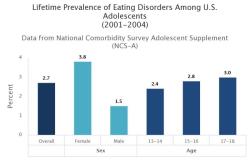
What are the negative effects of anxiety?
Anxiety is a natural and adaptive response to stress, but when it becomes chronic or overwhelming, it can have a range of negative effects on both mental and physical health. The negative effects of anxiety can vary from person to person and may include:
1. Mental Health Effects:
Excessive Worry: Anxiety often involves persistent and excessive worrying about a wide range of issues, which can be distressing and distracting.
Fear and Panic Attacks: Anxiety disorders can lead to sudden and intense feelings of fear or panic, often accompanied by physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and trembling.
Negative Thought Patterns: Anxiety can lead to negative thought patterns, including self-doubt, catastrophic thinking, and an inability to stop ruminating on perceived threats.
Difficulty Concentrating: Anxiety can make it challenging to focus and concentrate on tasks, impacting work, school, and daily responsibilities.
Irritability: Anxiety can lead to irritability and mood swings, making it difficult to maintain healthy relationships.
Avoidance Behavior: Some individuals with anxiety may avoid situations or activities that trigger their anxiety, limiting their life experiences and opportunities for personal growth.
2. Physical Health Effects:
Muscle Tension: Chronic anxiety can cause muscle tension, leading to headaches, neck and back pain, and other physical discomforts.
Sleep Disturbances: Anxiety often disrupts sleep, leading to insomnia, frequent awakenings, and poor sleep quality.
Gastrointestinal Problems: Anxiety can contribute to gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), stomachaches, and digestive problems.
Cardiovascular Effects: Prolonged anxiety can raise blood pressure and heart rate, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Immune System Weakening: Chronic stress and anxiety can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to illness.
3. Behavioral and Functional Effects:
Social Isolation: Anxiety can lead to social withdrawal and isolation as individuals may avoid social situations due to fear and discomfort.
Procrastination: Anxiety can lead to procrastination and difficulty completing tasks or making decisions.
Substance Abuse: Some individuals turn to alcohol, drugs, or other substances as a way to self-medicate and cope with anxiety, which can lead to addiction issues.
Impaired Functioning: Anxiety can impair a person's ability to function effectively at work, school, or in daily life.
Negative Impact on Relationships: Anxiety can strain relationships, as the symptoms of anxiety can make it challenging to communicate and connect with others.
It's important to recognize that anxiety is a treatable condition, and there are effective therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle changes, that can help manage anxiety and mitigate its negative effects. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, seeking professional help from a mental health provider is advisable to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Unmasking the Negative Effects of Anxiety on Mental and Physical Health
Anxiety is a normal and often healthy emotion. However, when anxiety becomes excessive or persistent, it can have a negative impact on mental and physical health.
Mental health effects of anxiety
- Worry: Anxiety is often characterized by excessive worry about the future or past events. This worry can be debilitating and interfere with daily life.
- Fear: Anxiety can also cause intense feelings of fear, even in situations that are not actually dangerous. These fears can be so overwhelming that they prevent people from doing things they enjoy or need to do.
- Panic attacks: Some people with anxiety experience panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear and physical symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, and heart palpitations. Panic attacks can be very frightening and can lead to social isolation and avoidance.
- Depression: Anxiety and depression often co-occur. People with anxiety may be more likely to develop depression, and vice versa.
Physical health effects of anxiety
- Headaches: Anxiety can cause headaches, muscle tension, and fatigue.
- Stomach problems: Anxiety can also cause stomach problems such as indigestion, nausea, and vomiting.
- Heart problems: Anxiety can increase the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
- Sleep problems: Anxiety can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Immune system problems: Anxiety can weaken the immune system, making people more susceptible to illness.
The Toll of Anxiety: How It Affects Your Well-Being and Quality of Life
Anxiety can have a significant impact on well-being and quality of life. People with anxiety may have difficulty:
- Concentrating and focusing at work or school
- Maintaining relationships
- Enjoying social activities
- Relaxing and sleeping
- Taking care of their physical health
Anxiety can also lead to substance abuse, self-harm, and suicidal thoughts.
Anxiety's Consequences: The Adverse Effects on Mind and Body
Anxiety is a complex condition with a variety of negative effects. It can affect mental health, physical health, and well-being. If you are experiencing anxiety, it is important to seek professional help. Treatment for anxiety can include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Here are some tips for managing anxiety:
- Talk to your doctor: If you are experiencing anxiety, talk to your doctor. They can assess your symptoms and recommend a treatment plan.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise is a great way to reduce stress and improve mood. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Get enough sleep: Most adults need 7-8 hours of sleep per night. When you are well-rested, you are better able to cope with stress and anxiety.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can improve your mood and energy levels. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine and alcohol.
- Learn relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can help to reduce anxiety and stress.
- Connect with others: Social support is important for mental health. Make time for friends and family, or join a support group for people with anxiety.
If you are struggling to manage anxiety on your own, there are many resources available to help you. Talk to your doctor, a therapist, or a trusted friend or family member.