How are CMT rates calculated?
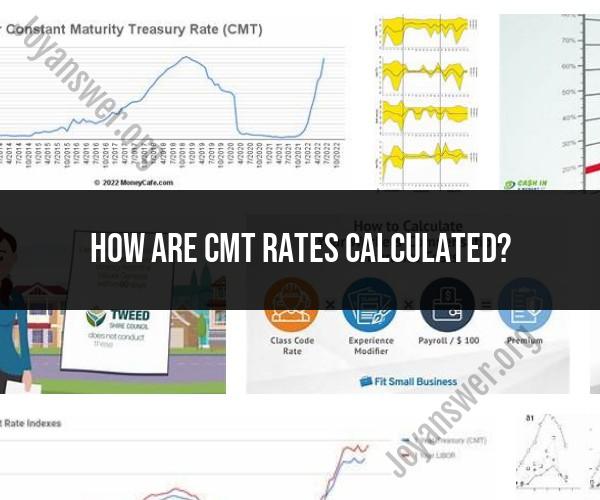
CMT rates, or Constant Maturity Treasury rates, are interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities with various maturities. They represent the yield curve for U.S. government debt and are widely used as a benchmark for interest rates in financial markets. CMT rates are typically published daily by the U.S. Federal Reserve and can be found at various maturities, such as 1-year, 5-year, 10-year, and 30-year.
The calculation of CMT rates involves several steps and is based on the prices of Treasury securities traded in the secondary market. Here's a step-by-step guide on how CMT rates are calculated:
Step 1: Selecting the Securities
The first step is to select a specific set of U.S. Treasury securities that will be used to calculate the CMT rates. These securities should have different maturities, such as 1-year, 5-year, 10-year, and 30-year Treasury notes and bonds.
Step 2: Collecting Price Data
Next, data on the prices of these selected Treasury securities are collected from the secondary market. These prices represent the market's assessment of the securities' value at a given point in time. The prices may be collected from various financial institutions and sources.
Step 3: Identifying the Maturity Dates
For each selected Treasury security, the specific maturity date is identified. This date is when the security will mature, and the principal will be repaid to the bondholder.
Step 4: Calculating the Yields
Using the prices of the Treasury securities and their respective maturity dates, yields are calculated for each security. The yield is the annualized rate of return an investor would earn if they held the security until maturity. Yields are calculated using a standard formula, often involving trial and error because yields are inversely related to bond prices.
Step 5: Smoothing the Yields
CMT rates are not based on the yields of individual securities but are derived from these yields. To do this, the yields are smoothed using a mathematical process, typically a cubic spline interpolation, to create a continuous yield curve that represents various maturities. This yield curve is used to estimate yields for maturities that may not have corresponding securities.
Step 6: Selecting the Specific CMT Rates
The final step is to select the specific CMT rates for different maturities. These rates are published daily and represent the yields for U.S. Treasury securities with specific maturities. Common CMT rates include the 1-year CMT rate, 5-year CMT rate, 10-year CMT rate, and 30-year CMT rate.
It's important to note that CMT rates are determined by market forces and can change daily based on the supply and demand for Treasury securities in the secondary market. These rates are widely used in financial markets for pricing various financial instruments, including mortgages and corporate bonds, and for making financial decisions.