they interfere with a person's life.
OCD is a treatable mental health condition. Regardless of severity, it is highly recommended to seek help from a mental health professional who specializes in OCD. Effective treatments, such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) with Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), and medication can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. The earlier OCD is addressed, the better the chances of managing its impact and preventing it from becoming more severe.
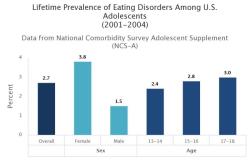
What is the impact and severity of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)?
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition that causes unwanted and intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions). People with OCD feel the need to perform compulsions in order to reduce anxiety or distress.
OCD can have a significant impact on a person's life. It can interfere with work, school, relationships, and hobbies. People with OCD may spend hours each day performing compulsions, and their obsessions may cause them to feel anxious, depressed, or ashamed.
The severity of OCD can vary from person to person. Some people may have mild symptoms that do not interfere with their daily lives. Others may have severe symptoms that make it difficult to function.
How does OCD affect individuals and their daily lives, and what are the symptoms?
OCD can affect individuals in many ways. Some common symptoms include:
- Obsessions: These are unwanted and intrusive thoughts, images, or urges that cause anxiety or distress. Common obsessions include fear of germs, contamination, or harm to oneself or others.
- Compulsions: These are repetitive behaviors or mental acts that a person feels driven to perform in order to reduce anxiety or distress. Common compulsions include hand washing, checking, cleaning, and arranging.
People with OCD may spend hours each day performing compulsions, and their obsessions may cause them to feel anxious, depressed, or ashamed. OCD can interfere with work, school, relationships, and hobbies.
What treatments and coping strategies are available for managing OCD?
There are a number of effective treatments available for OCD, including:
- Therapy: Therapy can help people to identify and change the negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to OCD. Common therapies used to treat OCD include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention (ERP).
- Medication: Medication can be used to reduce the severity of OCD symptoms. Common medications used to treat OCD include antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications.
In addition to treatment, there are a number of coping strategies that people with OCD can use to manage their symptoms. Some common coping strategies include:
- Identifying triggers: Knowing what triggers your OCD symptoms can help you to avoid them or cope with them in a healthy way.
- Creating a relapse prevention plan: Having a plan in place for how you will get back on track if you have a relapse can help you to recover more quickly.
- Joining a support group: Support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment for people with OCD to share their experiences and learn from others.
If you or someone you know has OCD, it is important to seek professional help. OCD is a treatable condition, and with the right support and treatment, people with OCD can live full and productive lives.