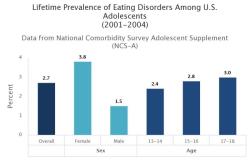
Does anxiety reduce life expectancy?
Anxiety, especially when chronic and severe, can have various negative effects on both mental and physical health. While anxiety itself may not directly reduce life expectancy, it can contribute to behaviors and health conditions that, in the long term, may have an impact on overall health and longevity. Here are some ways in which anxiety can potentially affect life expectancy:
Increased Risk of Physical Health Issues: Chronic anxiety is associated with a higher risk of developing physical health problems such as heart disease, hypertension, gastrointestinal issues, and immune system dysfunction. These conditions, if left unmanaged, can contribute to a shorter lifespan.
Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Some people with anxiety turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, overeating, or sedentary lifestyles. These behaviors can increase the risk of health problems and reduce life expectancy.
Impact on Sleep: Anxiety can lead to sleep disturbances, including insomnia. Poor sleep quality and chronic sleep deprivation are linked to various health issues, including an increased risk of accidents and certain chronic diseases.
Mental Health Conditions: Anxiety often co-occurs with other mental health conditions such as depression. If left untreated, these conditions can significantly affect a person's overall well-being and quality of life.
Reduced Quality of Life: Chronic anxiety can lead to a reduced quality of life, which may impact overall happiness and satisfaction. Quality of life is an important factor in assessing overall well-being and longevity.
It's essential to note that not everyone with anxiety will experience these negative outcomes, and many individuals effectively manage their anxiety through therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of these approaches. Seeking professional help and support is crucial for managing anxiety and reducing its potential negative impact on health and life expectancy.
Furthermore, the relationship between anxiety and life expectancy is complex and influenced by individual factors such as genetics, socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and lifestyle choices. While anxiety can be a risk factor for certain health issues, addressing and managing anxiety can lead to improved overall health and well-being, potentially mitigating any negative effects on life expectancy.
There is a growing body of research that suggests that anxiety can have a negative impact on life expectancy. For example, a 2014 study published in the journal PLOS Medicine found that people with anxiety disorders were more likely to die prematurely, even after controlling for other factors such as age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
The link between anxiety and life expectancy is likely due to a number of factors, including:
- Increased risk of chronic health conditions. Anxiety can lead to a number of chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. These conditions can shorten a person's lifespan.
- Unhealthy behaviors. People with anxiety are more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking, drinking alcohol excessively, and eating unhealthy foods. These behaviors can also shorten a person's lifespan.
- Reduced quality of life. Anxiety can make it difficult to enjoy life and can lead to social isolation. This can have a negative impact on both physical and mental health.
If you are concerned about the impact of anxiety on your life expectancy, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you to develop a treatment plan to manage your anxiety and reduce your risk of chronic health conditions.
Here are some tips for managing anxiety and living a longer, healthier life:
- Get regular exercise. Exercise is a great way to reduce stress and improve your overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Eat a healthy diet. Eating a healthy diet can help to improve your mood and energy levels. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine and alcohol.
- Get enough sleep. When you're well-rested, you're better able to cope with stress and anxiety. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Learn relaxation techniques. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help to reduce anxiety and stress.
- Connect with others. Social support is important for mental and physical health. Make time for activities that you enjoy and spend time with people who make you feel good.
- Seek professional help. If you're struggling to manage your anxiety on your own, talk to a therapist or counselor. They can teach you coping skills and help you to develop a treatment plan.
Remember, it's never too late to start living a healthier lifestyle. By managing your anxiety and taking care of yourself, you can reduce your risk of chronic health conditions and live a longer, healthier life.