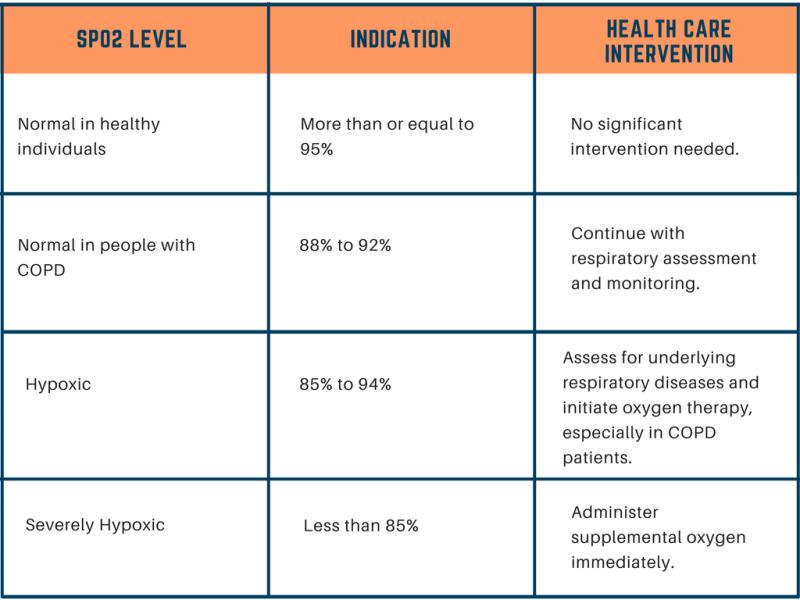
What causes low blood oxygen levels at night?
Several factors can contribute to nocturnal low blood oxygen levels, a condition known as nocturnal hypoxemia. Some common causes include:
Sleep Apnea: Obstructive sleep apnea is a prevalent condition where the upper airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing or shallow breathing. These interruptions can result in drops in blood oxygen levels during the night.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Individuals with COPD, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, often experience nocturnal hypoxemia due to impaired lung function, leading to difficulty in maintaining adequate oxygen levels during sleep.
Heart Conditions: Certain heart conditions, such as congestive heart failure, can cause fluid buildup in the lungs, reducing the efficiency of oxygen exchange and leading to low blood oxygen levels during sleep.
Anemia: Low levels of red blood cells or insufficient hemoglobin can limit the blood's ability to carry oxygen, resulting in decreased oxygen saturation during sleep.
High Altitude: Sleeping at high altitudes, where oxygen levels are lower, can lead to nocturnal hypoxemia due to reduced oxygen availability in the air.
Neuromuscular Disorders: Conditions affecting the nerves and muscles involved in breathing, such as muscular dystrophy or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), can lead to inadequate breathing patterns during sleep, causing low blood oxygen levels.
Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can contribute to obstructive sleep apnea, leading to nocturnal hypoxemia.
Central Sleep Apnea: Unlike obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea is a neurological condition where the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing, causing breathing interruptions during sleep.
If someone experiences symptoms like excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, morning headaches, or restless sleep accompanied by snoring or gasping for breath, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform tests like overnight oximetry, polysomnography (sleep study), or blood tests to diagnose the underlying cause of nocturnal low blood oxygen levels and recommend appropriate treatment options.
What are the common causes contributing to low blood oxygen levels during sleep?
Low blood oxygen levels during sleep, also known as nocturnal hypoxemia, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some of the most common causes include:
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): OSA is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of complete or partial blockage of the airway during sleep. These blockages can cause drops in blood oxygen levels, as the body is unable to take in enough oxygen.
Central sleep apnea (CSA): CSA is a sleep disorder characterized by a lack of central respiratory drive during sleep. This means that the brain does not send signals to the muscles that control breathing, leading to pauses in breathing and drops in blood oxygen levels.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): COPD is a group of chronic lung diseases that cause obstruction of airflow from the lungs. This obstruction can make it difficult to breathe and can lead to low blood oxygen levels, especially during sleep.
Congestive heart failure (CHF): CHF is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. This can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe and causing low blood oxygen levels, especially during sleep.
Obesity: Obesity can increase the risk of sleep apnea and other conditions that can cause low blood oxygen levels during sleep. Excess body weight can put pressure on the chest and abdomen, making it more difficult to breathe.
Altitude: Living at high altitudes can cause lower blood oxygen levels overall, as the air is thinner and contains less oxygen. This can also worsen low blood oxygen levels during sleep in people with underlying conditions.
Medications: Some medications, such as sedatives and pain relievers, can depress the central nervous system and affect respiratory control, potentially leading to low blood oxygen levels during sleep.
Smoking: Smoking can damage the lungs and impair their ability to take in oxygen. This can worsen low blood oxygen levels during sleep, especially in people with underlying lung conditions.
If you experience symptoms of low blood oxygen levels during sleep, such as shortness of breath, snoring, gasping for air, or morning headaches, it is important to see a doctor to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve sleep quality.