What is the difference between regression and retesting?
Regression testing and retesting are both important testing techniques in software testing, but they serve different purposes and are conducted at different stages of the testing process. Here's a brief overview of the differences between regression testing and retesting:
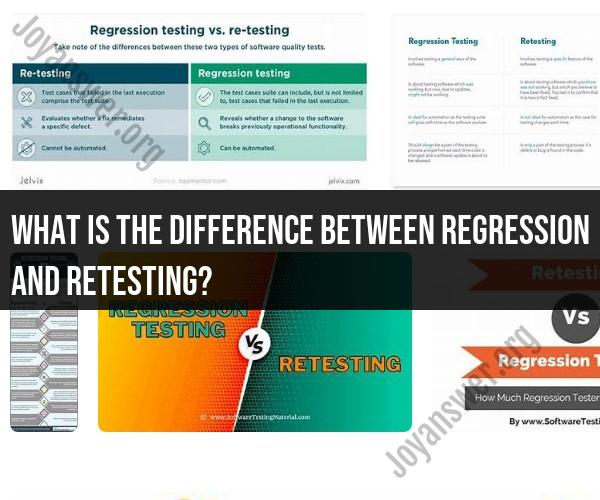
Regression Testing:
Purpose: Regression testing is conducted to ensure that recent code changes or modifications to the software do not introduce new defects or negatively impact existing functionality.
Scope: It involves re-running a comprehensive set of test cases, which cover not only the area where changes were made but also related and potentially affected areas of the software.
Test Cases: Regression test cases are typically a suite of existing test cases that have been designed to verify the software's core functionality.
Frequency: It is conducted frequently throughout the software development process, often after each code change or addition.
Automation: Regression testing is highly amenable to automation, and automated test suites are often used to quickly identify regressions.
Test Data: Regression tests are executed with a consistent set of test data and conditions to ensure consistency and repeatability.
Bug Detection: The main goal is to detect and identify any new defects or unintended side effects caused by recent code changes.
Retesting:
Purpose: Retesting is conducted to verify that specific defects identified in previous testing phases have been successfully fixed.
Scope: It focuses on testing only the specific areas or functionalities related to the reported defects.
Test Cases: Retesting uses the same test cases that initially uncovered the defects. These are often test cases designed to reproduce the issues.
Frequency: Retesting is conducted as needed, specifically when defects have been reported and fixed.
Automation: While automation can assist with regression testing, retesting is often more manual in nature since it requires verifying the specific defects.
Test Data: Retesting is conducted with the same test data or scenarios that led to the discovery of the initial defects.
Bug Verification: The primary goal is to verify that the reported defects have been fixed and that the software now behaves as expected in the areas associated with those defects.
In summary, regression testing aims to ensure that recent changes do not break existing functionality, while retesting is focused on confirming that specific reported defects have been addressed. Both testing techniques are essential for maintaining software quality and reliability throughout the development and maintenance process.
Differentiating Regression and Retesting in Statistical Analysis
Regression analysis and retesting are two distinct statistical methods, but they are often used in conjunction to provide a comprehensive assessment of data.
Regression analysis is a statistical method that is used to model the relationship between two or more variables. It can be used to predict the value of one variable based on the values of other variables. Regression analysis is a powerful tool that can be used to identify patterns and trends in data, as well as to make predictions about future outcomes.
Retesting is the practice of repeating a test or experiment to confirm the results. It is a quality control measure that is used to ensure that the results of a study are reliable and reproducible. Retesting can also be used to identify any changes in the data over time.
The Purposes and Procedures of Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Prediction: Regression analysis can be used to predict the value of one variable based on the values of other variables. For example, regression analysis could be used to predict the price of a house based on the size of the house, the number of bedrooms, and the location of the house.
- Explanation: Regression analysis can be used to identify the factors that influence a particular variable. For example, regression analysis could be used to identify the factors that influence student test scores, such as the student's socioeconomic status, the student's parents' education level, and the student's teacher's experience.
- Comparison: Regression analysis can be used to compare the relationships between different variables across different groups of people. For example, regression analysis could be used to compare the relationship between income and education level for men and women.
Understanding Retesting as a Quality Control Practice
Retesting is a quality control practice that is used to ensure that the results of a study are reliable and reproducible. It is important to retest studies to identify any errors in the data collection or analysis process. Retesting can also be used to identify any changes in the data over time.
There are a number of different ways to retest a study. One common approach is to repeat the study with a different sample of people. Another approach is to repeat the study using a different method of data collection or analysis.
Regression Analysis vs. Retesting in Hypothesis Testing
Regression analysis and retesting are both used in statistical analysis, but they have different purposes. Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between two or more variables, while retesting is used to confirm the results of a study.
Regression analysis can be used to test hypotheses about the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher could use regression analysis to test the hypothesis that there is a positive relationship between income and education level.
Retesting is not used to test hypotheses. Instead, retesting is used to confirm the results of a study and to identify any errors in the data collection or analysis process.
Combining Regression and Retesting for Comprehensive Data Assessment
Regression analysis and retesting can be combined to provide a comprehensive assessment of data. For example, a researcher could use regression analysis to model the relationship between two or more variables and then retest the study to confirm the results.
Combining regression analysis and retesting can help to ensure that the results of a study are reliable and reproducible. It can also help to identify any patterns or trends in the data that may not be evident from the regression analysis alone.
Conclusion
Regression analysis and retesting are two distinct statistical methods, but they are often used in conjunction to provide a comprehensive assessment of data. Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between two or more variables, while retesting is used to confirm the results of a study and to identify any errors in the data collection or analysis process. Combining regression analysis and retesting can help to ensure that the results of a study are reliable and reproducible.