What are the best skills for a resume?
In today’s competitive job market, a résumé often serves as your first, and sometimes only, chance to make an impression. Recruiters and hiring managers typically spend mere seconds scanning each application, quickly looking for keywords and relevant experience. This means that showcasing the right skills, presented effectively, can be the determining factor in whether your application progresses or gets filed away.
A truly impactful résumé goes beyond merely listing past job titles; it strategically highlights a balanced mix of abilities. This includes hard skills, which are your technical, teachable abilities, as well as soft skills, the crucial interpersonal and personal attributes that dictate how you interact and perform in a team environment. Together, these skills paint a comprehensive picture of your professional capabilities.
This article will guide you through identifying the best skills for a resume, explain the crucial difference between hard and soft skills, provide practical advice on how to list skills on a resume to capture attention, reveal the most in-demand skills for 2025, and offer strategies for continuous skill improvement to foster ongoing career growth. Get ready to transform your résumé into a powerful tool that helps you stand out to any employer.
What Are the Best Skills to Include on a Resume?
In a professional context, "skills" refer to the specific abilities, knowledge, and proficiencies that enable you to perform tasks effectively and contribute meaningfully to a role or organization. These are the tools in your professional toolkit.
The "best" skills to include on your resume are highly dependent on several factors: the specific job description you're applying for, the industry you're targeting, and your current career level. However, some universal, high-value skills consistently catch employers' eyes across various sectors.
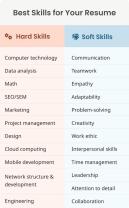
Here are examples of skills employers love to see:
Communication and Teamwork
Active Listening: The ability to fully concentrate on what is being said, understand, respond, and remember.
Verbal Communication: Clearly articulating ideas and information in spoken form.
Written Communication: Producing clear, concise, and persuasive written content (reports, emails, proposals).
Teamwork/Collaboration: Working effectively with others to achieve a common goal, sharing responsibilities, and supporting colleagues.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Problem-Solving: Identifying complex problems, reviewing related information, developing and evaluating options, and implementing solutions.
Critical Thinking: Objectively analyzing and evaluating information to form a judgment, identifying biases, and making reasoned decisions.
Research: Systematically investigating and studying materials and sources to establish facts and reach new conclusions.
Time Management and Organization
Time Management: Prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and managing workload efficiently.
Organization: Maintaining structured systems for information, tasks, and resources to ensure efficiency.
Project Management: Planning, executing, and closing projects, often involving coordination of resources and teams.
Leadership and Adaptability
Leadership: Guiding, motivating, and directing teams or individuals to achieve goals.
Adaptability/Flexibility: Adjusting to new conditions, changes, and unforeseen challenges with ease and a positive attitude.
Initiative: Proactively identifying opportunities or problems and taking action without needing explicit instruction.
Technical Proficiency (Hard Skills Examples)
Microsoft Office Suite: Excel (advanced functions, pivot tables), Word (document formatting, mail merge), PowerPoint (presentations).
Data Analysis: SQL, Python (Pandas, NumPy), R, statistical software (SPSS, SAS).
Coding/Programming Languages: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, HTML/CSS.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: SAP, Oracle, NetSuite.
Digital Marketing Tools: Google Analytics, SEO tools (SEMrush, Ahrefs), email marketing platforms (Mailchimp).
Pro Tip: To maximize your resume's impact, thoroughly review the job description for each role you apply to. Identify key skills and action verbs used by the employer and tailor your skills section and experience descriptions to match those keywords. This strategy is crucial for passing Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), which many companies use to filter resumes before a human ever sees them.
How Do Hard Skills and Soft Skills Differ on a Resume?
Understanding the distinction between hard and soft skills is vital for crafting a well-rounded resume that appeals to recruiters. Both types are essential, but they demonstrate different facets of your professional capability.
Hard Skills
Hard skills are measurable, teachable abilities that are specific to a job or industry. You typically acquire these through formal education, training, certifications, or hands-on experience. They are often quantifiable and easily demonstrated.
Examples:
Programming Languages: Python, Java, C++
Software Proficiency: Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator), Microsoft Excel (advanced), Salesforce
Foreign Languages: Spanish (Fluent), French (Conversational)
Technical Knowledge: SEO optimization, financial modeling, cloud computing, statistical analysis
Certifications: PMP (Project Management Professional), CPA (Certified Public Accountant)
Soft Skills
Soft skills, also known as interpersonal skills or personal attributes, are non-technical qualities that describe how you work and interact with others. They are less about what you know and more about how you apply your knowledge and handle yourself in the workplace. These skills are often transferable across different jobs and industries.
Examples:
Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others.
Collaboration: Working effectively in teams to achieve shared objectives.
Creativity: Generating new ideas, concepts, or solutions.
Problem-Solving: Identifying and resolving issues efficiently.
Critical Thinking: Analyzing information objectively and making reasoned judgments.
Adaptability: Adjusting to new conditions and changes.
Leadership: Motivating and guiding others.
Why Recruiters Look for Both
Recruiters seek a harmonious blend of hard and soft skills because they indicate both capability and compatibility.
Hard skills demonstrate that you possess the technical expertise to perform the core functions of the job. They answer the question, "Can this person do the job?"
Soft skills reveal your work ethic, interpersonal effectiveness, and how well you'll integrate into the company culture. They answer the question, "Will this person fit in and thrive in our workplace?"
A candidate with strong hard skills but poor soft skills might struggle with teamwork or client interactions, while someone with excellent soft skills but lacking crucial hard skills might not be able to perform the job's technical requirements. The ideal candidate effectively combines both.
How Can You Highlight Skills Effectively in Resume Writing?
Successfully highlighting your skills on a resume goes beyond simply listing them. It involves strategic placement, clear articulation, and, where possible, demonstrating their impact.
Where to Include Skills:
Dedicated “Skills” Section: This is the most common and efficient way for recruiters (and Applicant Tracking Systems) to quickly scan your proficiencies.
Placement: Typically placed after your experience section or near the top of your resume, depending on your experience level and industry.
Categorization: Consider dividing this section into "Technical Skills" (hard skills) and "Soft Skills" to enhance readability.
Format: Use bullet points or a clean, categorized list.
Example Snippet for Skills Section:Technical Skills: Python (NumPy, Pandas), SQL, Tableau, Salesforce, Google Analytics, Microsoft Excel (Advanced), HTML/CSSSoft Skills: Project Management, Cross-functional Collaboration, Strategic Planning, Client Relationship Management, Mentorship
Embedded Naturally in Work Experience Descriptions: This is where you demonstrate your skills in action, rather than just stating them. Use strong action verbs and quantify your achievements.
✅ Instead of: "Responsible for problem-solving."
✅ Try: "Spearheaded a cross-functional team to identify and resolve systemic operational bottlenecks, leading to a 15% improvement in processing efficiency." (Highlights: Problem-solving, Leadership, Teamwork, Efficiency)
✅ Instead of: "Used Asana for projects."
✅ Try: "Utilized project management tools like Asana and Trello to streamline cross-departmental collaboration, enhancing project delivery times by 10%." (Highlights: Project Management, Collaboration, Tool Proficiency)
In Your Professional Summary or Profile: Located at the top of your resume, this concise paragraph (or bulleted list) is an excellent place to integrate 2-3 of your most relevant and impactful skills.
✅ "Highly motivated Marketing Professional with 7+ years of experience in digital marketing strategy and data analysis, skilled in leveraging SEO and content strategy to drive measurable ROI."
Formatting Tips:
Use Bullet Points: They are easy to scan and read.
Avoid Generic Terms: Instead of "computer skills," list specific software. Instead of "good communication," provide examples or context.
Quantify Results Where Possible: Numbers make your skills tangible. "Managed a budget" vs. "Managed a $50,000 budget, reducing overhead by 10%."
Match Keywords: Always tailor your skills to align with the keywords found in the job description to optimize for Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS). If the job mentions 'CRM software,' list 'Salesforce' or 'HubSpot' if you know them.
Be Specific: If you list a language, specify your proficiency level (e.g., Fluent, Conversational, Basic).
By strategically placing and effectively articulating your skills, your resume will not just list what you can do, but vividly demonstrate the value you bring to a prospective employer.
What Skills Are Most In-Demand by Employers?
The job market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting economic landscapes, and new ways of working. Staying current with in-demand skills 2025 is crucial for career longevity and success. While specific needs vary by industry, here's a look at the current top skills employers are actively seeking:
Top In-Demand Hard Skills:
These are often technical, quantifiable abilities that drive innovation and efficiency:
Data Analysis and Visualization: The ability to collect, interpret, and present complex data to inform business decisions. (Tools: SQL, Python, R, Tableau, Power BI, Excel)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Understanding and applying AI/ML concepts, frameworks, and tools to develop intelligent systems and automate processes. (Tools: Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn)
Cloud Computing and Cybersecurity: Expertise in cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) for infrastructure management, data storage, and ensuring digital security against threats.
Digital Marketing (Advanced): Beyond basic social media, this includes advanced SEO strategies, analytics interpretation, content strategy, paid advertising (PPC), and marketing automation.
Project Management and Agile Methodologies: The ability to plan, execute, and oversee projects efficiently, often using agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban, to adapt to changing requirements. (Certifications: PMP, CSM)
Top In-Demand Soft Skills:
These interpersonal and cognitive abilities are increasingly critical for navigating complex work environments and fostering collaboration:
Emotional Intelligence (EQ): The capacity to understand and manage one's own emotions, and to perceive and influence the emotions of others. Crucial for leadership, teamwork, and client interactions.
Adaptability and Resilience: The ability to quickly adjust to new technologies, processes, and work environments, and to recover from setbacks.
Collaboration and Teamwork: Working effectively with diverse teams, often remotely, leveraging different strengths to achieve shared objectives.
Leadership and Mentoring: Inspiring and guiding individuals or teams, fostering growth, and delegating effectively.
Critical Thinking and Creativity: The capacity to analyze information, solve complex problems innovatively, and think outside the box to generate new ideas and solutions.
Industry-Specific Demands:
Healthcare: Telehealth proficiency, electronic health record (EHR) management, data privacy (HIPAA compliance).
Information Technology (IT): DevOps, blockchain, mobile development, UI/UX design.
Marketing: Video production, influencer marketing, analytics interpretation.
Education: Online teaching platforms, instructional design, digital literacy.
To stay ahead, regularly reference job market reports from platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, or industry-specific associations. These resources often publish annual skill trends, offering invaluable insights into what employers are actively seeking.
How Can You Continuously Improve Skills for Career Growth?
The notion that learning ends after formal education is long outdated. In today's dynamic job market, skill-building is a lifelong process. Continuous improvement is not just beneficial; it’s essential for career growth, staying competitive, and remaining adaptable in any market.
Here are effective ways to continuously improve your skills:
Take Online Courses and Certifications:
Platforms: Coursera, Udemy, edX, LinkedIn Learning, Google Skillshop, HubSpot Academy. These platforms offer thousands of courses in both hard and soft skills, often taught by university professors or industry experts.
Certifications: Pursue industry-recognized certifications (e.g., PMP for project management, Google Ads certification for marketing, AWS certifications for cloud computing) to validate your expertise.
Attend Workshops, Webinars, and Conferences:
These events provide concentrated learning, often with hands-on components, and offer opportunities to network with peers and learn about emerging trends. Many are available virtually.
Seek Mentorship and Feedback:
Mentors: A mentor can provide invaluable guidance, share their experience, and help you identify areas for growth.
Supervisors/Colleagues: Actively ask for feedback on your performance, especially regarding soft skills like communication or leadership. Be open to constructive criticism.
Volunteer or Take on Side Projects:
Volunteering: Offer your skills to a non-profit organization or community group. This is a low-pressure way to practice new skills or gain experience in a different industry.
Side Projects: Start a personal project that requires you to learn new software, a programming language, or manage a small "project" from start to finish. This provides real-world experience to add to your resume.
Read Industry Publications and Follow Thought Leaders:
Stay informed about trends, new technologies, and best practices in your field by regularly reading relevant blogs, journals, and news sites. Follow key influencers and experts on social media or professional networks like LinkedIn.
Create a Personal Development Plan:
Set Measurable Goals: Identify 2-3 skills you want to develop or enhance.
Outline Steps: Define specific actions you will take (e.g., 'complete Python course by June,' 'lead one team meeting per week to practice leadership').
Set Timelines: Give yourself deadlines for achieving your goals.
Track Progress: Regularly review your plan and celebrate milestones.
By adopting a growth mindset and actively pursuing skill development, you not only enhance your current capabilities but also future-proof your career. Staying adaptable, continuously learning, and strategically adding new skills to your repertoire will keep you employable and valuable in any market, regardless of how quickly industries evolve.
Conclusion
In the fast-evolving landscape of the modern workforce, a meticulously crafted résumé is your most powerful advocate. The best résumés are those that strategically combine relevant, clearly presented, and continuously updated skills that resonate with prospective employers. It’s a delicate balance, where both your technical prowess (hard skills) and your interpersonal strengths (soft skills) play equally crucial roles in demonstrating your comprehensive value.
By understanding the distinction between these skill types, strategically embedding them throughout your resume, and proactively seeking opportunities for improvement, you position yourself as an invaluable candidate. Remember to regularly review and refresh your résumé to align with current job market trends and the specific demands of the roles you covet. This proactive approach ensures your resume not only passes initial screening but truly stands out, opening doors to exciting career opportunities and fostering sustained professional growth.













ExperiencedJobHunter
on October 09, 2025A great reminder that skill-building is a lifelong process. The motivation to seek out mentorship and create a personal development plan is the key to maintaining relevance in any rapidly changing industry.