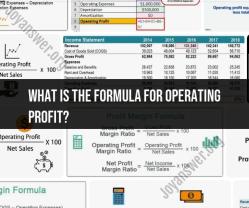
What is the difference between buying and leasing?
Buying and leasing are two different methods of acquiring and using assets, such as vehicles, real estate, or equipment. The main difference between buying and leasing lies in ownership, financial commitment, and the duration of use. Here's a breakdown of the key differences:
Buying:
- Ownership: When you buy an asset, you become the owner. You have full control over it, and it becomes your property.
- Upfront Cost: Buying typically requires a larger upfront payment, which can include a down payment, taxes, and other fees.
- Financing: You can finance the purchase with a loan (e.g., auto loan or mortgage), and you'll make regular payments to pay off the loan over time.
- Depreciation: The asset's value may depreciate over time, which can affect its resale value.
- Customization: You can customize or modify the asset to suit your preferences or needs.
- Usage: There are no restrictions on how much you can use the asset, and you can keep it for as long as you want.
- Maintenance: You are responsible for all maintenance and repair costs.
Leasing:
- Ownership: When you lease an asset, you do not own it. You have the right to use it for a specified period, but the ownership remains with the lessor (the leasing company or individual).
- Upfront Cost: Leasing typically involves lower upfront costs, such as a security deposit, acquisition fee, and the first month's payment.
- Payments: Instead of paying off the asset's full value, you make regular lease payments for the duration of the lease term.
- Depreciation: You do not bear the risk of depreciation because you return the asset to the lessor at the end of the lease term.
- Customization: Customizing or modifying the asset may be restricted or require prior approval from the lessor.
- Usage: Leases often come with usage limits, such as mileage restrictions for leased vehicles.
- End of Lease: At the end of the lease term, you have options, which typically include returning the asset, purchasing it at a predetermined price (buyout option), or renewing the lease for a new term.
Choosing between buying and leasing depends on your individual financial situation, preferences, and needs. Some factors to consider include your budget, how long you plan to use the asset, your desire for ownership, and your willingness to handle maintenance and depreciation. Both options have their advantages and drawbacks, so it's essential to evaluate which aligns better with your specific circumstances and goals.
Buying vs. Leasing: Understanding the Key Differences
Buying and leasing are two different ways to acquire a car. Buying means that you purchase the car outright and take ownership of it. Leasing means that you rent the car for a specific period of time, typically two to four years.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between buying and leasing:
| Feature | Buying | Leasing |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | You own the car. | You do not own the car. |
| Monthly payments | Typically higher than lease payments. | Typically lower than monthly payments for a car loan. |
| Down payment | Typically required. | May or may not be required. |
| Mileage limits | None. | May have mileage limits. |
| Wear and tear | You are responsible for all wear and tear. | The leasing company is responsible for most wear and tear. |
| At the end of the term | You can keep the car, sell it, or trade it in. | You must return the car to the leasing company. |
Car Ownership Options: Comparing Buying and Leasing
There are a few factors to consider when deciding whether to buy or lease a car:
- Budget: Lease payments are typically lower than monthly payments for a car loan. However, you may have to make a down payment when you lease a car.
- Ownership: If you want to own your car at the end of the term, then buying is a better option. If you don't mind returning the car to the leasing company at the end of the term, then leasing may be a good option for you.
- Mileage: If you drive a lot of miles, then buying may be a better option for you. Leasing companies typically have mileage limits, and you may have to pay a fee for every mile you drive over the limit.
- Wear and tear: If you are worried about wear and tear, then leasing may be a better option for you. The leasing company is responsible for most wear and tear, so you will not have to worry about paying for repairs.
Financial Choices: Exploring the Contrast Between Buying and Leasing
There are both financial benefits and drawbacks to buying and leasing a car.
- Buying:
- Pros: You own the car at the end of the term, and you can sell it or trade it in. You can also drive as many miles as you want without having to pay extra fees.
- Cons: Monthly payments are typically higher than lease payments, and you may have to make a down payment. You are also responsible for all wear and tear on the car.
- Leasing:
- Pros: Monthly payments are typically lower than monthly payments for a car loan, and you may not have to make a down payment. The leasing company is also responsible for most wear and tear on the car.
- Cons: You do not own the car at the end of the term, and you may have to pay a fee for every mile you drive over the limit.
Conclusion
The best way to decide whether to buy or lease a car is to consider your individual needs and budget. If you are not sure which option is right for you, talk to a financial advisor.