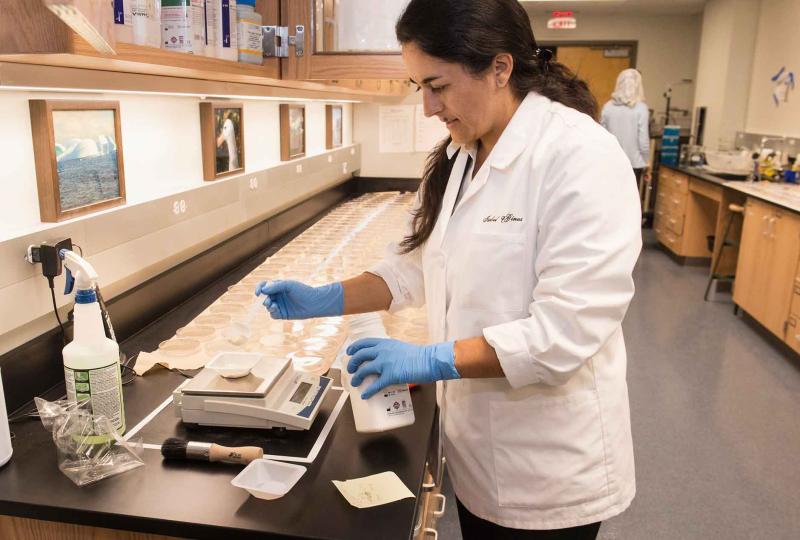
What is a biology in college?
In college, the study of biology encompasses a broad and in-depth exploration of living organisms and their interactions with each other and their environments. Biology is a natural science that focuses on the structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy of living organisms.
Here are some key aspects of studying biology in college:
Core Concepts:
- Cellular Biology: Understanding the structure and function of cells, the basic units of life.
- Genetics: Examining the principles of inheritance, DNA structure, and gene expression.
- Ecology: Exploring the relationships between organisms and their environments.
- Evolutionary Biology: Investigating the processes that drive the diversity and adaptation of species over time.
Laboratory Work:
- Biology programs often include laboratory components where students engage in hands-on experiments, gaining practical skills and reinforcing theoretical concepts.
Specializations:
- Depending on the college and program, students may have the opportunity to specialize in areas such as microbiology, botany, zoology, molecular biology, ecology, or biochemistry.
Interdisciplinary Studies:
- Biology is often integrated with other disciplines, such as chemistry, physics, mathematics, and environmental science. This interdisciplinary approach enhances the understanding of complex biological phenomena.
Research Opportunities:
- Many biology programs offer research opportunities for students to work on independent or collaborative projects under the guidance of faculty members.
Technology and Techniques:
- Students learn to use advanced laboratory techniques, tools, and technologies such as microscopy, DNA sequencing, and bioinformatics.
Fieldwork:
- Depending on the program, students may participate in field studies to observe and study organisms in their natural habitats, contributing to a more holistic understanding of biology.
Critical Thinking and Analysis:
- Biology courses emphasize critical thinking skills and the ability to analyze and interpret scientific data. Students are often required to communicate their findings through written reports and presentations.
Ethics and Social Implications:
- Some programs incorporate discussions on the ethical implications of biological research and its applications in society.
Capstone Projects:
- In some cases, students may undertake a capstone project or senior thesis, demonstrating their ability to conduct independent research and apply their knowledge.
In summary, studying biology in college involves a comprehensive exploration of the principles and processes that govern living organisms, providing students with a strong foundation for various career paths, including research, healthcare, education, and environmental science. The specific curriculum and focus areas can vary between colleges and universities.
1. Studying Biology in College:
Core Concepts:
- Living Organisms: You'll delve deeper into the complex structures, functions, and processes of life, including cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
- Evolution and Genetics: Explore the mechanisms of evolution, understand the role of genetics in inheritance and variation, and learn about genetic engineering and its applications.
- Ecology and Biodiversity: Gain insights into the relationships between organisms and their environments, study diverse ecosystems, and analyze the impact of human activities on nature.
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: Investigate the chemical processes underlying life, delve into the structure and function of biomolecules, and learn about metabolic pathways and cellular respiration.
Curriculum:
- Coursework: You'll take a range of core biology courses like cell biology, genetics, ecology, biochemistry, and evolution.
- Labs: Expect hands-on experience in labs, conducting experiments, analyzing data, and developing research skills.
- Electives: Choose courses specific to your interests, such as microbiology, immunology, neuroscience, plant biology, or animal behavior.
- Research: Participate in faculty research projects, gain practical experience, and contribute to scientific knowledge.
Skills Developed:
- Critical Thinking: Analyze complex biological data, draw conclusions, and formulate hypotheses.
- Problem Solving: Apply scientific principles to solve real-world problems in healthcare, environmental conservation, and food production.
- Communication: Effectively present scientific findings in written and oral formats.
- Laboratory Techniques: Master practical skills in handling biological materials, conducting experiments, and using laboratory equipment.
- Data Analysis: Interpret scientific data, perform statistical analyses, and draw meaningful conclusions.
2. College vs. High School Biology:
Depth and Breadth:
- College: Covers a wider range of topics in greater depth, including advanced concepts and specialized fields within biology.
- High School: Introduces fundamental biological principles and focuses on introductory concepts in genetics, cell biology, and ecology.
Learning Approach:
- College: Emphasizes independent learning, critical analysis of scientific literature, and research participation.
- High School: Focuses on structured learning through textbooks, lectures, and basic laboratory exercises.
Assessment:
- College: Utilizes diverse assessment methods, including exams, research papers, presentations, and critical analyses.
- High School: Primarily relies on standardized tests, quizzes, and lab reports.
Level of Inquiry:
- College: Encourages students to question, analyze, and propose solutions to complex biological problems.
- High School: Primarily focuses on understanding established scientific concepts and applying them to solve basic problems.
3. Career Paths for Biology Majors:
- Healthcare: Medical doctor, physician assistant, nurse, researcher, pharmacist, genetic counselor.
- Research: Research scientist, laboratory technician, professor, environmental scientist, biochemist, bioengineer.
- Education: Biology teacher, science educator, curriculum developer, science communicator.
- Environment: Wildlife biologist, conservation scientist, environmental consultant, ecologist, park ranger.
- Agriculture: Agricultural scientist, plant breeder, food scientist, soil scientist, animal nutritionist.
- Biotechnology: Biotechnologist, bioinformatician, biochemist, pharmaceutical scientist, genetic engineer.
- Government: Policy analyst, public health official, food safety inspector, environmental regulator.
- Law: Patent attorney, environmental lawyer, food safety lawyer, healthcare lawyer.
The specific career paths available depend on your interests, specialization, and educational level. Further education, such as a master's or doctorate degree, can open doors to advanced research positions, specialized healthcare professions, and leadership roles in government or industry.