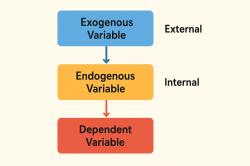
What does empirical study mean?
An empirical study is a type of research that relies on empirical evidence, which is information acquired through direct observation, measurement, or experimentation. Empirical studies are conducted to answer specific research questions, test hypotheses, or investigate phenomena by collecting and analyzing data from real-world observations or experiments.
Here are some key characteristics and components of empirical studies:
Data Collection: Empirical studies involve the systematic collection of data. This data can take various forms, including surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, and measurements.
Objective Observation: Empirical research aims to be objective and unbiased. Researchers strive to gather data in a way that minimizes personal bias and subjectivity.
Hypothesis Testing: Many empirical studies are designed to test hypotheses or research questions. Researchers formulate hypotheses based on existing knowledge or theories, collect data to test these hypotheses, and draw conclusions based on the results.
Quantitative or Qualitative Data: Empirical studies can involve quantitative data (numeric data that can be measured and analyzed statistically) or qualitative data (non-numeric data that can provide insights into attitudes, behaviors, and experiences).
Statistical Analysis: When dealing with quantitative data, empirical studies often employ statistical analysis to examine relationships, patterns, and significance.
Replicability: Empirical research should ideally be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies using the same methods and obtain similar results.
Peer Review: Empirical studies are typically subject to peer review, where other experts in the field evaluate the research methodology, data analysis, and conclusions before publication in a scientific journal.
Conclusions and Generalizability: Empirical studies aim to draw conclusions based on the collected data. The degree to which these conclusions can be generalized to a broader population or context depends on the study's design and methodology.
Empirical studies play a crucial role in various fields, including science, social sciences, psychology, economics, and many others. They provide valuable insights into real-world phenomena, inform decision-making, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in academic and practical settings.