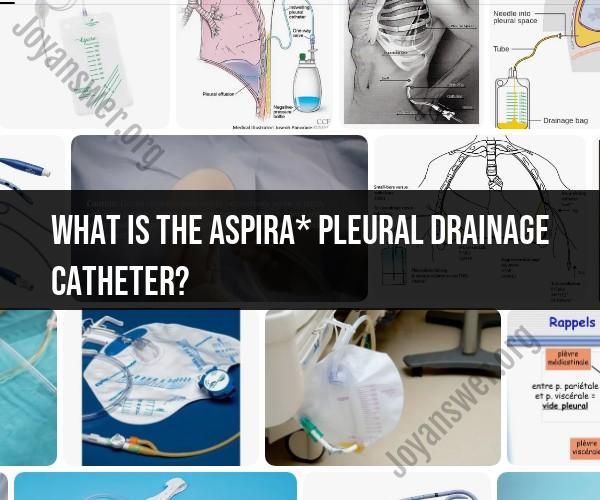
What is the ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter?
The ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter is a medical device used for the drainage of fluid or air that has accumulated in the pleural space, which is the area between the two layers of the pleura (the thin membrane that lines the lungs and chest cavity). The device is designed to help manage conditions that lead to pleural effusion or pneumothorax, which can cause difficulty breathing and discomfort.
Here is an overview of the ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter and its usage:
Purpose:
- The primary purpose of the ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter is to remove excess fluid (pleural effusion) or air (pneumothorax) from the pleural space. This helps alleviate symptoms, such as shortness of breath and chest pain, and may be used as part of the treatment for various medical conditions.
Design:
- The ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter is a thin, flexible tube made of medical-grade materials. It typically has multiple side holes or fenestrations along its length to allow for the drainage of fluid or air.
Insertion:
- The catheter is typically inserted into the pleural space through a small incision made in the chest wall. This procedure is often performed under local anesthesia or sedation to minimize discomfort.
Drainage and Collection:
- Once in place, the catheter is connected to a drainage system. This system may include a collection bag or container and may use gravity or suction to facilitate the removal of fluid or air. The drainage system allows healthcare providers to monitor the volume and characteristics of the drained fluid.
Indications:
- The ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter is used to manage conditions that lead to pleural effusion or pneumothorax. Common indications include congestive heart failure, pneumonia, cancer, trauma, and lung infections.
Benefits:
- The catheter provides a means to drain and manage pleural effusions and pneumothoraces in a controlled and continuous manner, allowing for the relief of symptoms and improvement in lung function.
Care and Maintenance:
- Patients with an ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter will require ongoing care and monitoring by healthcare providers. This includes assessing the drainage system, checking for signs of infection, and ensuring proper function of the catheter.
Removal:
- The catheter is typically removed once the underlying condition has been treated, and there is minimal or no fluid or air in the pleural space. Removal is a relatively simple procedure performed by a healthcare provider.
It's important to note that the use of the ASPIRA* pleural drainage catheter and the management of pleural effusion or pneumothorax should be done under the supervision of trained medical professionals. The specific treatment plan and duration of catheter use will depend on the individual patient's condition and response to treatment.
ASPIRA Pleural Drainage Catheter: Advancements in Medical Technology*
The ASPIRA* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the pleural cavity. It is a significant advancement in medical technology, as it offers a number of advantages over traditional pleural drainage methods.
One of the main advantages of the ASPIRA* catheter is that it is minimally invasive. The catheter is inserted through a small incision in the chest wall, and it can be left in place for weeks or even months. This eliminates the need for repeated thoracentesis, which can be uncomfortable and painful for patients.
Another advantage of the ASPIRA* catheter is that it allows for continuous drainage of pleural fluid. This can be beneficial for patients with recurrent or symptomatic pleural effusions, as it can help to prevent the fluid from building up and causing symptoms.
The ASPIRA* catheter is also equipped with a number of safety features, such as a one-way valve that prevents air from entering the pleural cavity. This helps to reduce the risk of complications, such as pneumothorax.
Overall, the ASPIRA* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a significant advancement in medical technology that offers a number of advantages over traditional pleural drainage methods. It is a minimally invasive, continuous drainage catheter that is equipped with a number of safety features.
Managing Pleural Effusion: Insights into the ASPIRA Catheter*
Pleural effusion is a condition in which fluid accumulates in the pleural space, the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including cancer, heart failure, and pneumonia.
The ASPIRA* catheter can be used to manage pleural effusion by draining the accumulated fluid from the pleural cavity. This can help to relieve symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest pain.
The ASPIRA* catheter is typically inserted by a radiologist or other healthcare professional. The catheter is inserted through a small incision in the chest wall, and it is then tunneled under the skin to the pleural space.
Once the catheter is in place, it can be used to drain the pleural fluid. The fluid can be drained manually or using a vacuum pump. The frequency and duration of drainage will vary depending on the individual patient's needs.
The ASPIRA* catheter can be left in place for weeks or even months. This allows for continuous drainage of pleural fluid, which can be beneficial for patients with recurrent or symptomatic pleural effusions.
ASPIRA Catheter: A Minimally Invasive Approach to Drainage*
The ASPIRA* catheter is a minimally invasive approach to pleural drainage. The catheter is inserted through a small incision in the chest wall, and it can be left in place for weeks or even months. This eliminates the need for repeated thoracentesis, which can be uncomfortable and painful for patients.
The ASPIRA* catheter is also equipped with a number of safety features, such as a one-way valve that prevents air from entering the pleural cavity. This helps to reduce the risk of complications, such as pneumothorax.
Overall, the ASPIRA* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a safe and effective way to manage pleural effusion. It is a minimally invasive, continuous drainage catheter that is equipped with a number of safety features.