What is a covered Part D drug?
In the context of Medicare Part D, a covered Part D drug refers to a prescription medication that is included in the formulary or list of drugs covered by a specific Medicare Part D prescription drug plan. Medicare Part D is the prescription drug coverage program offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare.
Here are key points to understand about covered Part D drugs:
Formulary Inclusions:
- Each Medicare Part D plan has a formulary, which is a list of prescription drugs covered by the plan. A covered Part D drug is any medication listed on this formulary.
Formulary Tiers:
- Formularies often categorize drugs into different tiers. The tier placement of a drug can affect the out-of-pocket costs for the beneficiary. Lower-tier drugs generally have lower costs than higher-tier drugs.
Plan-Specific Coverage:
- The specific drugs covered by a Part D plan can vary between plans. Different plans may have different formularies, so beneficiaries should review the drug list of a plan to ensure that their medications are covered.
Changes in Coverage:
- Part D plans may periodically update their formularies. This means that a drug that was covered in the past may not be covered in the future, or vice versa. Beneficiaries should be aware of any changes in the plan's formulary.
Coverage Determinations:
- Before enrolling in a Part D plan, beneficiaries can review the plan's formulary to check if their specific medications are covered. If a drug is not covered, beneficiaries may need to explore alternative medications or consider other plan options.
Exceptions and Appeals:
- If a beneficiary believes that a drug should be covered, they have the right to request an exception or appeal the plan's decision. This process allows beneficiaries to make a case for coverage based on medical necessity or other relevant factors.
Generic and Brand-Name Drugs:
- Formularies often include both generic and brand-name drugs. Generic drugs are generally more cost-effective, and plans may encourage their use through lower co-payment or co-insurance amounts.
Preferred vs. Non-Preferred Drugs:
- Some plans distinguish between preferred and non-preferred drugs. Preferred drugs may have lower out-of-pocket costs for beneficiaries compared to non-preferred drugs.
It's important for Medicare beneficiaries to carefully review the drug coverage of different Part D plans during the annual enrollment period and select a plan that best meets their medication needs and budget. Additionally, beneficiaries can consult with their healthcare providers to explore therapeutic alternatives or discuss coverage options if needed.
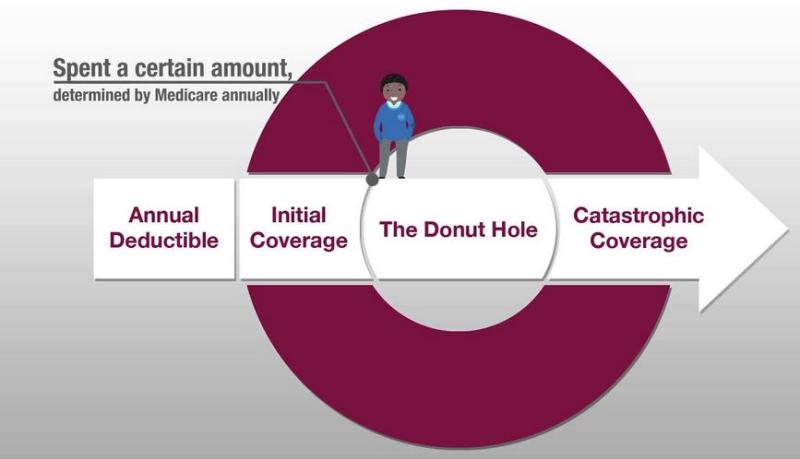
Defining covered Part D drugs and their inclusion in the plan's formulary
Part D, also known as the Medicare Prescription Drug Plan, helps cover the cost of prescription medications for individuals enrolled in Medicare. Part D plans are offered by private insurance companies and have their own formularies, which are lists of covered medications.
A covered Part D drug is a medication that is included in the plan's formulary and is available to be covered for eligible beneficiaries. The plan will typically pay for a portion of the cost of the medication, while the beneficiary pays the remaining cost, known as the coinsurance or copay.
The decision of whether or not to include a medication in the formulary is made by the plan's pharmacy and therapeutics (P&T) committee. The committee considers a number of factors, including the medication's effectiveness, safety, and cost.
Tiered Pricing Structure for Part D Drugs
Part D plans use a tiered pricing structure to determine the cost of covered medications. The tiered pricing structure typically consists of three tiers:
Generic: Generic medications are copies of brand-name drugs that have the same active ingredients and dosage forms. Generic drugs are typically less expensive than brand-name drugs.
Preferred Brand: Preferred brand drugs are brand-name drugs that the plan has negotiated a lower price for with the manufacturer. Preferred brand drugs typically cost more than generic drugs, but less than non-preferred brand drugs.
Non-Preferred Brand: Non-preferred brand drugs are brand-name drugs that the plan has not negotiated a lower price for with the manufacturer. Non-preferred brand drugs typically cost the most.
The beneficiary's coinsurance or copay for a medication will vary depending on the tier in which the medication is placed. For example, a beneficiary may have a $20 copay for a generic medication, a $40 copay for a preferred brand medication, and an $80 copay for a non-preferred brand medication.
Determining Whether a Specific Medication is Covered under Part D
Beneficiaries can determine whether a specific medication is covered under their Part D plan by using the plan's formulary and drug list. The formulary and drug list are typically available on the plan's website or can be obtained by calling the plan's customer service number.
The formulary and drug list will list all of the covered medications, along with the tier in which they are placed. The beneficiary can search for the medication by name or by generic name.
If the medication is not listed in the formulary or drug list, it is not covered under the plan. The beneficiary may have to pay the full cost of the medication out of pocket.
It is important to note that the formulary and drug list can change at any time. Beneficiaries should check the formulary and drug list regularly to make sure that their medications are still covered.